The HD44780 is a classic character LCD controller ideal for displaying text with simple interface requirements, while the SSD1306 is a versatile OLED graphic display controller supporting high-resolution monochrome images and complex graphics. Discover how each controller can enhance your project by exploring their unique features and applications in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
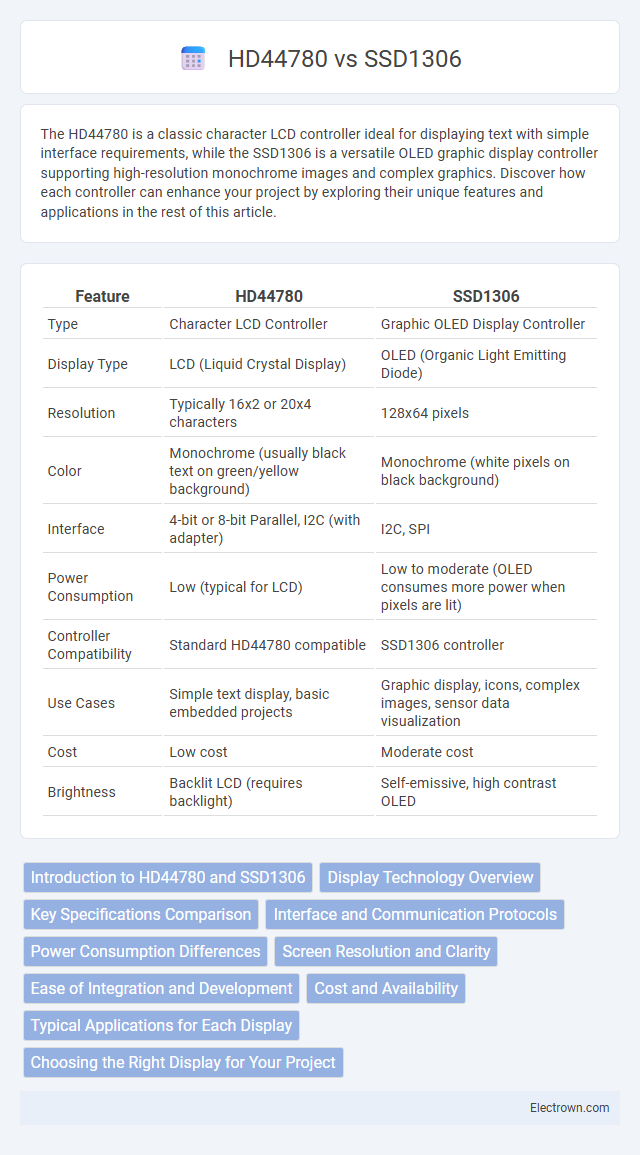
| Feature | HD44780 | SSD1306 |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Character LCD Controller | Graphic OLED Display Controller |
| Display Type | LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) | OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) |
| Resolution | Typically 16x2 or 20x4 characters | 128x64 pixels |
| Color | Monochrome (usually black text on green/yellow background) | Monochrome (white pixels on black background) |
| Interface | 4-bit or 8-bit Parallel, I2C (with adapter) | I2C, SPI |
| Power Consumption | Low (typical for LCD) | Low to moderate (OLED consumes more power when pixels are lit) |
| Controller Compatibility | Standard HD44780 compatible | SSD1306 controller |
| Use Cases | Simple text display, basic embedded projects | Graphic display, icons, complex images, sensor data visualization |
| Cost | Low cost | Moderate cost |
| Brightness | Backlit LCD (requires backlight) | Self-emissive, high contrast OLED |
Introduction to HD44780 and SSD1306
The HD44780 is a widely used character LCD controller known for its simplicity and reliable performance in displaying text on alphanumeric LCD screens, commonly found in embedded systems. The SSD1306 is a popular OLED display driver that supports graphical output with high contrast and low power consumption, often used in modern wearable and IoT devices. Both controllers serve distinct purposes with the HD44780 excelling in character display and the SSD1306 offering versatile, high-resolution graphics capabilities.
