Modbus RTU operates over serial communication for reliable device-level data exchange, while Modbus TCP leverages Ethernet networks for faster, scalable industrial automation. Discover which protocol best fits Your system by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
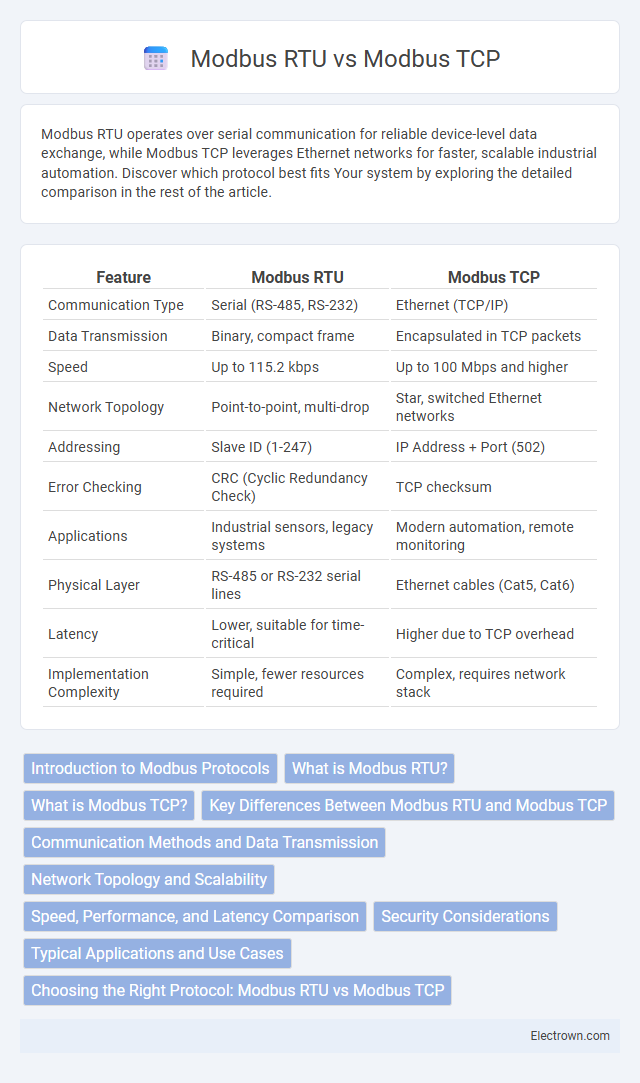
| Feature | Modbus RTU | Modbus TCP |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Serial (RS-485, RS-232) | Ethernet (TCP/IP) |
| Data Transmission | Binary, compact frame | Encapsulated in TCP packets |
| Speed | Up to 115.2 kbps | Up to 100 Mbps and higher |
| Network Topology | Point-to-point, multi-drop | Star, switched Ethernet networks |
| Addressing | Slave ID (1-247) | IP Address + Port (502) |
| Error Checking | CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) | TCP checksum |
| Applications | Industrial sensors, legacy systems | Modern automation, remote monitoring |
| Physical Layer | RS-485 or RS-232 serial lines | Ethernet cables (Cat5, Cat6) |
| Latency | Lower, suitable for time-critical | Higher due to TCP overhead |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple, fewer resources required | Complex, requires network stack |
Introduction to Modbus Protocols
Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP are two widely used communication protocols in industrial automation, designed for reliable data exchange between devices such as PLCs, sensors, and controllers. Modbus RTU operates over serial communication lines like RS-485, offering efficient binary data transmission with error-checking mechanisms, making it ideal for long-distance and noise-prone environments. Modbus TCP leverages Ethernet networks, enabling faster, scalable, and more flexible communication while maintaining compatibility with Modbus function codes, providing your systems seamless integration across modern industrial networks.
What is Modbus RTU?
Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) is a serial communication protocol widely used in industrial automation for connecting devices like sensors, PLCs, and meters over RS-485 or RS-232 interfaces. It transmits data in a compact binary format, optimizing bandwidth and ensuring rapid communication between master and slave devices within a local network. Modbus RTU is preferred for its simplicity, low latency, and reliability in real-time control systems.
What is Modbus TCP?
Modbus TCP is an Ethernet-based communication protocol designed for efficient data exchange between industrial devices using TCP/IP networks. It encapsulates Modbus RTU frames within TCP packets, enabling faster communication speeds and seamless integration with modern network infrastructure. This protocol supports multiple simultaneous connections, enhancing scalability and remote monitoring capabilities in complex automation systems.
Key Differences Between Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP
Modbus RTU transmits data over serial communication lines using binary format, while Modbus TCP runs over Ethernet networks using TCP/IP protocol, enabling faster data transfer and easier integration with modern systems. Modbus RTU is limited by serial cable length and device addressing, whereas Modbus TCP supports larger networks with flexible device connectivity and enhanced scalability. Understanding these key differences can help you choose the appropriate protocol for your industrial automation needs, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility.
Communication Methods and Data Transmission
Modbus RTU uses serial communication over RS-485 or RS-232, transmitting data in a compact binary format optimized for reliable, low-bandwidth environments. Modbus TCP operates over standard Ethernet networks, leveraging TCP/IP protocols to enable faster, more flexible data exchange with larger payloads and improved scalability. Your choice depends on network infrastructure and required data transmission speed, where Modbus RTU suits simple, point-to-point setups, and Modbus TCP supports complex, multi-device systems with higher throughput.
Network Topology and Scalability
Modbus RTU operates on a serial bus topology, typically supporting up to 32 devices per segment with limited cable lengths, which restricts large-scale network expansion. Modbus TCP utilizes an Ethernet star topology, allowing for extensive scalability with hundreds of devices interconnected through switches and routers over standard network infrastructures. Your choice between Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP impacts network design flexibility and future scalability based on the physical layout and device count requirements.
Speed, Performance, and Latency Comparison
Modbus TCP offers significantly higher speed and lower latency compared to Modbus RTU due to its Ethernet-based communication, supporting data rates up to 100 Mbps, whereas Modbus RTU relies on serial communication with speeds typically limited to 115.2 kbps. Performance in Modbus TCP is enhanced by its ability to handle multiple simultaneous connections and reduced overhead, improving real-time data exchange in complex automation systems. Modbus RTU experiences higher latency caused by serial data transmission and slower error detection, making it less suitable for applications requiring rapid and large-scale data transfer.
Security Considerations
Modbus RTU relies on serial communication, making it inherently less vulnerable to network-based cyberattacks but more susceptible to physical tampering and eavesdropping without proper physical security measures. Modbus TCP operates over Ethernet, which exposes Your systems to various cyber threats like spoofing, man-in-the-middle attacks, and unauthorized access, necessitating robust network security protocols such as TLS, VPNs, and firewalls. Implementing encryption and authentication mechanisms is crucial for both protocols to ensure data integrity and protect against unauthorized control commands in industrial environments.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Modbus RTU is commonly used in industrial environments where reliable serial communication over RS-485 or RS-232 is essential, such as in factory automation, HVAC systems, and PLC-to-field device connections. Modbus TCP, leveraging Ethernet networks, suits applications requiring faster data transfer and easier integration with IT infrastructure, including SCADA systems, building management, and remote monitoring. Your choice depends on network topology, communication speed, and scalability requirements.
Choosing the Right Protocol: Modbus RTU vs Modbus TCP
Choosing the right protocol between Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP depends on application-specific requirements such as communication speed, network complexity, and infrastructure cost. Modbus RTU excels in simple, cost-effective serial communication over RS-485, offering robust performance in industrial environments with limited networking capabilities. Modbus TCP leverages Ethernet networks to provide faster data transmission, scalability, and easier integration with IT infrastructure, making it ideal for complex systems requiring high-speed communication and remote access.
Modbus RTU vs Modbus TCP Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com