OLED displays offer vibrant colors and high contrast by using organic light-emitting diodes that illuminate individually, providing deep blacks and energy efficiency. Understanding the key differences between OLED and AMOLED displays can help you choose the best screen technology for your device, so explore the rest of the article for detailed insights.
Table of Comparison
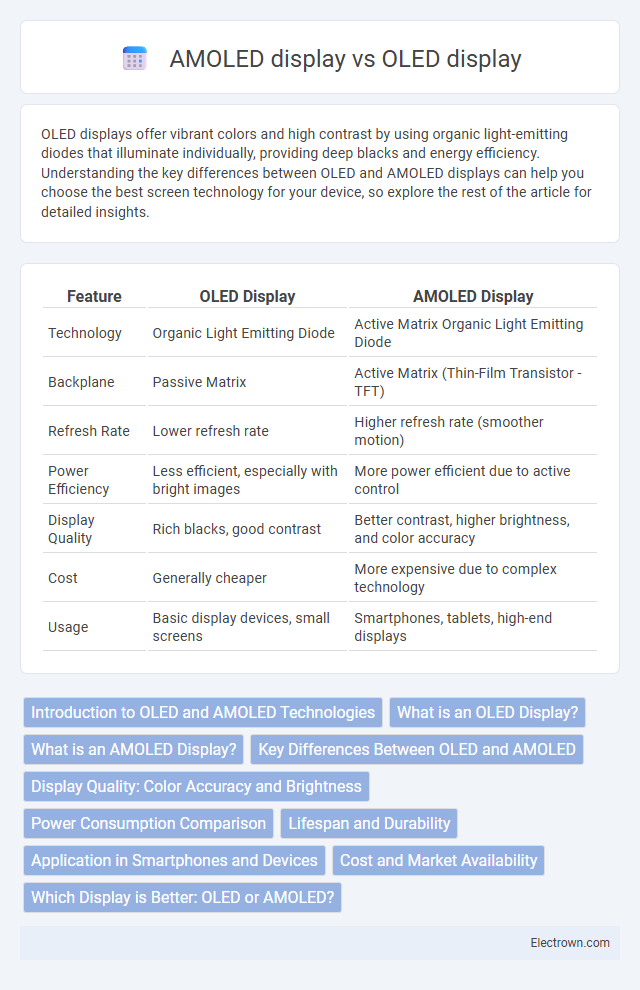
| Feature | OLED Display | AMOLED Display |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Organic Light Emitting Diode | Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode |
| Backplane | Passive Matrix | Active Matrix (Thin-Film Transistor - TFT) |
| Refresh Rate | Lower refresh rate | Higher refresh rate (smoother motion) |
| Power Efficiency | Less efficient, especially with bright images | More power efficient due to active control |
| Display Quality | Rich blacks, good contrast | Better contrast, higher brightness, and color accuracy |
| Cost | Generally cheaper | More expensive due to complex technology |
| Usage | Basic display devices, small screens | Smartphones, tablets, high-end displays |
Introduction to OLED and AMOLED Technologies
OLED displays use organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through, delivering vibrant colors and deep blacks with energy efficiency. AMOLED technology builds on OLED by integrating an active matrix of thin-film transistors to control individual pixels, enabling faster response times and improved image quality. Your choice between OLED and AMOLED impacts display performance, especially in brightness, color accuracy, and power consumption.
What is an OLED Display?
An OLED display is a screen technology that uses organic compounds emitting light when an electric current passes through, enabling self-illuminating pixels for superior contrast and true blacks compared to traditional LCDs. This technology allows for thinner, more flexible displays with faster response times and wider viewing angles. Understanding what an OLED display offers can help you choose the best screen for vibrant color reproduction and energy efficiency in your devices.
What is an AMOLED Display?
An AMOLED display, or Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode, integrates an active matrix of thin-film transistors (TFTs) to control individual pixels, offering faster response times and higher refresh rates compared to traditional OLED panels. This technology provides superior contrast ratios, vibrant colors, and efficient power consumption by lighting pixels individually without a backlight. AMOLED displays are widely used in high-end smartphones, wearables, and TVs for their ability to deliver deep blacks and enhanced visual performance.
Key Differences Between OLED and AMOLED
OLED displays use organic light-emitting diodes to produce vibrant colors and deep blacks by individually lighting each pixel, while AMOLED screens incorporate an active matrix of thin-film transistors that allow faster pixel switching and higher refresh rates. AMOLED technology offers better power efficiency and improved display responsiveness, making it ideal for smartphones and wearables requiring smooth animations and touch sensitivity. Your choice between OLED and AMOLED depends on whether you prioritize display quality or enhanced performance features for your device.
Display Quality: Color Accuracy and Brightness
OLED displays offer excellent color accuracy with deep blacks and high contrast ratios due to their self-emissive nature. AMOLED displays enhance this further by integrating an active matrix of thin-film transistors, resulting in faster pixel response times and higher brightness levels. This combination in AMOLED technology produces more vivid colors and improved visibility in bright environments compared to standard OLED panels.
Power Consumption Comparison
OLED displays generally consume less power than AMOLED displays when displaying darker images because OLED pixels emit light individually and turn off completely to produce true blacks. AMOLED displays, a type of OLED with an active matrix backplane, typically use more power due to their faster refresh rates and higher brightness levels, especially when displaying bright or white content. Power efficiency in AMOLED can be improved through adaptive brightness and pixel-shifting technologies, but OLED's simpler architecture often results in lower overall power consumption during typical use.
Lifespan and Durability
OLED displays generally have a shorter lifespan compared to AMOLED displays due to organic material degradation caused by continuous usage and exposure to ambient conditions. AMOLED technology incorporates an active matrix layer that enhances pixel control, resulting in improved durability and longer operational life, often exceeding 30,000-50,000 hours. Manufacturers use advanced encapsulation techniques in AMOLED panels to reduce moisture and oxygen damage, significantly extending device longevity compared to traditional OLED screens.
Application in Smartphones and Devices
OLED displays provide vibrant colors and deep blacks, making them ideal for smartphones and wearable devices seeking energy efficiency and thin design. AMOLED displays enhance this experience with faster refresh rates and better brightness, improving visibility in bright conditions and delivering smoother touch response for mobile gaming and video playback. Your smartphone benefits from AMOLED technology's superior contrast and reduced power consumption, resulting in longer battery life and richer visuals.
Cost and Market Availability
OLED displays generally have a lower manufacturing cost compared to AMOLED due to simpler construction and fewer integrated components. AMOLED displays, featuring active matrix technology for faster response times and better image quality, tend to be more expensive but dominate premium smartphone and wearable markets. Market availability of OLED is broader in budget and mid-range devices, while AMOLED is primarily found in high-end consumer electronics.
Which Display is Better: OLED or AMOLED?
AMOLED displays are an advanced type of OLED technology, integrating a thin-film transistor (TFT) layer to improve pixel response time and enable touch functionality, making them better suited for smartphones and wearable devices. OLED displays offer excellent color accuracy and deep blacks but lack the enhanced refresh rates and power efficiency found in AMOLED screens. For your device, choosing AMOLED ensures brighter visuals, faster refresh rates, and improved battery life compared to standard OLED panels.
OLED display vs AMOLED display Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com