Industrial Ethernet is designed to withstand harsh environments with robust hardware and real-time communication features, ensuring reliable performance in factories and critical infrastructure. Your choice between industrial and commercial Ethernet depends on the specific needs of your network; discover the key differences and benefits by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
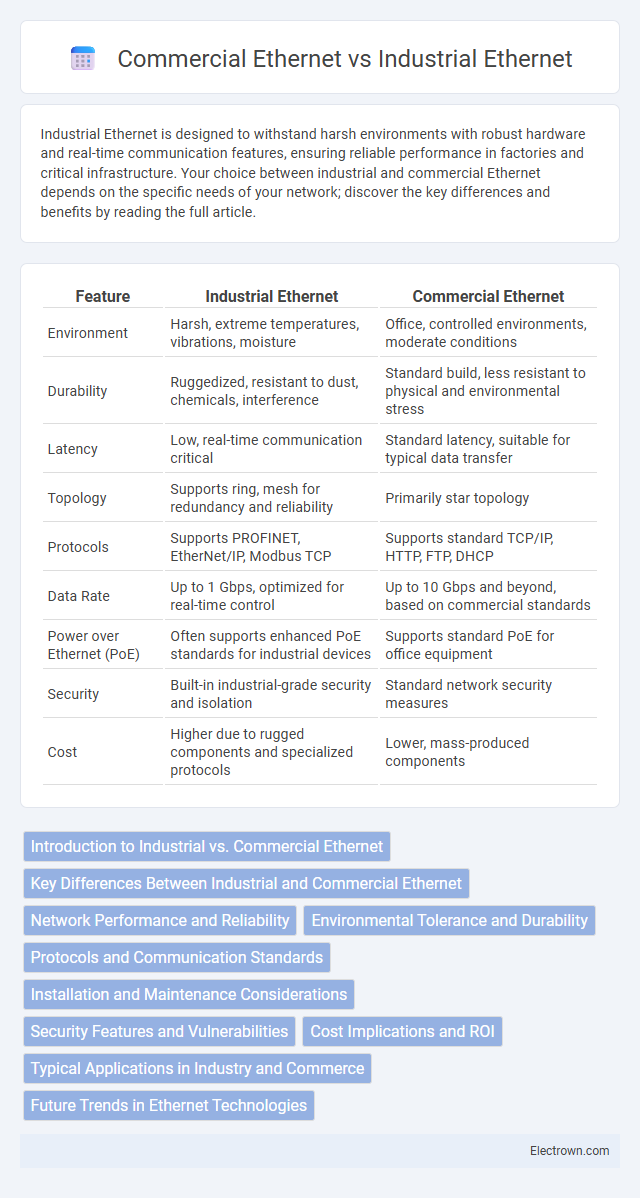
| Feature | Industrial Ethernet | Commercial Ethernet |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Harsh, extreme temperatures, vibrations, moisture | Office, controlled environments, moderate conditions |
| Durability | Ruggedized, resistant to dust, chemicals, interference | Standard build, less resistant to physical and environmental stress |
| Latency | Low, real-time communication critical | Standard latency, suitable for typical data transfer |
| Topology | Supports ring, mesh for redundancy and reliability | Primarily star topology |
| Protocols | Supports PROFINET, EtherNet/IP, Modbus TCP | Supports standard TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP, DHCP |
| Data Rate | Up to 1 Gbps, optimized for real-time control | Up to 10 Gbps and beyond, based on commercial standards |
| Power over Ethernet (PoE) | Often supports enhanced PoE standards for industrial devices | Supports standard PoE for office equipment |
| Security | Built-in industrial-grade security and isolation | Standard network security measures |
| Cost | Higher due to rugged components and specialized protocols | Lower, mass-produced components |
Introduction to Industrial vs. Commercial Ethernet
Industrial Ethernet is designed to withstand harsh environments with features like enhanced durability, real-time data processing, and robust security protocols essential for manufacturing and automation systems. Commercial Ethernet typically supports office or consumer settings, emphasizing cost-efficiency, ease of installation, and scalability for general data communication needs. Understanding these differences ensures your network infrastructure matches performance and reliability requirements.
