Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) serve distinct purposes in technology; ESB facilitates seamless integration and communication between disparate software applications in enterprise environments, while BLE enables low-power wireless communication for IoT and wearable devices. Understanding the differences and use cases of ESB and BLE can enhance Your strategy in selecting the right technology for connectivity and data exchange--explore the details in the full article.
Table of Comparison
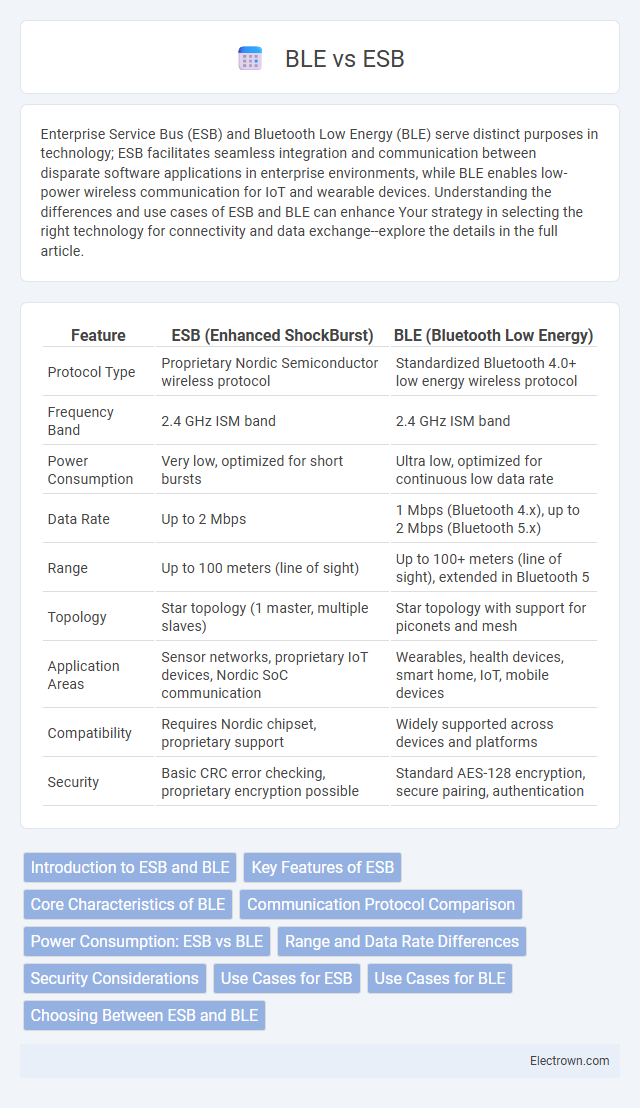
| Feature | ESB (Enhanced ShockBurst) | BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Proprietary Nordic Semiconductor wireless protocol | Standardized Bluetooth 4.0+ low energy wireless protocol |
| Frequency Band | 2.4 GHz ISM band | 2.4 GHz ISM band |
| Power Consumption | Very low, optimized for short bursts | Ultra low, optimized for continuous low data rate |
| Data Rate | Up to 2 Mbps | 1 Mbps (Bluetooth 4.x), up to 2 Mbps (Bluetooth 5.x) |
| Range | Up to 100 meters (line of sight) | Up to 100+ meters (line of sight), extended in Bluetooth 5 |
| Topology | Star topology (1 master, multiple slaves) | Star topology with support for piconets and mesh |
| Application Areas | Sensor networks, proprietary IoT devices, Nordic SoC communication | Wearables, health devices, smart home, IoT, mobile devices |
| Compatibility | Requires Nordic chipset, proprietary support | Widely supported across devices and platforms |
| Security | Basic CRC error checking, proprietary encryption possible | Standard AES-128 encryption, secure pairing, authentication |
Introduction to ESB and BLE
ESB (Enhanced ShockBurst) is a proprietary wireless protocol developed by Nordic Semiconductor for efficient and low-power data transmission in short-range applications. BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) is a standardized wireless communication technology designed for low-energy consumption and interoperability across a wide range of devices in the Internet of Things (IoT). Both ESB and BLE operate in the 2.4 GHz ISM band but serve different use cases, with ESB optimized for simple, low-latency data exchange and BLE emphasizing broad device compatibility and robust connectivity.
