A bus holder maintains the last logic state on a data bus to prevent floating values, while a pull-down resistor ensures a default low logic level by connecting the line to ground when no active signal is present. Discover how understanding these components can optimize your circuit stability by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
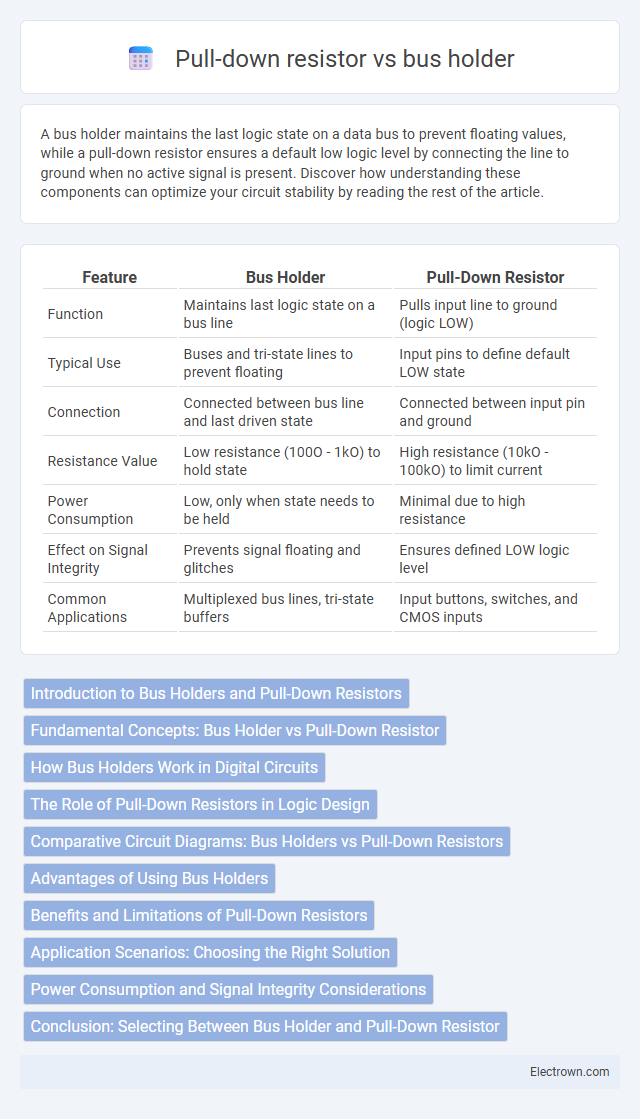
| Feature | Bus Holder | Pull-Down Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Maintains last logic state on a bus line | Pulls input line to ground (logic LOW) |
| Typical Use | Buses and tri-state lines to prevent floating | Input pins to define default LOW state |
| Connection | Connected between bus line and last driven state | Connected between input pin and ground |
| Resistance Value | Low resistance (100O - 1kO) to hold state | High resistance (10kO - 100kO) to limit current |
| Power Consumption | Low, only when state needs to be held | Minimal due to high resistance |
| Effect on Signal Integrity | Prevents signal floating and glitches | Ensures defined LOW logic level |
| Common Applications | Multiplexed bus lines, tri-state buffers | Input buttons, switches, and CMOS inputs |
Introduction to Bus Holders and Pull-Down Resistors
Bus holders maintain signal states on a data bus by holding the last driven value, preventing floating inputs and reducing power consumption in digital circuits. Pull-down resistors, connected between a signal line and ground, ensure a defined logic low level when no active driver is present, avoiding undefined states. Your choice between using a bus holder or pull-down resistor depends on the specific application requirements for signal stability and power efficiency.
Fundamental Concepts: Bus Holder vs Pull-Down Resistor
A bus holder maintains the last driven logic state on a bus line, preventing it from floating by weakly driving the line to its previous value, whereas a pull-down resistor ensures a defined logic LOW level by connecting the line to ground through a resistor. Bus holders are crucial in high-speed digital circuits to reduce noise and improve signal integrity without significantly loading the bus, while pull-down resistors provide a static reference voltage but can slow signal transitions due to their resistive loading. Understanding the difference lies in their function: bus holders dynamically preserve the last state, while pull-down resistors enforce a fixed default LOW state when no active driver is present.
