FreeRTOS offers a lightweight, simple real-time operating system ideal for resource-constrained microcontrollers, while Zephyr provides a more feature-rich, scalable platform suited for complex IoT applications with extensive hardware support. Explore this article to understand which RTOS best fits your project requirements and development goals.
Table of Comparison
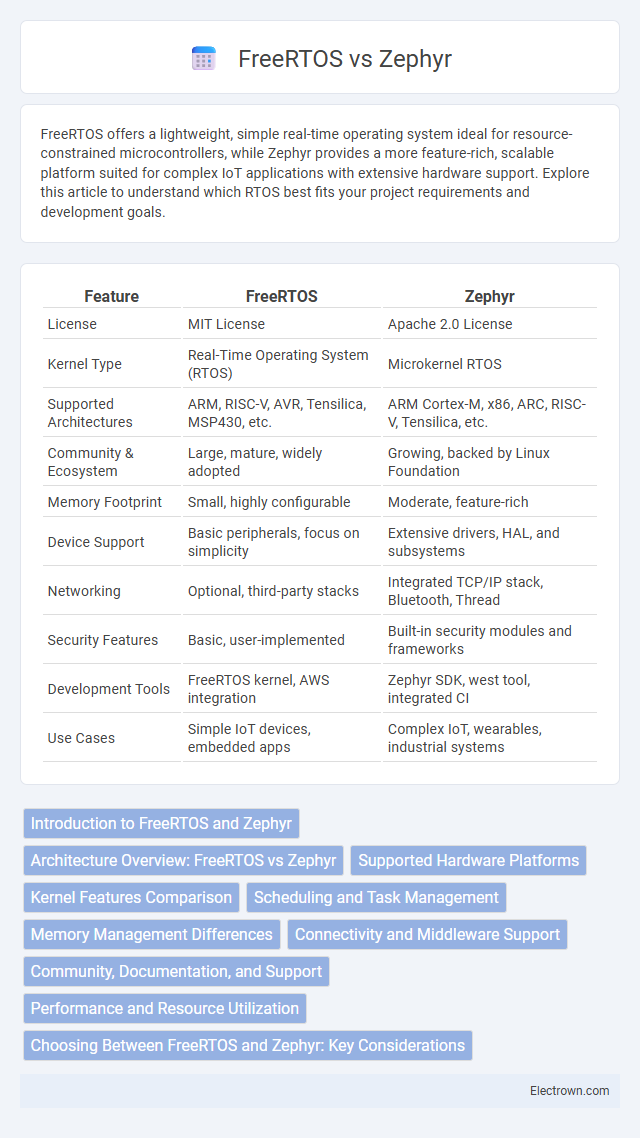
| Feature | FreeRTOS | Zephyr |
|---|---|---|
| License | MIT License | Apache 2.0 License |
| Kernel Type | Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) | Microkernel RTOS |
| Supported Architectures | ARM, RISC-V, AVR, Tensilica, MSP430, etc. | ARM Cortex-M, x86, ARC, RISC-V, Tensilica, etc. |
| Community & Ecosystem | Large, mature, widely adopted | Growing, backed by Linux Foundation |
| Memory Footprint | Small, highly configurable | Moderate, feature-rich |
| Device Support | Basic peripherals, focus on simplicity | Extensive drivers, HAL, and subsystems |
| Networking | Optional, third-party stacks | Integrated TCP/IP stack, Bluetooth, Thread |
| Security Features | Basic, user-implemented | Built-in security modules and frameworks |
| Development Tools | FreeRTOS kernel, AWS integration | Zephyr SDK, west tool, integrated CI |
| Use Cases | Simple IoT devices, embedded apps | Complex IoT, wearables, industrial systems |
Introduction to FreeRTOS and Zephyr
FreeRTOS is a popular open-source real-time operating system designed for embedded devices, known for its lightweight architecture and extensive community support. Zephyr OS is a scalable, modular real-time operating system optimized for secure, connected IoT devices, supporting multiple hardware architectures and offering advanced connectivity features. Your choice between FreeRTOS and Zephyr depends on specific project requirements such as hardware compatibility, real-time capabilities, and ecosystem preferences.
