A watchdog timer monitors system activity to reset the device if it becomes unresponsive, ensuring reliability during software failures, while a brownout detector safeguards your electronics by monitoring voltage levels and triggering a reset during power drops. Discover the key differences and how these components protect your hardware in the full article.
Table of Comparison
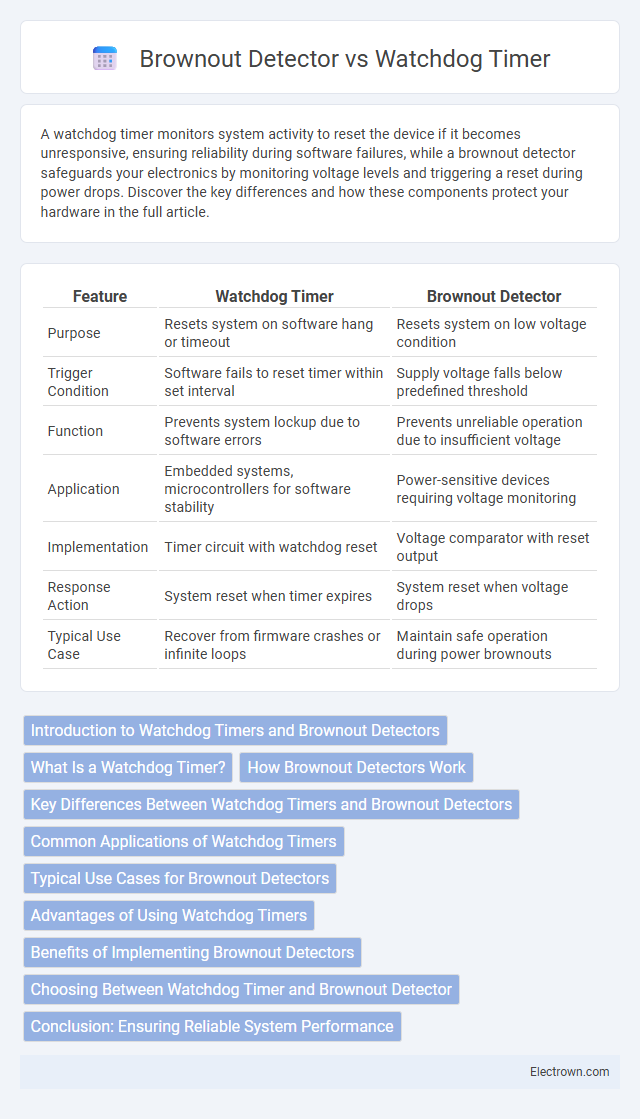
| Feature | Watchdog Timer | Brownout Detector |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Resets system on software hang or timeout | Resets system on low voltage condition |
| Trigger Condition | Software fails to reset timer within set interval | Supply voltage falls below predefined threshold |
| Function | Prevents system lockup due to software errors | Prevents unreliable operation due to insufficient voltage |
| Application | Embedded systems, microcontrollers for software stability | Power-sensitive devices requiring voltage monitoring |
| Implementation | Timer circuit with watchdog reset | Voltage comparator with reset output |
| Response Action | System reset when timer expires | System reset when voltage drops |
| Typical Use Case | Recover from firmware crashes or infinite loops | Maintain safe operation during power brownouts |
Introduction to Watchdog Timers and Brownout Detectors
Watchdog timers and brownout detectors are critical components in embedded systems for maintaining operational reliability. Watchdog timers reset your system when software malfunctions or hangs, preventing system crashes by monitoring program execution. Brownout detectors safeguard your device from unstable voltage levels by triggering a reset when the supply voltage dips below a defined threshold, ensuring stable power conditions.
What Is a Watchdog Timer?
A Watchdog Timer is a hardware timer used in embedded systems to detect and recover from system malfunctions by resetting the microcontroller if the software becomes unresponsive or enters an infinite loop. It operates by requiring the system to regularly reset the timer before it reaches a preset limit, ensuring continuous operation and preventing system hangs. This mechanism is critical for maintaining system reliability and stability in real-time applications.
How Brownout Detectors Work
Brownout detectors monitor supply voltage levels and trigger a reset when voltage falls below a predefined threshold, preventing erratic microcontroller behavior during undervoltage conditions. They operate by comparing the supply voltage against an internal reference voltage, ensuring the system only runs when the power supply is stable. This contrasts with watchdog timers, which detect system malfunctions by monitoring program execution rather than voltage levels.
Key Differences Between Watchdog Timers and Brownout Detectors
Watchdog timers monitor system activity and trigger a reset if a program becomes unresponsive, ensuring your device recovers from software faults. Brownout detectors, on the other hand, detect voltage drops below a critical threshold and reset the system to prevent malfunction caused by insufficient power. The key difference lies in their focus: watchdog timers safeguard against software lock-ups, while brownout detectors protect hardware stability during power fluctuations.
Common Applications of Watchdog Timers
Watchdog timers are commonly used in embedded systems for monitoring processor activity and ensuring system reliability by triggering a reset if the system hangs or becomes unresponsive. Their applications include automotive control units, industrial automation systems, and consumer electronics, where continuous operation is critical. Your device benefits from watchdog timers by preventing software crashes and maintaining stable performance in safety-critical environments.
Typical Use Cases for Brownout Detectors
Brownout detectors are primarily used in embedded systems to monitor supply voltage levels and prevent erratic behavior during undervoltage conditions by triggering system resets or safe shutdowns. Common applications include microcontroller units in battery-powered devices, automotive electronics, and critical industrial control systems where stable voltage is essential for reliable operation. These detectors enhance system stability by ensuring that processors only operate within specified voltage thresholds, avoiding data corruption and unpredictable system states.
Advantages of Using Watchdog Timers
Watchdog timers enhance system reliability by automatically resetting a microcontroller when software anomalies or unexpected behaviors occur, minimizing downtime and data corruption. Unlike brownout detectors that monitor voltage levels to prevent erratic operation during power fluctuations, watchdog timers provide active monitoring of software execution, ensuring your embedded system recovers from crashes without manual intervention. Their ability to detect software freezes and timing errors makes watchdog timers essential for maintaining robust, resilient operation in critical applications.
Benefits of Implementing Brownout Detectors
Brownout detectors protect microcontrollers by monitoring voltage levels and triggering a reset when power dips below a safe threshold, preventing erratic system behavior. Unlike watchdog timers that rely on software execution to detect failures, brownout detectors offer hardware-level reliability during power fluctuations, enhancing system stability. Implementing brownout detectors ensures your devices avoid corrupted operations and unexpected resets caused by voltage drops, improving overall robustness in embedded systems.
Choosing Between Watchdog Timer and Brownout Detector
Choosing between a watchdog timer and a brownout detector depends on the specific reliability needs of your embedded system. A watchdog timer primarily safeguards against software failures by resetting the system if the program becomes unresponsive, while a brownout detector focuses on maintaining stable operation during low voltage conditions by triggering resets when voltage drops below a critical threshold. Selecting the appropriate component hinges on whether voltage stability or software fault recovery is the priority for your device's operational integrity.
Conclusion: Ensuring Reliable System Performance
Watchdog timers and brownout detectors play crucial roles in ensuring reliable system performance by preventing failures caused by software faults and power instability. Watchdog timers reset the system if the software becomes unresponsive, while brownout detectors safeguard against low voltage conditions that can cause erratic behavior or data corruption. Integrating both mechanisms enhances system robustness by maintaining stable operation and reducing unexpected downtime.
Watchdog timer vs brownout detector Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com