IO expanders increase the number of input/output pins available on a microcontroller through communication protocols like I2C or SPI, helping you manage multiple peripherals efficiently. Shift registers, on the other hand, extend outputs by converting serial data into parallel outputs, ideal for simple LED displays or button arrays; explore the article to understand which component best fits your project needs.
Table of Comparison
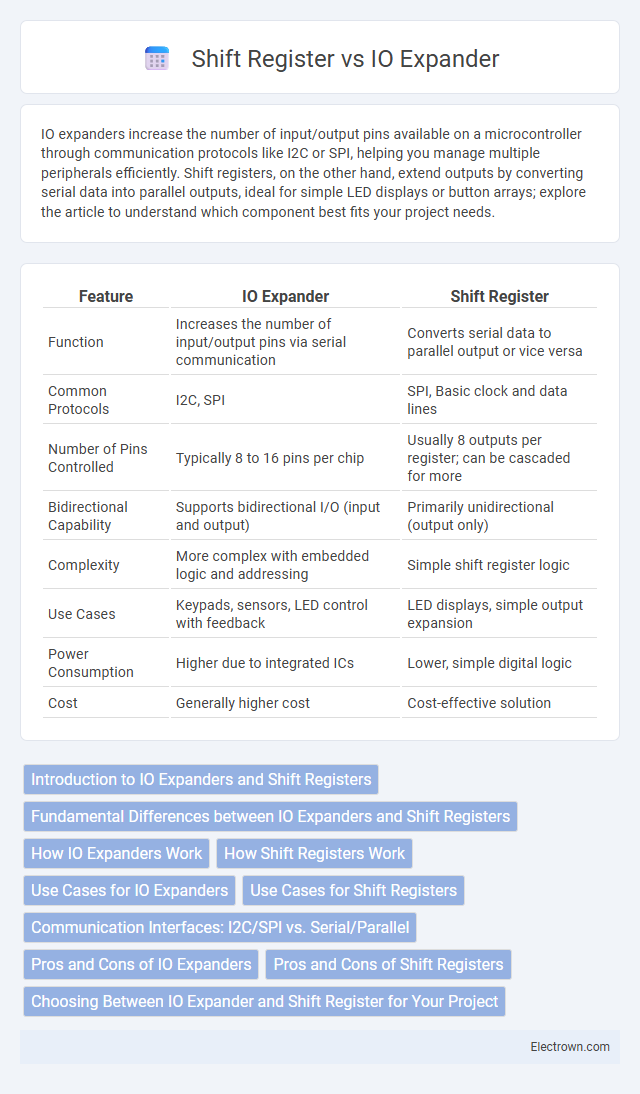
| Feature | IO Expander | Shift Register |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Increases the number of input/output pins via serial communication | Converts serial data to parallel output or vice versa |
| Common Protocols | I2C, SPI | SPI, Basic clock and data lines |
| Number of Pins Controlled | Typically 8 to 16 pins per chip | Usually 8 outputs per register; can be cascaded for more |
| Bidirectional Capability | Supports bidirectional I/O (input and output) | Primarily unidirectional (output only) |
| Complexity | More complex with embedded logic and addressing | Simple shift register logic |
| Use Cases | Keypads, sensors, LED control with feedback | LED displays, simple output expansion |
| Power Consumption | Higher due to integrated ICs | Lower, simple digital logic |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Cost-effective solution |
Introduction to IO Expanders and Shift Registers
IO expanders increase the number of available input/output pins on a microcontroller using protocols like I2C or SPI, allowing control of multiple peripherals with minimal GPIO usage. Shift registers, such as the 74HC595, enable serial-to-parallel conversion to extend output lines by shifting data through cascaded stages. Both components optimize microcontroller pin efficiency but differ in communication complexity and application flexibility.
Fundamental Differences between IO Expanders and Shift Registers
IO expanders provide direct, addressable input/output ports managed via communication protocols like I2C or SPI, allowing multiple devices to be controlled independently on the same bus. Shift registers function by serially shifting bits in and out, enabling expansion of input or output lines through cascading but require sequential data transfer and additional control signals. The fundamental difference lies in IO expanders offering random access to multiple IO pins with individual configuration, whereas shift registers rely on serial data flow for port expansion without individual pin addressing.
