NOR flash offers fast random access speeds and executes code directly from the memory, making it ideal for embedded systems and firmware storage. In contrast, NAND flash provides higher storage capacity and faster write/erase cycles, suited for mass data storage like SSDs and USB drives; explore the rest of this article to understand which flash memory type best suits your needs.
Table of Comparison
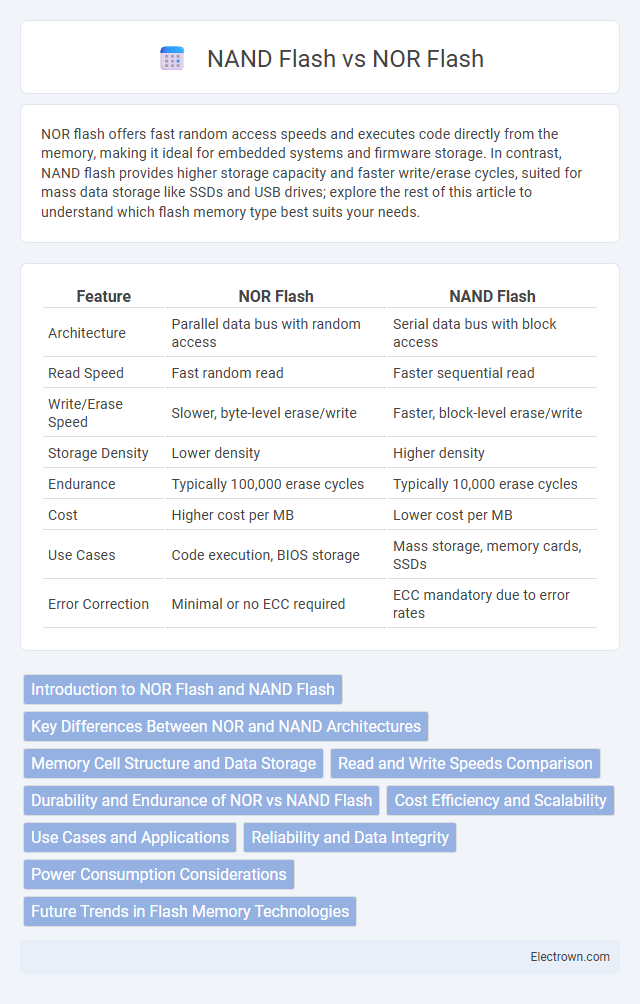
| Feature | NOR Flash | NAND Flash |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Parallel data bus with random access | Serial data bus with block access |
| Read Speed | Fast random read | Faster sequential read |
| Write/Erase Speed | Slower, byte-level erase/write | Faster, block-level erase/write |
| Storage Density | Lower density | Higher density |
| Endurance | Typically 100,000 erase cycles | Typically 10,000 erase cycles |
| Cost | Higher cost per MB | Lower cost per MB |
| Use Cases | Code execution, BIOS storage | Mass storage, memory cards, SSDs |
| Error Correction | Minimal or no ECC required | ECC mandatory due to error rates |
Introduction to NOR Flash and NAND Flash
NOR flash memory offers fast read speeds and byte-level random access, making it ideal for code storage and execution in embedded systems. NAND flash provides higher storage density and faster write and erase cycles, suited for data storage in smartphones, USB drives, and SSDs. Both types use different cell architectures, with NOR employing a parallel connection for reliability and NAND using a serial connection for efficiency.
Key Differences Between NOR and NAND Architectures
NOR flash features a parallel architecture with individual memory cells connected directly to bit lines, enabling fast random access and efficient execute-in-place capabilities, making it ideal for code storage in embedded systems. NAND flash uses a series-connected architecture that optimizes density and write/erase speeds, making it suitable for high-capacity data storage like solid-state drives and memory cards. Your choice between NOR and NAND flash depends on whether rapid code execution or large-scale data storage is the primary requirement.
Memory Cell Structure and Data Storage
NOR flash memory features a parallel architecture with each cell connected directly to the bit line, enabling fast random access and code execution in place (XIP). NAND flash employs a series-connected cell structure, optimizing for high-density data storage and faster write/erase cycles but with slower random access speeds. The structural differences impact performance: NOR excels in reliability and XIP functionality, while NAND is preferred for bulk data storage due to its cost-effectiveness and higher capacity.
Read and Write Speeds Comparison
NOR flash offers faster read speeds with random access capability ideal for code execution, while NAND flash provides higher write speeds and greater storage density suited for large data storage. NOR flash typically achieves read latencies as low as 25-50 nanoseconds, whereas NAND flash read speeds vary from 10 to 100 microseconds but excels in sequential write performance reaching up to hundreds of MB/s. NAND flash's efficient write cycles and faster erase times make it preferred for high-capacity applications, contrasting with NOR's slower, byte-level write and erase operations.
Durability and Endurance of NOR vs NAND Flash
NOR flash memory generally offers higher endurance with typical write/erase cycles ranging from 10,000 to 100,000, making it suitable for code storage and execution in embedded systems. NAND flash, designed primarily for high-capacity data storage, provides endurance between 1,000 and 10,000 cycles per cell but compensates with wear-leveling algorithms and error correction to extend lifespan. The durability of NOR flash exceeds NAND in terms of write/erase cycles, whereas NAND flash achieves longevity through advanced management techniques and higher storage density.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
NAND flash offers superior cost efficiency and scalability compared to NOR flash due to its higher data density and simpler cell architecture, resulting in lower production costs per gigabyte. NOR flash excels in random access speed but is significantly more expensive and less scalable, making it less ideal for large-capacity storage solutions. Manufacturers favor NAND flash for applications requiring massive storage and economical scaling, such as SSDs and mobile devices.
Use Cases and Applications
NOR flash excels in code execution and storage solutions requiring fast read speeds and random access, making it ideal for embedded systems, firmware, and automotive applications. NAND flash offers higher storage capacity and faster write/erase cycles, suited for consumer electronics, SSDs, USB drives, and large data storage. The choice depends on the specific requirement for speed, density, and durability in applications like mobile devices or industrial controllers.
Reliability and Data Integrity
NOR flash offers higher reliability and better data integrity due to its robust error correction capabilities and resistance to bit errors, making it ideal for critical code storage and frequent read operations. NAND flash, while offering higher density and faster write speeds, is more susceptible to wear and requires advanced error management techniques like ECC to maintain data integrity over time. Your choice between NOR and NAND flash should consider the reliability demands and integrity requirements of your specific application.
Power Consumption Considerations
NOR flash typically consumes more power during write and erase operations compared to NAND flash, making NAND flash a preferred choice for energy-efficient storage solutions. NAND flash's architecture allows for faster data programming with lower current requirements, which extends battery life in portable devices. When optimizing your system for power consumption, choosing NAND flash can significantly reduce overall energy usage.
Future Trends in Flash Memory Technologies
NOR flash offers faster read speeds and better execute-in-place capabilities, making it ideal for code storage, while NAND flash excels in higher density and lower cost, preferred for mass data storage. Future trends in flash memory focus on increasing storage density through 3D stacking, enhancing endurance, and integrating artificial intelligence for improved error correction and performance. You can expect advancements like QLC NAND and emerging technologies such as SLC and PLC memory cells to drive faster, more reliable, and cost-effective solutions in both NOR and NAND flash markets.
NOR flash vs NAND flash Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com