Key Features of ESB
ESB (Enhanced ShockBurst) offers reliable wireless communication with adaptive data rates up to 2 Mbps, low power consumption, and automatic packet handling including acknowledgments and retransmissions. Its simple protocol enables efficient one-to-one or one-to-many connections without extensive host intervention. Your devices benefit from robust data integrity and minimal latency, making ESB ideal for applications requiring fast and dependable wireless links.
Core Characteristics of BLE
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) offers ultra-low power consumption, making it ideal for battery-operated devices and long-term use cases. It supports rapid connection and transmission intervals, ensuring efficient data exchange with minimal latency. Your IoT and wearable devices benefit from BLE's optimized balance of range, speed, and power efficiency compared to traditional ESB (Enhanced ShockBurst) protocols.
Communication Protocol Comparison
ESB (Enhanced ShockBurst) and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) are communication protocols designed for wireless data transfer with distinct use cases and efficiencies. ESB offers a simpler, proprietary protocol optimized for low-latency and low-power sensor communication ideal for short-range applications, while BLE provides a standardized, widely-supported protocol with robust security features and longer range suited for consumer electronics and IoT devices. Your choice depends on factors like interoperability requirements, power consumption constraints, and desired data throughput.
Power Consumption: ESB vs BLE
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) offers significantly lower power consumption compared to ESB (Enhanced ShockBurst), making it ideal for battery-operated devices requiring long-life performance. ESB, while efficient for reliable communication, generally consumes more energy due to its continuous packet transmissions and lack of advanced power-saving features found in BLE. Your choice between ESB and BLE should consider this trade-off to optimize device longevity and energy efficiency.
Range and Data Rate Differences
ESB (Enhanced ShockBurst) typically provides a range of up to 100 meters with data rates around 2 Mbps, optimized for low-latency, reliable communication in short to medium distances. BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) offers a variable range from 10 to 240 meters depending on the version and transmission power, with data rates commonly at 1 Mbps and higher in BLE 5.0 and beyond, focusing on low power consumption for intermittent data transmission. The choice between ESB and BLE depends on the specific application requirements for range, data rate, and energy efficiency in wireless communications.
Security Considerations
ESB (Enhanced ShockBurst) offers basic security features such as 32-bit CRC and encryption, but lacks advanced authentication mechanisms compared to BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy), which incorporates AES-128 encryption and device authentication for secure data transfer. BLE supports security modes like Just Works, Passkey Entry, and Numeric Comparison, providing flexible authentication depending on application requirements. For critical applications requiring robust security, BLE's comprehensive protocol and security stack ensure stronger protection against eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
Use Cases for ESB
ESB (Enhanced ShockBurst) excels in use cases requiring low power consumption and reliable communication in short-range wireless devices, such as remote controls, wireless sensors, and game controllers. Its efficient packet handling and low latency make it ideal for applications needing rapid response times and minimal energy usage. You can leverage ESB in scenarios where consistent data delivery with minimal retransmissions is crucial, especially in battery-powered IoT devices.
Use Cases for BLE
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) excels in use cases requiring low power consumption and intermittent data transmission, such as fitness trackers, smart home devices, and medical monitoring systems. Its ability to maintain long battery life while supporting reliable connections makes it ideal for wearable technology and Internet of Things (IoT) applications where continuous or frequent communication is necessary. You can leverage BLE for cost-effective, energy-efficient wireless data transfer in scenarios demanding minimal latency and maximized device longevity.
Choosing Between ESB and BLE
Choosing between ESB (Enhanced ShockBurst) and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) depends on specific application requirements such as range, power consumption, and compatibility. ESB offers low latency and high reliability for short-range point-to-point communication, making it ideal for simple wireless links and proprietary systems. BLE provides broader device interoperability and supports mesh networking, optimized for low power consumption in IoT and wearable devices.
ESB vs BLE Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com