Peripheral Library (PLIB) offers a collection of pre-built functions designed to control microcontroller peripherals directly, providing efficient, low-level access. Your choice between PLIB and Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) depends on whether you prioritize granular control or ease of portability; explore the rest of the article to understand their key differences and best use cases.
Table of Comparison
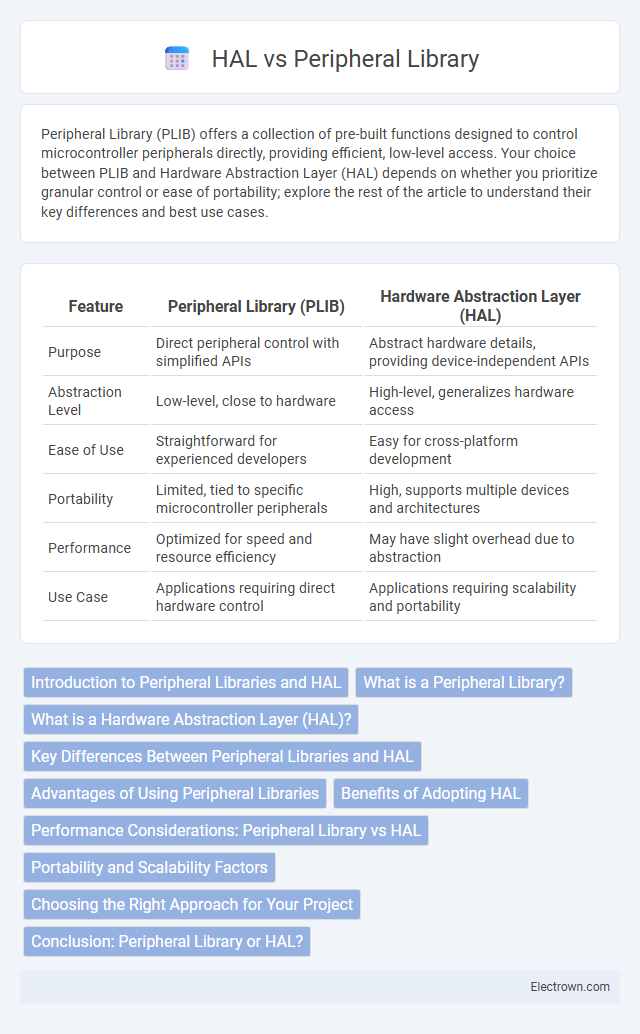
| Feature | Peripheral Library (PLIB) | Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Direct peripheral control with simplified APIs | Abstract hardware details, providing device-independent APIs |
| Abstraction Level | Low-level, close to hardware | High-level, generalizes hardware access |
| Ease of Use | Straightforward for experienced developers | Easy for cross-platform development |
| Portability | Limited, tied to specific microcontroller peripherals | High, supports multiple devices and architectures |
| Performance | Optimized for speed and resource efficiency | May have slight overhead due to abstraction |
| Use Case | Applications requiring direct hardware control | Applications requiring scalability and portability |
Introduction to Peripheral Libraries and HAL
Peripheral Libraries provide low-level access to microcontroller hardware, offering direct control over individual registers and peripherals for maximum efficiency in embedded systems. Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) simplifies development by offering a standardized, higher-level interface that abstracts hardware details, enhancing portability and ease of use across different microcontroller platforms. Understanding the differences between Peripheral Libraries and HAL helps you choose the right approach for balancing control, complexity, and code portability in your embedded application.
What is a Peripheral Library?
A Peripheral Library is a collection of pre-written software functions designed to simplify the control and management of microcontroller peripherals, such as timers, ADCs, and communication interfaces. It provides low-level access to hardware features with optimized and reusable code, ensuring efficient development and consistent performance. Your use of a Peripheral Library can significantly speed up application development by abstracting complex register configurations into straightforward function calls.
What is a Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL)?
A Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) is a software interface that enables applications to interact with hardware devices in a standardized way, abstracting the low-level hardware details. Unlike Peripheral Libraries, which provide direct control over specific hardware components, HAL offers uniform APIs to manage diverse hardware platforms, improving portability and scalability. This abstraction simplifies development by allowing software to operate independently of specific hardware implementations.
Key Differences Between Peripheral Libraries and HAL
Peripheral Libraries provide low-level, hardware-specific functions for direct control of microcontroller peripherals, offering fine-grained access and optimized performance. Hardware Abstraction Layers (HAL) offer a higher-level, standardized API that abstracts hardware details, simplifying cross-platform development and enhancing code portability. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize performance and control (Peripheral Libraries) or ease of development and portability (HAL).
Advantages of Using Peripheral Libraries
Peripheral Libraries offer streamlined access to microcontroller peripherals with precise, low-level control, enabling optimized performance for time-critical applications. Their lightweight design reduces overhead, resulting in faster execution and smaller code footprints compared to abstracted layers like HAL. You benefit from enhanced customization and direct hardware manipulation, critical for advanced embedded system development.
Benefits of Adopting HAL
Adopting Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) provides improved portability across different microcontrollers by abstracting low-level hardware details, which reduces development time and effort. HAL simplifies code maintenance and enhances scalability, allowing your applications to adapt seamlessly to future hardware updates. This approach ensures consistent API usage, promoting easier debugging and integration compared to Peripheral Libraries.
Performance Considerations: Peripheral Library vs HAL
Peripheral Library offers more direct control over hardware registers, resulting in faster execution and lower latency compared to HAL. The Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) introduces abstraction layers that simplify development but may incur additional overhead and reduced performance. For time-critical applications, Peripheral Library often delivers optimized performance due to minimal abstraction and efficient hardware access.
Portability and Scalability Factors
Peripheral Library offers limited portability as it is closely tied to specific microcontroller architectures, restricting scalability across different hardware platforms. In contrast, Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) provides a higher level of portability by abstracting hardware details, enabling scalable firmware development for diverse microcontrollers. HAL's standardized APIs facilitate easier code reuse and system expansion, enhancing adaptability in embedded system designs.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Peripheral Library offers low-level, fine-tuned control over microcontroller hardware, making it ideal for projects requiring maximum performance and minimal overhead. HAL (Hardware Abstraction Layer) provides a higher level of abstraction, simplifying code development and enhancing portability across various hardware platforms. Choosing the right approach depends on your project's complexity, performance requirements, and the need for scalability or code maintainability.
Conclusion: Peripheral Library or HAL?
Choosing between Peripheral Library and HAL depends on your project's complexity and development speed needs. Peripheral Library offers low-level, fine-tuned control ideal for experienced developers optimizing specific hardware functions. HAL provides a higher abstraction layer with broader device support, simplifying code reuse and speeding up development, making it suitable for applications where rapid prototyping and maintainability are priorities.
Peripheral Library vs HAL Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com