How IO Expanders Work
IO expanders work by increasing the number of input/output pins available to a microcontroller through serial communication protocols like I2C or SPI, enabling control of multiple devices with fewer GPIO pins. These chips internally manage multiplexing and buffering, allowing your system to read or set the state of many pins via a single communication interface. As a result, IO expanders efficiently extend microcontroller capabilities for complex projects requiring numerous digital inputs or outputs.
How Shift Registers Work
Shift registers work by receiving serial input data and shifting it through a series of flip-flops or storage elements with each clock pulse, effectively converting serial data into parallel outputs. This mechanism allows for expanding the number of output pins on microcontrollers or digital circuits without requiring additional I/O pins. Compared to IO expanders, shift registers offer a simpler and faster way to increase output capabilities but generally lack input reading functionality and complex communication protocols.
Use Cases for IO Expanders
IO expanders are ideal for increasing the number of input/output pins on microcontrollers in projects requiring multiple sensors, switches, or LEDs without redesigning the mainboard. Your embedded system benefits from IO expanders when you need precise control over numerous buttons or analog signals, enabling efficient data acquisition and user interface implementation. These devices simplify wiring complexity and allow for scalable designs in automation, robotics, and home automation applications.
Use Cases for Shift Registers
Shift registers excel in applications requiring serial-to-parallel or parallel-to-serial data conversion, such as LED matrix control, data storage, and communication interfaces. They efficiently expand the number of output pins from a microcontroller by shifting data bits through a register chain, ideal for driving large arrays of LEDs or managing limited I/O lines. Your projects involving synchronous data transfer or serialization benefit from shift registers' ability to handle multiple bits with minimal pin usage.
Communication Interfaces: I2C/SPI vs. Serial/Parallel
IO Expanders typically use I2C or SPI communication interfaces, enabling efficient two-wire or four-wire serial communication for expanding microcontroller GPIOs with minimal pin usage. Shift Registers rely on simple serial or parallel interfaces, shifting data bits serially to expand outputs but often require more pins and additional timing control. Your choice depends on the required interface complexity, pin availability, and the speed of expansion needed in the application.
Pros and Cons of IO Expanders
IO Expanders offer the advantage of increasing the number of input/output pins via dedicated integrated circuits like the MCP23017, enabling easier and more flexible microcontroller interfacing without complex wiring. Their pros include built-in features such as interrupt handling, configurable ports, and I2C or SPI communication, allowing efficient and reliable signal management. However, IO Expanders generally have higher cost and power consumption compared to shift registers, and may introduce latency due to communication protocols, which can be critical in time-sensitive applications.
Pros and Cons of Shift Registers
Shift registers offer the advantage of simple serial communication, requiring fewer microcontroller pins for expanding outputs, which makes them cost-effective for controlling multiple LEDs or switches. However, their limitations include slower data update rates compared to IO expanders and the lack of built-in input capabilities, reducing flexibility for complex input/output tasks. Your project benefits from shift registers when minimizing pin usage is crucial, but consider IO expanders if bidirectional I/O and faster response times are required.
Choosing Between IO Expander and Shift Register for Your Project
When choosing between an IO Expander and a Shift Register for your project, consider the number of input/output pins required and communication protocols supported; IO Expanders typically offer more flexibility with I2C or SPI interfaces and allow bidirectional control, while Shift Registers provide a cost-effective solution for expanding outputs using fewer microcontroller pins but are primarily unidirectional. IO Expanders like the MCP23017 support multiple inputs and outputs with interrupt capabilities, making them suitable for complex sensor arrays, whereas Shift Registers such as the 74HC595 excel in driving numerous LEDs or relays with serial data input. Your decision should align with project requirements for speed, pin count, and complexity of signal management to optimize performance and resource utilization.
IO Expander vs Shift Register Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com