Level shifters and voltage translators both enable communication between circuits operating at different voltage levels but differ in complexity and application scope, with level shifters often handling more specific protocols like I2C or SPI, while voltage translators provide broader bi-directional voltage compatibility. Discover how to choose the right device for Your design needs and ensure reliable signal integrity by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
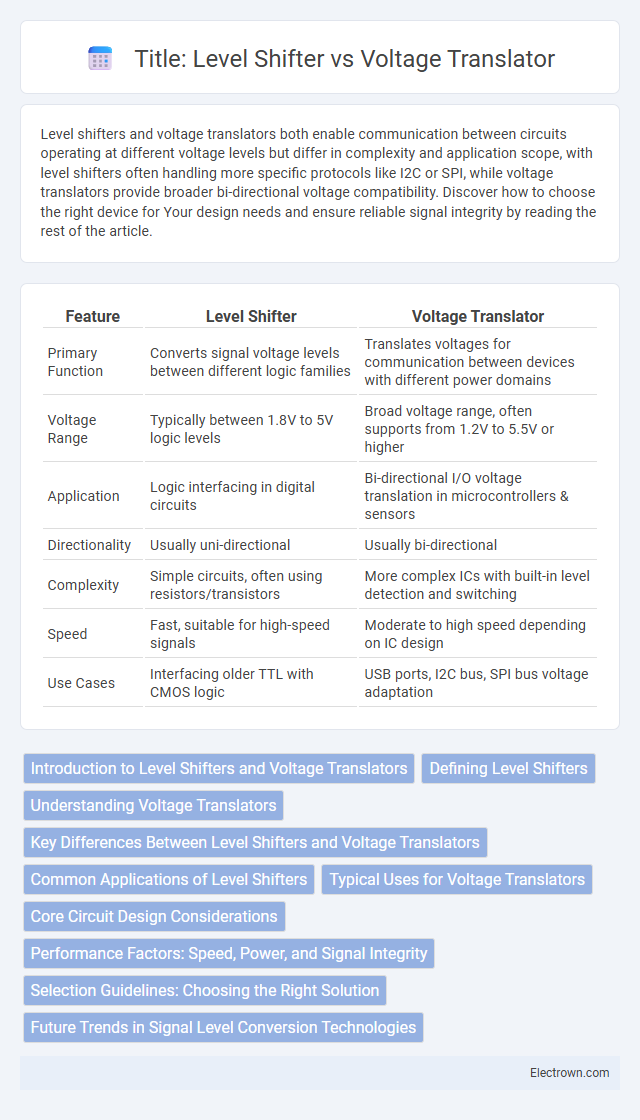
| Feature | Level Shifter | Voltage Translator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Converts signal voltage levels between different logic families | Translates voltages for communication between devices with different power domains |
| Voltage Range | Typically between 1.8V to 5V logic levels | Broad voltage range, often supports from 1.2V to 5.5V or higher |
| Application | Logic interfacing in digital circuits | Bi-directional I/O voltage translation in microcontrollers & sensors |
| Directionality | Usually uni-directional | Usually bi-directional |
| Complexity | Simple circuits, often using resistors/transistors | More complex ICs with built-in level detection and switching |
| Speed | Fast, suitable for high-speed signals | Moderate to high speed depending on IC design |
| Use Cases | Interfacing older TTL with CMOS logic | USB ports, I2C bus, SPI bus voltage adaptation |
Introduction to Level Shifters and Voltage Translators
Level shifters and voltage translators are essential components in electronic circuits for interfacing devices operating at different voltage levels. Level shifters adjust the signal voltage from one logic level to another, enabling communication between components with incompatible voltage domains, commonly found in digital circuits like microcontrollers and sensors. Voltage translators perform a similar function but often focus on bidirectional level shifting and are crucial in applications requiring seamless data transfer across varying voltage supplies.
