Modbus RTU offers faster data transmission and more efficient use of bandwidth than Modbus ASCII, making it ideal for time-sensitive industrial applications. Explore the differences in error-checking methods, message framing, and compatibility to determine which protocol best suits Your needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
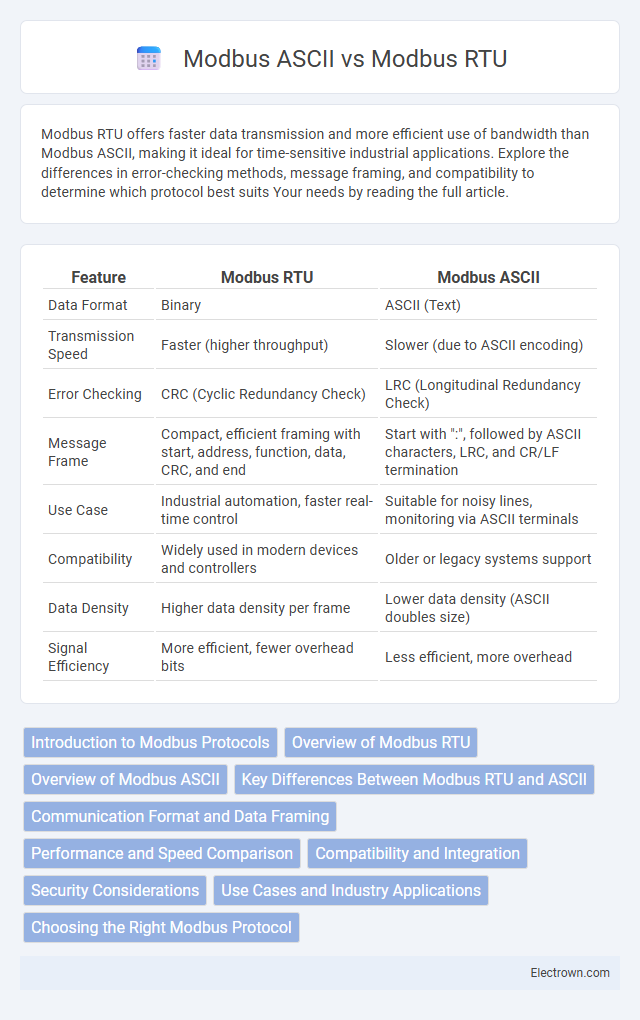
| Feature | Modbus RTU | Modbus ASCII |
|---|---|---|
| Data Format | Binary | ASCII (Text) |
| Transmission Speed | Faster (higher throughput) | Slower (due to ASCII encoding) |
| Error Checking | CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) | LRC (Longitudinal Redundancy Check) |
| Message Frame | Compact, efficient framing with start, address, function, data, CRC, and end | Start with ":", followed by ASCII characters, LRC, and CR/LF termination |
| Use Case | Industrial automation, faster real-time control | Suitable for noisy lines, monitoring via ASCII terminals |
| Compatibility | Widely used in modern devices and controllers | Older or legacy systems support |
| Data Density | Higher data density per frame | Lower data density (ASCII doubles size) |
| Signal Efficiency | More efficient, fewer overhead bits | Less efficient, more overhead |
Introduction to Modbus Protocols
Modbus Protocols are widely used communication standards in industrial automation, with Modbus RTU and Modbus ASCII being two primary variants. Modbus RTU transmits data in binary format, offering faster communication and efficient error checking via CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check). Modbus ASCII encodes data in ASCII characters, providing easier readability and simpler debugging at the cost of slower transmission speeds.
Overview of Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU is a widely used serial communication protocol that transmits data in a compact binary format, offering efficient and fast communication ideal for industrial automation systems. It uses a continuous stream of bits with cyclic redundancy check (CRC) error checking to ensure data integrity over RS-485 or RS-232 interfaces. Your Modbus RTU setup benefits from robust, low-latency exchanges, making it suitable for real-time monitoring and control applications.
Overview of Modbus ASCII
Modbus ASCII is a serial communication protocol used in industrial automation, transmitting data in ASCII characters, which makes it easier to read and debug compared to Modbus RTU. It sends each byte as two ASCII characters, resulting in lower data density and slower communication speed than Modbus RTU, which uses binary encoding for faster performance. Modbus ASCII operates effectively over longer distances and noisy environments due to its simple and robust error-checking mechanism based on LRC (Longitudinal Redundancy Check).
Key Differences Between Modbus RTU and ASCII
Modbus RTU uses a compact binary format for faster communication, while Modbus ASCII transmits data in readable ASCII characters, making it easier to debug but slower. RTU frames are shorter and include a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for error detection, whereas ASCII frames are longer with a longitudinal redundancy check (LRC). Your choice depends on whether speed or readability is more critical for your industrial automation setup.
Communication Format and Data Framing
Modbus RTU uses a binary communication format with data framed by precise timing gaps, allowing faster and more efficient data transmission compared to Modbus ASCII, which employs an ASCII-coded format with start and stop characters for each byte, resulting in longer message lengths. The RTU frame includes a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for error checking, while ASCII frames use a longitudinal redundancy check (LRC) to ensure data integrity. Due to its compact binary structure, Modbus RTU is preferred in environments requiring high-speed and high-reliability communication, whereas Modbus ASCII suits applications where data readability and simplicity are prioritized.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Modbus RTU offers faster communication speeds and higher performance due to its binary data transmission, enabling more efficient use of bandwidth compared to the slower, ASCII-encoded Modbus ASCII. RTU mode supports baud rates typically ranging from 1,200 to 115,200 bits per second, while ASCII mode is limited, leading to longer message frame times and increased latency. When optimizing Your industrial network for speed and real-time control, Modbus RTU is generally the preferred choice.
Compatibility and Integration
Modbus RTU and Modbus ASCII offer distinct compatibility advantages based on communication requirements and device capabilities. Modbus RTU is widely supported in industrial systems due to its efficient binary data transmission, making it ideal for compatibility with modern PLCs and automation devices. Modbus ASCII enhances integration with older or simpler devices through human-readable ASCII characters, facilitating easier troubleshooting and easier integration in slower or serial communication environments.
Security Considerations
Modbus RTU offers faster data transmission with binary encoding, which can reduce exposure to certain types of interception compared to the ASCII format used in Modbus ASCII, but both lack inherent encryption making them vulnerable to unauthorized access. Implementing external security measures such as VPNs, firewalls, or Modbus-specific security protocols is essential to protect the integrity and confidentiality of data transmitted via both Modbus RTU and ASCII. Network segmentation and regular monitoring further enhance security by limiting attack surfaces and detecting potential intrusions in Modbus communication environments.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Modbus RTU is widely used in industrial automation for its compact binary format, making it ideal for applications requiring fast and efficient communication in environments like manufacturing plants and process control systems. Modbus ASCII, with its readable text format, suits lower-speed data communication and is favored in systems where manual troubleshooting or monitoring is necessary, such as building automation and remote device diagnostics. Understanding your specific use case helps determine the best protocol for reliable data exchange and system performance.
Choosing the Right Modbus Protocol
Choosing the right Modbus protocol depends on your specific application requirements, such as communication speed, data integrity, and environmental noise. Modbus RTU offers faster transmission and better error-checking with its binary format, making it ideal for industrial environments requiring efficient and reliable data exchange. Your decision should consider the trade-offs between Modbus RTU's performance advantages and Modbus ASCII's ease of readability and simplicity in debugging.
Modbus RTU vs Modbus ASCII Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com