WiFi offers high-speed internet connectivity suitable for streaming and online gaming, while LoRa excels in long-range, low-power communication ideal for IoT devices and remote sensing. Explore the differences in range, power consumption, and use cases to determine which technology best fits Your connectivity needs.
Table of Comparison
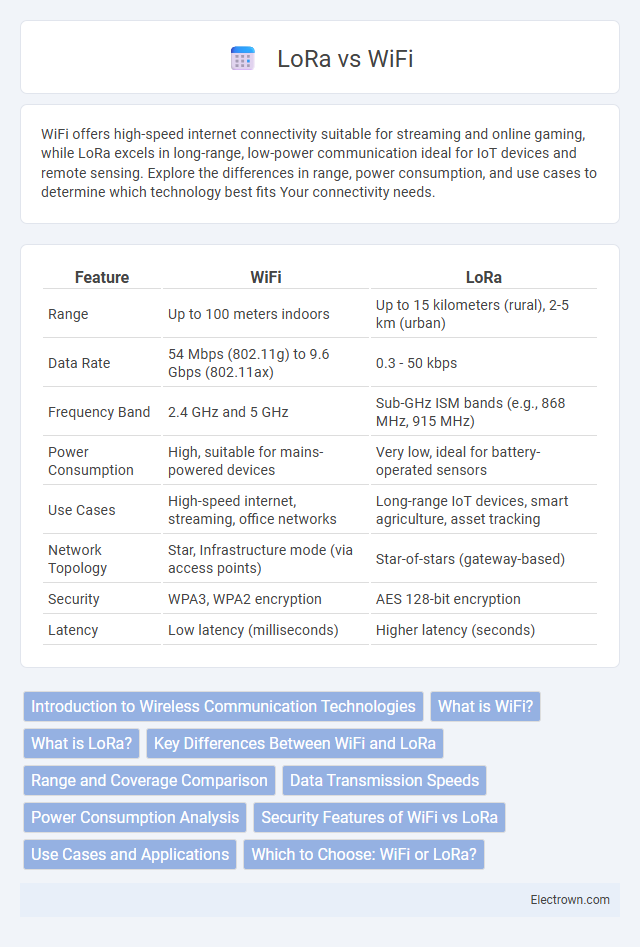
| Feature | WiFi | LoRa |
|---|---|---|
| Range | Up to 100 meters indoors | Up to 15 kilometers (rural), 2-5 km (urban) |
| Data Rate | 54 Mbps (802.11g) to 9.6 Gbps (802.11ax) | 0.3 - 50 kbps |
| Frequency Band | 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz | Sub-GHz ISM bands (e.g., 868 MHz, 915 MHz) |
| Power Consumption | High, suitable for mains-powered devices | Very low, ideal for battery-operated sensors |
| Use Cases | High-speed internet, streaming, office networks | Long-range IoT devices, smart agriculture, asset tracking |
| Network Topology | Star, Infrastructure mode (via access points) | Star-of-stars (gateway-based) |
| Security | WPA3, WPA2 encryption | AES 128-bit encryption |
| Latency | Low latency (milliseconds) | Higher latency (seconds) |
Introduction to Wireless Communication Technologies
WiFi operates on high-frequency bands, providing high data rates suitable for applications like video streaming and internet browsing. LoRa utilizes low-power, long-range communication ideal for IoT devices and sensor networks requiring extended battery life and wide-area coverage. Both technologies serve distinct purposes within wireless communication, with WiFi prioritizing speed and LoRa emphasizing range and power efficiency.
What is WiFi?
WiFi is a wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to provide high-speed internet and network connections over short to medium ranges, typically within homes, offices, and public hotspots. It operates primarily on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, enabling devices like smartphones, laptops, and smart home gadgets to connect seamlessly to the internet. Your devices benefit from WiFi's ability to support high data rates, low latency, and ease of setup, making it ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications such as streaming and online gaming.
What is LoRa?
LoRa (Long Range) is a wireless communication technology designed for low-power, wide-area networks (LPWAN), enabling long-distance data transmission with minimal energy consumption. Unlike WiFi, which offers high-speed connectivity over short ranges primarily for internet access, LoRa excels in connecting IoT devices across vast areas, often spanning several kilometers in urban environments and up to tens of kilometers in rural settings. Its key advantage lies in supporting battery-operated sensors and devices for smart cities, agriculture, and industrial applications where low data rates and extended range are critical.
Key Differences Between WiFi and LoRa
WiFi operates on higher frequencies (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) offering faster data rates up to several Gbps but with limited range typically around 100 meters, while LoRa uses sub-GHz bands (e.g., 868 MHz, 915 MHz) providing low data rates up to 50 kbps and extended range up to 15 kilometers in rural areas. WiFi is suited for high-bandwidth applications like video streaming and internet browsing, whereas LoRa targets low-power IoT devices needing long-range connectivity with minimal energy consumption. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize speed and local coverage or energy-efficient, wide-area communication.
Range and Coverage Comparison
WiFi typically offers a range of up to 100 meters indoors and 300 meters outdoors, making it suitable for high-speed internet access within homes or offices. LoRa provides significantly greater coverage, reaching up to 15 kilometers in rural areas and 5 kilometers in urban environments, ideal for long-range, low-power IoT applications. The extensive range of LoRa supports wide-area sensor networks and smart city deployments, while WiFi excels in high-bandwidth, short-range connectivity.
Data Transmission Speeds
WiFi technology supports high data transmission speeds ranging from 54 Mbps with WiFi 4 to over 9.6 Gbps with WiFi 6E, ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications like video streaming and online gaming. LoRa, on the other hand, offers significantly lower data rates between 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps but excels in long-range communication and low power consumption. This makes LoRa suitable for IoT devices requiring long battery life and low data throughput, whereas WiFi is better for applications demanding fast, high-volume data transfers.
Power Consumption Analysis
WiFi consumes significantly more power compared to LoRa, making LoRa ideal for battery-operated devices and long-term deployments. LoRa's low power consumption enables extended device uptime, often lasting years on a single battery, whereas WiFi typically requires frequent recharging or continuous power. Understanding your device's power needs helps optimize connectivity choices, ensuring efficient energy use and network performance.
Security Features of WiFi vs LoRa
WiFi employs WPA3 encryption, offering robust protection against unauthorized access and is regularly updated to address emerging vulnerabilities, ensuring secure data transmission. LoRa uses AES-128 encryption at the network, application, and device levels, providing lightweight but strong security tailored for low-power, long-range IoT communications. Your choice between WiFi and LoRa should consider the specific security requirements of your network, with WiFi suited for high-throughput, short-range security and LoRa optimized for secure, energy-efficient sensor data transfers over extensive distances.
Use Cases and Applications
WiFi excels in high-bandwidth applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and smart home devices within confined areas like homes, offices, or public hotspots. LoRa supports long-range, low-power IoT use cases such as agriculture monitoring, smart city infrastructure, and asset tracking, where data is transmitted infrequently over several kilometers. Your choice depends on whether speed and bandwidth or range and power efficiency are more critical for your specific application.
Which to Choose: WiFi or LoRa?
WiFi offers high data rates and seamless internet connectivity suitable for bandwidth-intensive applications and short-range communication within homes or offices. LoRa provides long-range, low-power communication ideal for IoT deployments requiring extended battery life and wide-area coverage, such as smart agriculture and asset tracking. Choosing between WiFi and LoRa depends on factors like required data throughput, range, power consumption, and specific use case scenarios.
WiFi vs LoRa Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com