Blob bootloaders are proprietary, closed-source firmware components with limited customization options and potential security risks, while open-source bootloaders provide transparency, flexibility, and community-driven support for enhancing your device's startup process. Explore the rest of the article to understand the key differences and decide which bootloader best suits your needs.
Table of Comparison
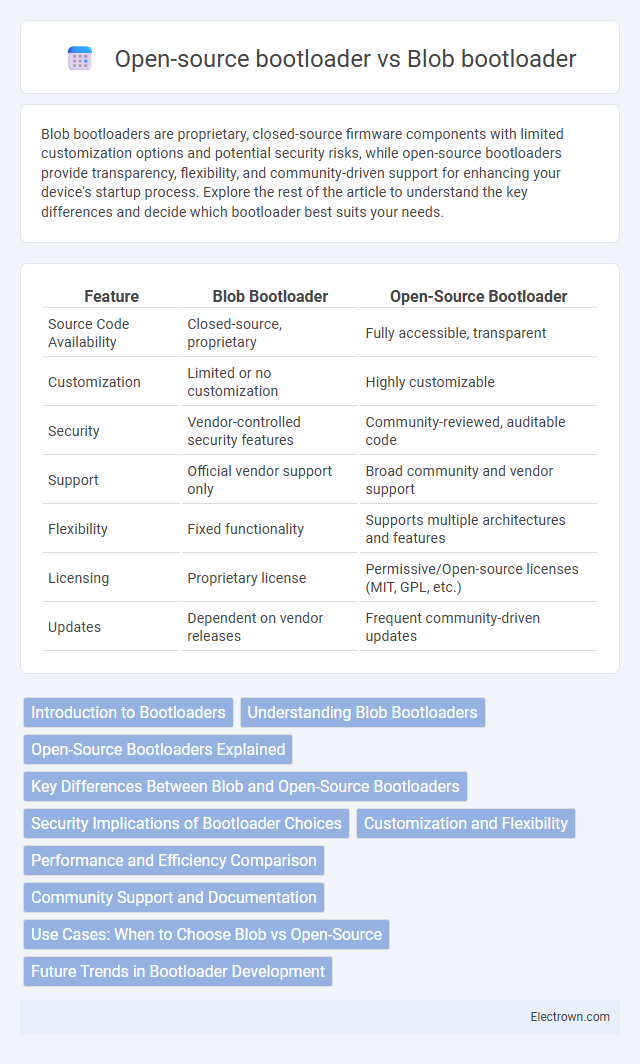
| Feature | Blob Bootloader | Open-Source Bootloader |
|---|---|---|
| Source Code Availability | Closed-source, proprietary | Fully accessible, transparent |
| Customization | Limited or no customization | Highly customizable |
| Security | Vendor-controlled security features | Community-reviewed, auditable code |
| Support | Official vendor support only | Broad community and vendor support |
| Flexibility | Fixed functionality | Supports multiple architectures and features |
| Licensing | Proprietary license | Permissive/Open-source licenses (MIT, GPL, etc.) |
| Updates | Dependent on vendor releases | Frequent community-driven updates |
Introduction to Bootloaders
Bootloaders are critical software programs that initialize hardware and load the main operating system during device startup. Blob bootloaders often consist of proprietary, binary-only firmware components, limiting customization and transparency. Open-source bootloaders like U-Boot or Coreboot enable developers to review, modify, and enhance the boot process, fostering greater security and adaptability across diverse hardware platforms.
Understanding Blob Bootloaders
Blob bootloaders contain proprietary binary code, lacking source code transparency and limiting customization options for developers. Open-source bootloaders provide full access to source code, enabling extensive modifications, security audits, and community-driven improvements. The closed nature of blob bootloaders often results in compatibility constraints and slower response to vulnerabilities compared to open-source alternatives.
Open-Source Bootloaders Explained
Open-source bootloaders provide transparent and customizable startup code, allowing developers to modify and optimize the boot process for specific hardware or software requirements. Unlike blob bootloaders, which are proprietary and closed-source, open-source options enhance security through community scrutiny and facilitate innovation by enabling access to the underlying code. Your ability to adapt and troubleshoot boot behavior improves significantly when using an open-source bootloader tailored to your system's needs.
Key Differences Between Blob and Open-Source Bootloaders
Blob bootloaders consist of proprietary, binary-only code with limited transparency and inability to modify or audit their firmware, while open-source bootloaders provide fully accessible source code enabling customization, security audits, and community-driven improvements. Blob bootloaders often restrict support to specific hardware platforms, restricting flexibility, whereas open-source bootloaders typically support a wide range of devices, facilitating cross-platform compatibility. Security and trust issues arise with blob bootloaders due to opaque operation, whereas open-source alternatives enhance security through transparency and collaborative vulnerability disclosure.
Security Implications of Bootloader Choices
Choosing a Blob bootloader versus an open-source bootloader significantly impacts device security, as Blob bootloaders often contain proprietary, opaque code that can harbor undisclosed vulnerabilities and backdoors. Open-source bootloaders offer greater transparency, allowing security audits, community scrutiny, and timely patching of identified flaws, enhancing trustworthiness. However, the security strength of any bootloader ultimately depends on active maintenance, code quality, and secure implementation practices rather than solely its open or closed-source nature.
Customization and Flexibility
Blob bootloaders offer limited customization and flexibility due to their proprietary nature and closed-source code, restricting developers to predefined functionalities and configurations. Open-source bootloaders provide extensive customization options, with accessible source code allowing developers to modify, extend, and tailor bootloader behavior to specific hardware and application requirements. The ability to adapt open-source bootloaders supports diverse use cases, accelerates development cycles, and enhances compatibility across multiple platforms.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Blob bootloaders often provide optimized performance tailored to specific hardware, resulting in faster boot times and efficient resource management compared to open-source bootloaders. Open-source bootloaders offer greater flexibility and customization, which may introduce slight overhead but enable better adaptability for diverse systems. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize raw efficiency or the ability to modify and optimize the bootloader's functionality.
Community Support and Documentation
Open-source bootloaders benefit from extensive community support, offering vast documentation, tutorials, and forums that facilitate troubleshooting and customization. Blob bootloaders, being proprietary, often provide limited documentation and rely on vendor-specific support channels, which can restrict your ability to modify or update the software independently. Access to open-source resources empowers you with greater flexibility and faster problem resolution compared to the closed nature of blob bootloaders.
Use Cases: When to Choose Blob vs Open-Source
Blob bootloaders, often proprietary and optimized for specific hardware, are ideal when you need guaranteed stability and vendor-supported updates for embedded systems or secure environments. Open-source bootloaders offer greater flexibility and customization, making them suitable for development projects, research, or devices where you need to modify or debug the boot process. You should choose a blob bootloader for quick deployment with vendor support and an open-source bootloader when your use case demands adaptability and transparency in boot-time operations.
Future Trends in Bootloader Development
Future trends in bootloader development emphasize open-source bootloaders for their transparency, customization, and community-driven improvements, outperforming proprietary blob bootloaders limited by closed-source constraints. Open-source solutions foster enhanced security, faster bug fixes, and adaptability to emerging hardware architectures, aligning with the increasing demand for flexible and secure firmware. Your choice of bootloader impacts long-term device compatibility and innovation, making open-source options a strategic advantage in evolving embedded systems.
Blob bootloader vs open-source bootloader Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com