Assembly language offers low-level hardware control with high efficiency and speed, while C provides a balance of low-level capabilities and high-level programming ease, enhancing portability and readability. Explore the full article to understand how your choice between Assembly and C can impact development and performance.
Table of Comparison
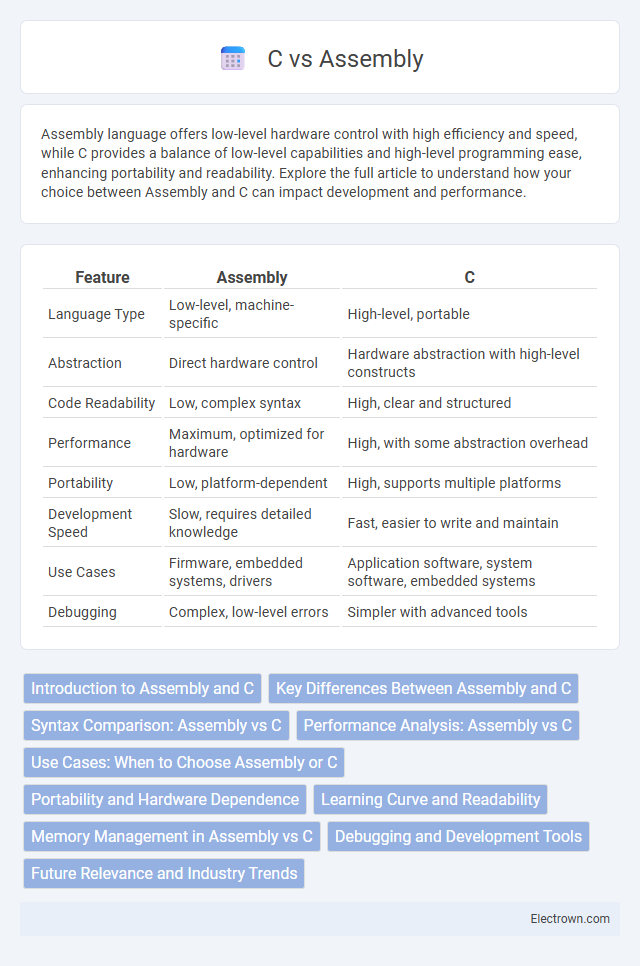
| Feature | Assembly | C |
|---|---|---|
| Language Type | Low-level, machine-specific | High-level, portable |
| Abstraction | Direct hardware control | Hardware abstraction with high-level constructs |
| Code Readability | Low, complex syntax | High, clear and structured |
| Performance | Maximum, optimized for hardware | High, with some abstraction overhead |
| Portability | Low, platform-dependent | High, supports multiple platforms |
| Development Speed | Slow, requires detailed knowledge | Fast, easier to write and maintain |
| Use Cases | Firmware, embedded systems, drivers | Application software, system software, embedded systems |
| Debugging | Complex, low-level errors | Simpler with advanced tools |
Introduction to Assembly and C
Assembly language provides low-level hardware control with direct memory access and CPU instruction manipulation, enabling optimized performance and precise resource management. C is a high-level programming language designed for system programming, offering portability and ease of use with structured syntax and abstractions. Assembly excels in speed and hardware interfacing, while C balances efficiency with readability and maintainability across various platforms.
Key Differences Between Assembly and C
Assembly language operates at a low level, providing direct control over hardware with opcode instructions specific to processor architecture, while C is a high-level programming language designed for portability across systems with abstracted hardware interactions. Assembly requires detailed knowledge of the CPU, registers, and memory management, resulting in faster execution and smaller code size, whereas C offers easier code maintenance, debugging, and complex data structure support. Assembly is commonly used for performance-critical tasks and embedded systems, while C serves as a general-purpose language for system programming, application development, and operating systems.
Syntax Comparison: Assembly vs C
Assembly language syntax consists of low-level, mnemonic codes directly representing machine instructions, requiring detailed knowledge of hardware registers and memory addressing. C syntax is high-level, using structured statements, functions, and variables that abstract hardware complexities, making code more readable and portable across platforms. Your choice affects development speed and control: Assembly offers precise hardware manipulation, while C provides easier syntax and maintainability.
Performance Analysis: Assembly vs C
Assembly language offers superior performance due to its low-level operations, enabling precise hardware control and optimization that high-level languages like C cannot fully match. C provides a balance between performance and portability, often generating efficient machine code via compilers but sometimes producing less optimized instructions compared to hand-coded assembly. For performance-critical tasks, optimizing your code in Assembly can yield faster execution times and lower resource usage than equivalent C programs.
Use Cases: When to Choose Assembly or C
Assembly language is ideal for performance-critical applications requiring direct hardware manipulation, such as embedded systems, firmware development, and real-time operating systems. C is preferred for system-level programming, including operating systems, compilers, and large-scale applications, due to its balance of efficiency and portability. Choosing Assembly is essential when maximum control, minimal overhead, and fine-tuned optimization are necessary, whereas C offers easier maintainability and faster development for complex software projects.
Portability and Hardware Dependence
Assembly language is highly hardware-dependent, designed for specific processor architectures, which limits its portability across different systems. C offers greater portability by abstracting hardware details, allowing your code to be compiled and run on various platforms with minimal modifications. This hardware independence makes C the preferred choice for developing cross-platform applications.
Learning Curve and Readability
Assembly language features a steep learning curve due to its low-level syntax and intricate hardware interactions, requiring detailed knowledge of processor architecture. C offers improved readability with a higher-level, structured syntax closer to human language, making it more accessible for those new to programming. Your choice between the two depends on whether you prioritize direct hardware control or easier code comprehension and faster development.
Memory Management in Assembly vs C
Assembly language offers direct control over memory management, allowing you to manipulate memory addresses and registers explicitly, which provides high efficiency but requires meticulous attention to avoid errors such as buffer overflows or memory leaks. In contrast, C provides a balance between control and convenience with built-in functions like malloc() and free() for dynamic memory allocation, along with automatic stack management for local variables, reducing the risk of memory mismanagement. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing performance and safety in low-level programming tasks.
Debugging and Development Tools
Assembly language offers limited debugging and development tools compared to C, as it lacks extensive integrated development environments (IDEs) and high-level debugging features. C benefits from robust toolchains like GCC and Clang, along with advanced debuggers such as GDB that support breakpoints, step execution, and variable inspection. Your development process can be significantly accelerated with C's rich ecosystem of diagnostics and automated testing tools, making debugging more efficient than low-level Assembly coding.
Future Relevance and Industry Trends
Assembly language, with its low-level hardware control, remains crucial for embedded systems and performance-critical applications despite the rising abstraction of modern programming languages. C continues to dominate as a versatile language for system programming, operating systems, and application development, benefiting from extensive community support and continuous updates. Your choice between Assembly and C should consider future relevance, where C's adaptability aligns with evolving industry trends, while Assembly's niche importance persists in specialized domains.
Assembly vs C Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com