Display Technology Overview
The HD44780 is a character-based LCD controller commonly used in monochrome alphanumeric displays with a segmented pixel arrangement, typically supporting a 5x8 dot matrix for each character. The SSD1306 is a versatile OLED controller designed for graphical displays, offering a high-resolution pixel matrix with superior contrast, wider viewing angles, and faster refresh rates. OLED technology in SSD1306 provides self-emissive pixels, resulting in deeper blacks and lower power consumption compared to the backlit LCDs driven by the HD44780.
Key Specifications Comparison
The HD44780 is a character LCD controller featuring a 16x2 or 20x4 character display with a resolution limited to character matrices, while the SSD1306 is an OLED graphic controller supporting resolutions up to 128x64 pixels with monochrome output. HD44780 operates using parallel interface protocols with low power consumption suitable for simple alphanumeric display applications, whereas SSD1306 provides higher contrast, faster refresh rates, and communicates primarily via I2C or SPI interfaces. Memory-wise, HD44780 has a built-in character generator ROM and a small RAM for display data, contrasted by SSD1306's internal graphic memory allowing complex image rendering and animations.
Interface and Communication Protocols
The HD44780 LCD primarily uses a parallel interface with a 4-bit or 8-bit data bus, coupled with control lines such as RS, RW, and E for communication, making it suitable for straightforward microcontroller connections. The SSD1306 OLED display employs an I2C or SPI serial interface, significantly reducing the number of required microcontroller pins and enabling faster data transfer rates compared to the HD44780. While HD44780's parallel interface offers simplicity and compatibility with many legacy systems, the SSD1306's serial communication protocols provide greater flexibility and ease of use in compact, modern designs.
Power Consumption Differences
The HD44780 LCD controller typically consumes more power due to its backlit display and character-based technology, often drawing around 2 to 3 mA without backlight, but can spike significantly with backlighting on. In contrast, the SSD1306 OLED display is more power-efficient overall, averaging between 20 to 30 mA during operation, although power consumption varies with pixel brightness since each pixel is individually lit. Understanding these differences helps you optimize your project's battery life by selecting the display technology that aligns with your power budget and usage patterns.
Screen Resolution and Clarity
The HD44780 features a basic 16x2 or 20x4 character LCD display, offering limited resolution suitable for simple text output. In contrast, the SSD1306 supports a high-resolution 128x64 pixel OLED screen, delivering superior clarity and the ability to render detailed graphics and custom fonts. This significant difference in pixel density makes the SSD1306 ideal for applications requiring sharp images and precise visual elements.
Ease of Integration and Development
The HD44780 LCD controller offers straightforward integration with a wide range of microcontrollers thanks to its well-documented parallel interface and extensive community support, making development faster for simple text displays. In contrast, the SSD1306 OLED controller provides more complex interfacing through I2C or SPI protocols, requiring additional libraries and configuration but enabling richer graphical content and higher display resolution. Developers can leverage abundant software resources for both, though HD44780 is favored for basic projects while SSD1306 suits advanced applications needing enhanced visuals.
Cost and Availability
The HD44780 LCD module is widely known for its low cost and high availability, making it a popular choice in budget-conscious projects and educational kits. In contrast, the SSD1306 OLED display generally comes at a higher price point due to its superior resolution and contrast capabilities but remains readily available through various electronics suppliers. Your decision should weigh the balance between budget constraints and the desired display quality, with HD44780 excelling in cost-effectiveness and SSD1306 offering advanced features at a moderate premium.
Typical Applications for Each Display
The HD44780 is commonly used in character-based applications such as digital clocks, calculators, and simple menu systems due to its low cost and ease of interfacing with microcontrollers. The SSD1306, being a graphic OLED display, is favored for more complex interfaces like wearable devices, portable instruments, and IoT gadgets that require high-resolution visual output and rich graphics. Both displays serve distinct niches, with the HD44780 excelling in text display tasks and the SSD1306 preferred for advanced visual presentations.
Choosing the Right Display for Your Project
When choosing between the HD44780 and SSD1306 displays, consider that the HD44780 is a character LCD ideal for projects requiring simple text output with low power consumption. The SSD1306 is an OLED display offering high-resolution graphics, better contrast, and wider viewing angles, suitable for detailed visuals and dynamic interfaces. Project requirements such as display size, resolution, power constraints, and data complexity play crucial roles in selecting the appropriate module.
HD44780 vs SSD1306 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com