Architecture Overview: FreeRTOS vs Zephyr
FreeRTOS employs a minimalist, real-time kernel architecture optimized for simplicity and performance in embedded systems, featuring task management, synchronization primitives, and lightweight memory management. Zephyr uses a modular, scalable microkernel-based architecture designed for resource-constrained IoT devices, with extensive hardware abstraction layers, device drivers, and configuration options supporting complex applications. The contrasting architectural approaches highlight FreeRTOS's efficiency in simple real-time tasks versus Zephyr's flexibility and broader ecosystem integration.
Supported Hardware Platforms
FreeRTOS supports a wide range of hardware platforms including ARM Cortex-M, RISC-V, PIC, and Renesas, making it ideal for diverse embedded applications. Zephyr extends support to more complex architectures such as ARM Cortex-A, Intel x86, ARC, and NXP i.MX RT, providing flexibility for IoT and real-time systems. Choosing between these platforms depends on Your hardware requirements, with FreeRTOS favored for constrained microcontrollers and Zephyr suited to more powerful, feature-rich devices.
Kernel Features Comparison
FreeRTOS features a minimalist, single-kernel design optimized for real-time applications, offering preemptive and cooperative multitasking with configurable tickless idle modes to enhance power efficiency. Zephyr provides a more comprehensive and modular kernel with support for multi-threading, priority-based scheduling, and advanced synchronization primitives, suitable for complex IoT systems. The kernel of Zephyr also integrates robust device driver management and real-time capabilities, surpassing FreeRTOS in scalability and hardware abstraction.
Scheduling and Task Management
FreeRTOS employs a preemptive real-time scheduler with fixed-priority scheduling and supports cooperative multitasking, enabling straightforward task management in resource-constrained embedded systems. Zephyr utilizes a more flexible priority-based preemptive scheduler with support for multiple scheduling policies, including round-robin and earliest deadline first (EDF), providing enhanced control over task execution and responsiveness. Both kernels manage tasks through threads, but Zephyr's API offers more advanced features such as dynamic thread creation, priority inheritance, and sophisticated synchronization primitives.
Memory Management Differences
FreeRTOS employs a simple, deterministic memory management system primarily using static allocation and limited dynamic allocation through heap_4 or heap_5 schemes, ensuring predictable real-time performance. Zephyr offers more flexible memory management with multiple heap and slab allocators, including dynamic memory, object pools, and memory domains, supporting complex applications and better memory protection. Zephyr's advanced features enable fine-grained control over memory regions, while FreeRTOS focuses on minimal footprint and real-time efficiency.
Connectivity and Middleware Support
FreeRTOS offers extensive connectivity options primarily through its support for TCP/IP stacks like FreeRTOS+TCP and middleware such as MQTT, enabling reliable IoT communication. Zephyr provides a broader range of built-in protocols including Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and Thread, along with comprehensive middleware libraries for networking, security, and device management. Your choice depends on the specific connectivity needs and middleware complexity required for your embedded application.
Community, Documentation, and Support
FreeRTOS boasts a large, mature community with extensive Amazon Web Services (AWS) backing, providing comprehensive documentation and numerous user-contributed resources. Zephyr offers a rapidly growing, open-source community supported by the Linux Foundation, featuring detailed documentation and active forums that encourage collaboration and real-time problem-solving. Your choice between FreeRTOS and Zephyr should consider the level of community engagement, the depth of documentation, and the availability of professional or community support suited to your project needs.
Performance and Resource Utilization
FreeRTOS excels in minimal resource utilization and low-latency performance, making it ideal for simple, resource-constrained embedded systems. Zephyr provides more advanced features and better scalability, but typically requires higher memory and CPU usage compared to FreeRTOS. Your choice depends on whether optimized performance with minimal overhead or richer functionality and extensibility is a priority for your project.
Choosing Between FreeRTOS and Zephyr: Key Considerations
FreeRTOS excels in simplicity, real-time performance, and widespread industry adoption, making it ideal for low-resource microcontrollers and straightforward applications. Zephyr offers a richer set of features, including built-in networking, file systems, and extensive hardware support, better suited for complex IoT devices requiring scalability and modularity. Decision factors include project complexity, hardware capabilities, community support, and ecosystem maturity for selecting the optimal RTOS framework.
FreeRTOS vs Zephyr Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com