ISP (Internet Service Provider) delivers internet access to your home or business, while ICP (Internet Content Provider) creates and distributes digital content online. Explore the differences and how they impact your online experience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
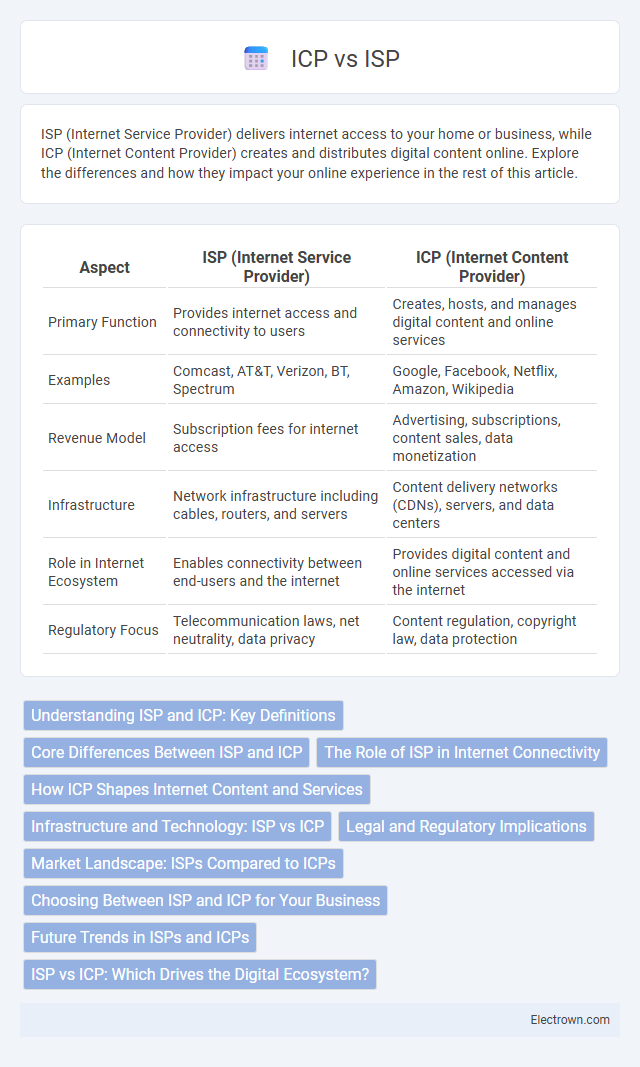
| Aspect | ISP (Internet Service Provider) | ICP (Internet Content Provider) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides internet access and connectivity to users | Creates, hosts, and manages digital content and online services |
| Examples | Comcast, AT&T, Verizon, BT, Spectrum | Google, Facebook, Netflix, Amazon, Wikipedia |
| Revenue Model | Subscription fees for internet access | Advertising, subscriptions, content sales, data monetization |
| Infrastructure | Network infrastructure including cables, routers, and servers | Content delivery networks (CDNs), servers, and data centers |
| Role in Internet Ecosystem | Enables connectivity between end-users and the internet | Provides digital content and online services accessed via the internet |
| Regulatory Focus | Telecommunication laws, net neutrality, data privacy | Content regulation, copyright law, data protection |
Understanding ISP and ICP: Key Definitions
ISP (Internet Service Provider) refers to a company that offers internet connectivity and related services to individuals and businesses, while ICP (Internet Content Provider) denotes entities that create, publish, or distribute digital content over the internet. Understanding ISP and ICP is crucial for optimizing network performance and content delivery strategies; ISPs manage infrastructure and bandwidth, whereas ICPs focus on generating and maintaining engaging web content. Your choice between ISP and ICP partnerships can significantly impact service quality and audience reach in the digital landscape.
Core Differences Between ISP and ICP
ISP (Internet Service Provider) delivers internet access services to end-users, enabling connection to the global web, while ICP (Internet Content Provider) creates and distributes digital content such as websites, videos, and applications over the internet. The core difference lies in the ISP's role as a conduit for internet connectivity versus the ICP's role in producing valuable online content for consumption. Your internet usage depends on ISPs for access and on ICPs for engaging content and services.
The Role of ISP in Internet Connectivity
ISP (Internet Service Provider) plays a crucial role in internet connectivity by offering access to the internet through various technologies such as DSL, fiber optics, and cable. ISPs manage the infrastructure and network services that enable users and businesses to connect, send, and receive data online. Their services include providing IP addresses, bandwidth allocation, and maintaining network security, which are essential for a stable and reliable internet experience.
How ICP Shapes Internet Content and Services
ICP (Internet Content Provider) fundamentally shapes internet content and services by controlling the creation, distribution, and management of digital materials such as websites, streaming platforms, and online applications. Unlike ISPs (Internet Service Providers), which facilitate user access to the internet infrastructure, ICPs dictate the quality, relevance, and variety of online content that users consume. Through targeted content strategies and data-driven service enhancements, ICPs drive user engagement and define digital experiences across multiple online channels.
Infrastructure and Technology: ISP vs ICP
ISPs (Internet Service Providers) deliver internet connectivity through extensive physical infrastructure like fiber optics, DSL, or cable networks, ensuring high-speed and reliable access. ICPs (Internet Content Providers) rely on data centers, cloud platforms, and content delivery networks (CDNs) to efficiently distribute digital content and services over the internet. Your online experience depends on ISPs maintaining robust network infrastructure while ICPs optimize technology to deliver seamless content access.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) face strict legal obligations regarding data privacy, content regulation, and network neutrality under telecommunications law. Internet Content Providers (ICPs) must comply with intellectual property rights, content liability, and censorship laws specific to their country's regulatory framework. Your compliance with these distinct legal requirements is crucial to avoid penalties and operate smoothly within the digital ecosystem.
Market Landscape: ISPs Compared to ICPs
The market landscape reveals Internet Service Providers (ISPs) primarily offer connectivity services, enabling access to the internet through wired, wireless, or fiber-optic networks, while Internet Content Providers (ICPs) focus on creating, curating, and distributing digital content such as videos, social media, and cloud services. ISPs generate revenue through subscription fees and infrastructure investment, whereas ICPs rely on advertising, subscriptions, and data monetization. The competitive dynamics highlight ISPs as essential infrastructure enablers, whereas ICPs drive user engagement and demand for bandwidth-intensive applications.
Choosing Between ISP and ICP for Your Business
Choosing between an ISP (Internet Service Provider) and an ICP (Internet Content Provider) depends on your business needs. ISPs offer the essential infrastructure and connectivity required to access the internet, while ICPs deliver online content and services that engage your audience. Understanding these roles helps you optimize your digital strategy, ensuring Your business leverages the right partner for internet access or content distribution.
Future Trends in ISPs and ICPs
Future trends in Internet Service Providers (ISPs) include the expansion of 5G networks and the integration of AI-driven network management to enhance speed and reliability. Internet Content Providers (ICPs) are increasingly leveraging edge computing and cloud-native platforms to deliver personalized, low-latency content experiences. Both ISPs and ICPs are investing in cybersecurity advancements to protect data privacy and combat emerging cyber threats.
ISP vs ICP: Which Drives the Digital Ecosystem?
ISP (Internet Service Provider) and ICP (Internet Content Provider) both play crucial roles in driving the digital ecosystem, serving distinct functions that complement each other. ISPs enable internet connectivity by providing access and infrastructure, while ICPs create and distribute digital content that fuels user engagement and online activity. The synergy between ISPs delivering fast, reliable networks and ICPs generating diverse, valuable content ultimately powers the growth and evolution of the digital landscape.
ISP vs ICP Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com