Key Differences Between Industrial and Commercial Ethernet
Industrial Ethernet is designed to withstand harsh environments, featuring rugged hardware and extended temperature ranges, unlike Commercial Ethernet which is optimized for office settings. It supports real-time communication protocols such as PROFINET and EtherNet/IP, ensuring high reliability and low latency, critical for automation and control systems. Commercial Ethernet prioritizes higher data throughput and cost-efficiency but lacks the robustness and deterministic performance required in industrial applications.
Network Performance and Reliability
Industrial Ethernet delivers superior network performance and reliability compared to Commercial Ethernet by incorporating ruggedized hardware designed to withstand harsh environments, extreme temperatures, and electromagnetic interference. It features deterministic data transmission with real-time protocols like PROFINET and EtherCAT, ensuring minimal latency and consistent packet delivery critical for automation and control systems. Your industrial applications benefit from enhanced uptime and reduced network failures, making Industrial Ethernet essential for mission-critical operations.
Environmental Tolerance and Durability
Industrial Ethernet is engineered to withstand extreme environmental conditions including high temperatures, humidity, vibration, and electrical noise, making it ideal for harsh factory settings and outdoor installations. Commercial Ethernet, designed for typical office environments, lacks the robust protective features, such as reinforced connectors and ruggedized cabling, found in industrial-grade equipment. Your choice between the two should consider the durability requirements and environmental tolerance necessary for reliable network performance in demanding industrial applications.
Protocols and Communication Standards
Industrial Ethernet employs robust protocols such as Modbus TCP, PROFINET, and EtherNet/IP designed for real-time, deterministic communication in harsh environments. Commercial Ethernet primarily utilizes standard TCP/IP protocols optimized for general office and consumer applications, prioritizing speed and ease of use over stringent reliability. Understanding these differences helps you select the appropriate communication standard to meet specific operational demands.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Industrial Ethernet installations require ruggedized connectors and cables designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions such as extreme temperatures, vibrations, and moisture, ensuring long-term reliability. Maintenance in Industrial Ethernet systems often demands specialized tools and expertise to diagnose network faults promptly and minimize downtime in critical applications. In contrast, Commercial Ethernet installations use standard cabling and connectors suited for controlled office environments, with simpler maintenance procedures and widely available support resources.
Security Features and Vulnerabilities
Industrial Ethernet incorporates robust security features such as enhanced encryption protocols, resilient firewall integration, and real-time monitoring systems to mitigate risks in harsh operational environments. Commercial Ethernet typically relies on standard security measures like basic firewalls and antivirus software, making it more vulnerable to cyberattacks and unauthorized access. Industrial Ethernet's specialized design addresses vulnerabilities related to physical tampering, electromagnetic interference, and strict compliance regulations, providing superior protection compared to commercial networks.
Cost Implications and ROI
Industrial Ethernet typically involves higher upfront costs due to ruggedized hardware, specialized connectors, and enhanced environmental protection, but it delivers superior reliability, reduced downtime, and longer equipment lifespan, leading to a higher return on investment (ROI) in harsh or mission-critical environments. Commercial Ethernet solutions offer lower initial expenditure with standard components suited for office settings but may incur increased maintenance and replacement costs over time when exposed to industrial conditions. Evaluating total cost of ownership (TCO) reveals that Industrial Ethernet's durability and minimized operational disruptions often result in more favorable ROI despite higher initial investments.
Typical Applications in Industry and Commerce
Industrial Ethernet is predominantly used in manufacturing, automation, and process control environments where robust, real-time communication with enhanced durability against harsh conditions is crucial. Commercial Ethernet supports office networking, data centers, and general business applications requiring high-speed data transfer, typically in controlled environments without exposure to extreme temperatures or vibrations. The industrial variant prioritizes reliability and deterministic performance, while commercial Ethernet emphasizes scalability and cost-efficiency for typical IT infrastructure.
Future Trends in Ethernet Technologies
Industrial Ethernet is evolving with advancements like Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and enhanced cybersecurity protocols to support real-time, deterministic communication essential for automation and smart manufacturing. Commercial Ethernet continues to expand bandwidth capabilities with technologies such as 400G and 800G Ethernet to meet growing data center and enterprise demands. Understanding these future trends helps you select Ethernet solutions that ensure scalability, reliability, and security across both industrial and commercial environments.
Industrial Ethernet vs Commercial Ethernet Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com