Defining Level Shifters
Level shifters are specialized electronic circuits designed to safely interface components operating at different voltage levels by converting signal voltages from one logic level to another. Unlike general voltage translators, level shifters ensure signal integrity and compatibility in digital communication by maintaining logic thresholds crucial for microcontrollers, FPGAs, and other integrated circuits. Your design benefits from level shifters when precise voltage domain crossing is required between systems operating at disparate voltage standards.
Understanding Voltage Translators
Voltage translators are critical components designed to interface circuits operating at different voltage levels, ensuring seamless communication without damaging sensitive parts. They manage bidirectional signal translation and are optimized for various protocols, including I2C, SPI, and UART, providing reliable voltage compatibility between low-voltage microcontrollers and higher-voltage peripherals. Understanding voltage translators involves recognizing their role in maintaining signal integrity and preventing data corruption in mixed-voltage systems.
Key Differences Between Level Shifters and Voltage Translators
Level shifters and voltage translators differ primarily in their functional roles and complexity within electronic circuits; level shifters adjust signal voltage levels primarily for logic compatibility between different ICs, often switching between low-voltage logic families like 1.8V and 3.3V. Voltage translators encompass a broader range of applications, including level shifting, but also focus on maintaining signal integrity across diverse voltage domains, supporting bidirectional communication and different signal standards such as I2C and SPI protocols. The key distinction lies in level shifters being dedicated to unidirectional logic level adjustments, while voltage translators offer versatile, typically bidirectional voltage domain translation with additional features for complex mixed-voltage environments.
Common Applications of Level Shifters
Level shifters are essential in interfacing devices operating at different voltage levels, commonly found in mixed-voltage systems such as microcontrollers, sensors, and memory modules. Typical applications include translating signals between 3.3V and 5V logic levels in embedded systems, ensuring data integrity in I2C, SPI, and UART communication protocols. Level shifters enable seamless integration of low-voltage components with legacy or higher voltage circuits in automotive, IoT, and consumer electronics.
Typical Uses for Voltage Translators
Voltage translators are typically used in applications requiring communication between devices operating at different voltage levels, such as interfacing 1.8V microcontrollers with 3.3V sensors. They ensure signal integrity in data buses like I2C, SPI, and UART by adapting voltage levels without distorting information. Your electronic designs benefit from voltage translators by enabling seamless, reliable communication across heterogeneous voltage domains.
Core Circuit Design Considerations
Level shifters and voltage translators both enable signal interoperability between different voltage domains, but core circuit design considerations differ significantly. Level shifters prioritize maintaining signal integrity and ensuring fast switching speeds with minimal propagation delay while handling noise margins across varying logic levels. Voltage translators focus on voltage compliance and protection mechanisms, often incorporating bidirectional capability and low power consumption for seamless integration in mixed-voltage systems.
Performance Factors: Speed, Power, and Signal Integrity
Level shifters and voltage translators differ significantly in performance factors such as speed, power consumption, and signal integrity. Level shifters typically offer faster switching speeds ideal for high-frequency applications but may consume more power due to their complex circuitry. Voltage translators prioritize signal integrity and low power usage, making them suitable for interfaces where maintaining clean signals and energy efficiency is critical for your system's reliability.
Selection Guidelines: Choosing the Right Solution
When selecting between a level shifter and a voltage translator, you should consider the voltage ranges, data rates, and signal types involved in your application. Level shifters are ideal for shifting logic signals between different voltage domains, commonly used in digital protocols like I2C or SPI with low-speed signals. Voltage translators offer broader compatibility across diverse voltage levels and higher frequency support, making them suitable for interfacing mixed-voltage systems in complex designs.
Future Trends in Signal Level Conversion Technologies
Emerging trends in signal level conversion technologies emphasize increased integration of Level Shifters and Voltage Translators within compact, energy-efficient semiconductor devices to support ever-growing data rates and diverse voltage domains in modern electronics. Advanced materials and novel architectures are driving improvements in speed, power consumption, and bidirectional communication capabilities, essential for IoT, automotive, and AI applications. Your choice between these components will hinge on specific performance criteria as future designs demand greater versatility and precision in voltage translation.
Level Shifter vs Voltage Translator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com