How Bus Holders Work in Digital Circuits
Bus holders maintain a stable logic level on a digital bus by weakly holding the last driven state without interfering with active signals, preventing floating lines and reducing power consumption. Unlike pull-down resistors that force the line to a fixed logic low, bus holders dynamically latch and retain the last valid logic value, ensuring signal integrity in tri-state or multiplexed buses. Your circuit benefits from bus holders through improved noise immunity and fewer unintended transitions, enhancing overall system reliability.
The Role of Pull-Down Resistors in Logic Design
Pull-down resistors ensure a defined logic level by connecting a signal line to ground, preventing floating inputs that cause unpredictable behavior in digital circuits. In logic design, they stabilize the voltage level when no active driver is present, allowing reliable interpretation of low states in microcontroller inputs or logic gates. Comparing bus holders, pull-down resistors offer a simpler fixed low reference without the dynamic feedback mechanism, making them essential for maintaining stable zeros in combinational and sequential logic systems.
Comparative Circuit Diagrams: Bus Holders vs Pull-Down Resistors
Bus holders maintain a stable logic state by weakly driving the signal line through a feedback mechanism, preventing floating inputs without continuous power draw, whereas pull-down resistors provide a defined logic low by connecting the node to ground through a fixed resistance, ensuring a predictable voltage level. Circuit diagrams of bus holders show a feedback transistor or inverter connected to the line, while pull-down resistor schematics depict a resistor bridging the line to ground, emphasizing simpler construction but higher static power dissipation. Your choice depends on circuit noise immunity and power efficiency requirements, with bus holders offering low power retention of the last known state and pull-down resistors guaranteeing a firm logic low during signal inactivity.
Advantages of Using Bus Holders
Bus holders maintain a stable logic state on a bus line without continuous current consumption, reducing power usage compared to pull-down resistors. They eliminate the need for external resistors, saving PCB space and minimizing component count, which simplifies circuit design. Bus holders also provide faster signal transitions and improved noise immunity by actively maintaining the last driven state on the bus.
Benefits and Limitations of Pull-Down Resistors
Pull-down resistors ensure a defined logic level by grounding the input when no active signal is present, preventing floating inputs and unintended switching. They offer a simple, cost-effective method for stabilizing signals but can cause increased power consumption as current continuously flows through the resistor. Your circuit design must consider the trade-off between stability and power efficiency when choosing pull-down resistors over alternatives like bus holders.
Application Scenarios: Choosing the Right Solution
Bus holders are ideal for maintaining signal integrity on shared data lines in FPGA and microcontroller applications where multiple devices communicate, preventing floating states without adding significant power consumption. Pull-down resistors are better suited for ensuring a stable low logic level on individual input pins, especially in simple circuits or when specific default states are required. When selecting between the two, consider your circuit's complexity and power constraints to determine whether a bus holder's dynamic feedback or the fixed reference of a pull-down resistor best fits your application scenario.
Power Consumption and Signal Integrity Considerations
Bus holders maintain a defined logic level on a shared bus by providing a weak feedback current, resulting in lower static power consumption compared to pull-down resistors that continuously draw current to hold the line low. Signal integrity is enhanced with bus holders due to reduced voltage level fluctuations and noise susceptibility, whereas pull-down resistors can cause signal attenuation and slower transitions by constantly sinking current. When designing your circuit, choosing a bus holder over a pull-down resistor can improve power efficiency and maintain cleaner signal levels.
Conclusion: Selecting Between Bus Holder and Pull-Down Resistor
Bus holders maintain a stable logic level on a bus line, preventing floating inputs without the continuous current draw typical of pull-down resistors. Pull-down resistors are simpler and cost-effective solutions for defining a default low state but consume more power due to constant current flow. Your choice depends on power consumption constraints and signal stability requirements, with bus holders preferred in high-speed, low-power applications and pull-down resistors suited for basic, low-speed circuits.
Bus holder vs pull-down resistor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com