Clock oscillators provide a stable frequency signal generated by an electronic circuit, while crystal oscillators utilize a quartz crystal to achieve higher precision and stability. Understanding the differences between these oscillators can help you choose the right component for your timing and frequency needs; read on to explore their characteristics in detail.
Table of Comparison
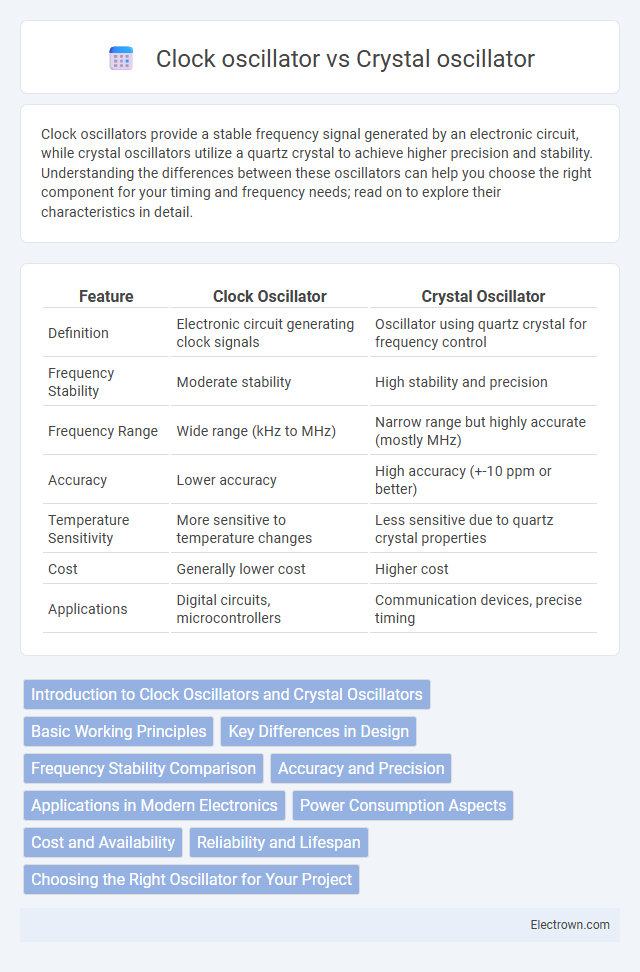
| Feature | Clock Oscillator | Crystal Oscillator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electronic circuit generating clock signals | Oscillator using quartz crystal for frequency control |
| Frequency Stability | Moderate stability | High stability and precision |
| Frequency Range | Wide range (kHz to MHz) | Narrow range but highly accurate (mostly MHz) |
| Accuracy | Lower accuracy | High accuracy (+-10 ppm or better) |
| Temperature Sensitivity | More sensitive to temperature changes | Less sensitive due to quartz crystal properties |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Digital circuits, microcontrollers | Communication devices, precise timing |
Introduction to Clock Oscillators and Crystal Oscillators
Clock oscillators generate stable timing signals using internal RC or LC circuits, commonly found in microcontrollers and digital systems for clock generation. Crystal oscillators utilize quartz crystal resonators to produce highly precise frequencies with minimal jitter, essential in applications requiring exact timing such as communication devices and GPS modules. Both components serve as fundamental timing sources but differ in accuracy, frequency stability, and cost.
Basic Working Principles
A clock oscillator generates a consistent timing signal through an electronic circuit using components like capacitors and inductors to produce a stable frequency. In contrast, a crystal oscillator relies on the piezoelectric properties of quartz crystals, which vibrate at precise frequencies when voltage is applied, ensuring highly accurate and stable oscillations. Your choice between these oscillators depends on the required frequency stability and accuracy for your electronic application.
Key Differences in Design
Clock oscillators use a built-in oscillating circuit with a quartz crystal and additional components to generate stable frequencies, while crystal oscillators rely solely on the piezoelectric properties of the quartz crystal to control frequency. Crystal oscillators require external circuitry for signal conditioning, whereas clock oscillators are complete modules ready for integration without extra components. Your choice depends on design complexity, size constraints, and the need for a fully integrated timing solution versus a customizable frequency source.
Frequency Stability Comparison
Crystal oscillators exhibit superior frequency stability due to their high Q-factor and temperature-compensated design, maintaining precise oscillation with minimal drift over time. Clock oscillators, often based on RC or LC circuits, have lower frequency stability, susceptible to variations caused by temperature changes and component aging. Your choice between these oscillators impacts the accuracy and reliability of time-dependent applications where stable frequency output is critical.
Accuracy and Precision
Clock oscillators typically offer lower accuracy and precision compared to crystal oscillators, as they are more susceptible to temperature variations and aging effects. Crystal oscillators achieve higher frequency stability due to the consistent mechanical resonance of the quartz crystal, ensuring minimal frequency drift over time. Your applications requiring precise timing and synchronization benefit significantly from the superior accuracy and precision of crystal oscillators.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Clock oscillators provide stable timing signals essential for microcontrollers, processors, and communication devices, ensuring synchronized operations in smartphones and computers. Crystal oscillators offer higher frequency stability and precision, making them ideal for GPS systems, radio transmitters, and precision medical equipment. Both oscillators play critical roles in maintaining accurate timing and signal integrity across diverse modern electronic applications.
Power Consumption Aspects
Clock oscillators generally consume more power than crystal oscillators because they include internal frequency control circuitry, which increases current draw. Crystal oscillators rely on the piezoelectric effect and have simpler designs, resulting in lower power consumption, making them ideal for battery-operated devices. Your choice between these two should consider power efficiency needs, especially for portable or low-power electronics.
Cost and Availability
Clock oscillators generally offer lower cost and higher availability due to their simpler design and mass production for widespread applications. Crystal oscillators, while more expensive, provide superior frequency stability and accuracy, which can justify the higher cost in precision-demanding environments. The choice between the two depends largely on budget constraints and the required performance specifications for the electronic system.
Reliability and Lifespan
Crystal oscillators provide superior reliability and longer lifespan compared to clock oscillators due to their stable frequency output and resistance to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and mechanical vibrations. Clock oscillators, often based on RC or LC circuits, tend to have shorter lifespans and less frequency stability, which can lead to timing errors over extended use. The inherent precision of quartz crystal resonators ensures consistent performance, making crystal oscillators ideal for applications demanding high reliability and durability.
Choosing the Right Oscillator for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate oscillator depends on the required frequency stability and application precision; crystal oscillators offer superior frequency accuracy and low phase noise, making them ideal for communication systems and precise timing circuits. Clock oscillators integrate a crystal and oscillator circuit into a single package, simplifying design and reducing component count, suited for general-purpose timing needs in microcontrollers and digital systems. Evaluate factors like frequency tolerance, power consumption, size, and cost to determine whether a standalone crystal oscillator or a packaged clock oscillator better fits your project requirements.
Clock oscillator vs Crystal oscillator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com