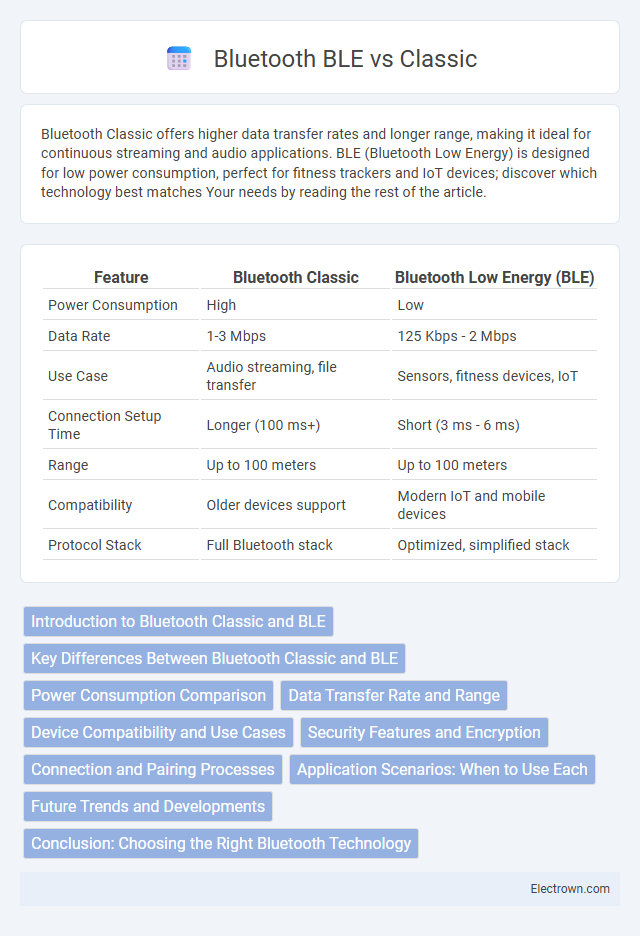
Bluetooth Classic offers higher data transfer rates and longer range, making it ideal for continuous streaming and audio applications. BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) is designed for low power consumption, perfect for fitness trackers and IoT devices; discover which technology best matches Your needs by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bluetooth Classic | Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) |
|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | High | Low |
| Data Rate | 1-3 Mbps | 125 Kbps - 2 Mbps |
| Use Case | Audio streaming, file transfer | Sensors, fitness devices, IoT |
| Connection Setup Time | Longer (100 ms+) | Short (3 ms - 6 ms) |
| Range | Up to 100 meters | Up to 100 meters |
| Compatibility | Older devices support | Modern IoT and mobile devices |
| Protocol Stack | Full Bluetooth stack | Optimized, simplified stack |
Introduction to Bluetooth Classic and BLE
Bluetooth Classic supports continuous, high data rate connections ideal for applications like audio streaming and file transfer, while Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is designed for intermittent, low power communication suitable for devices like fitness trackers and smart home sensors. Bluetooth Classic operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band with data rates up to 3 Mbps, whereas BLE offers lower data rates and reduced energy consumption to extend battery life. Understanding these differences helps you choose the appropriate technology based on your device's power constraints and data transfer needs.
Key Differences Between Bluetooth Classic and BLE
Bluetooth Classic offers higher data transfer rates up to 3 Mbps, making it ideal for continuous streaming applications such as audio and video. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) prioritizes power efficiency with significantly lower energy consumption, designed for intermittent data transmission in IoT devices and wearable technology. BLE achieves faster connection times and supports extensive device scalability compared to Bluetooth Classic's emphasis on sustained connections.
Power Consumption Comparison
Bluetooth Classic consumes significantly more power than Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), making BLE the preferred choice for battery-sensitive applications such as wearable devices and IoT sensors. BLE achieves energy efficiency by using short bursts of data transmission and extended sleep periods, while Bluetooth Classic maintains a continuous connection that drains the battery faster. Your device will benefit from longer battery life and reduced energy costs when utilizing BLE for low-bandwidth, periodic data communication.
Data Transfer Rate and Range
Bluetooth Classic offers a higher data transfer rate, typically up to 3 Mbps, making it suitable for applications requiring continuous, high-bandwidth connections like audio streaming. In contrast, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) emphasizes power efficiency and extends range, often reaching up to 100 meters, but supports lower data rates around 1 Mbps or less. Your choice between Bluetooth Classic and BLE should depend on whether higher throughput or longer range with energy savings is prioritized for your device's use case.
Device Compatibility and Use Cases
Bluetooth Classic offers broad device compatibility, especially with audio devices, smartphones, and laptops, making it ideal for applications requiring continuous, high-bandwidth connections like wireless headphones and car audio systems. BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) excels in low-power, intermittent data transmission, suited for fitness trackers, medical devices, and smart home sensors, where battery life efficiency is critical. Your choice depends on whether sustained data throughput or minimal energy consumption aligns better with your specific device and use case requirements.
Security Features and Encryption
Bluetooth Classic employs Secure Simple Pairing (SSP) with authentication and encryption based on the ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman) key exchange, providing robust protection against eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) uses AES-128 CCM (Counter with CBC-MAC) encryption and supports multiple pairing methods including Just Works, Passkey Entry, and Numeric Comparison, enhancing security flexibility for low-power devices. BLE's Bluetooth 5.0 and later versions introduce LE Secure Connections with improved cryptographic strength, offering stronger protection and resistance to passive and active attacks compared to Bluetooth Classic.
Connection and Pairing Processes
Bluetooth Classic relies on a traditional pairing process involving device discovery, authentication, and secure link establishment, which can take several seconds and uses a higher power handshake. BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) employs a streamlined connection and pairing protocol optimized for quick interactions and reduced power consumption, using a simplified bonding process that maintains security with less resource usage. Your choice between Bluetooth Classic and BLE directly impacts device responsiveness and battery life during connection and pairing.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Each
Bluetooth Classic excels in applications requiring continuous streaming of high-quality audio, such as wireless headphones and car infotainment systems. BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) is ideal for devices with intermittent data transmission needs and low power consumption, including fitness trackers, smart home sensors, and medical devices. Selecting Bluetooth Classic or BLE depends on balancing data throughput demands with battery life requirements in specific use cases.
Future Trends and Developments
Bluetooth Classic is evolving with enhanced data rates and improved audio quality to meet the demands of multimedia applications, while Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is advancing in power efficiency and mesh networking capabilities, enabling large-scale IoT deployments. Emerging developments include Bluetooth LE Audio, which integrates BLE with Classic audio profiles to provide superior sound quality and multi-stream support in low power consumption modes. Future trends emphasize greater interoperability, improved security features, and expanded use in smart home, healthcare, and wearable technologies.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Bluetooth Technology
Choosing the right Bluetooth technology depends on the specific use case and power requirements. Bluetooth Classic excels in continuous data streaming applications like audio playback, while Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is optimized for intermittent transmission and minimal power consumption, ideal for IoT devices and sensor networks. Prioritizing battery life and data throughput needs ensures the selection aligns with device functionality and user experience.
Bluetooth Classic vs BLE Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com