PIN diodes offer fast response times and are widely used for general photodetection, while avalanche photodiodes (APDs) provide higher sensitivity and internal gain by operating with avalanche multiplication, making them ideal for low-light applications. Explore the rest of the article to understand which photodiode best suits your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
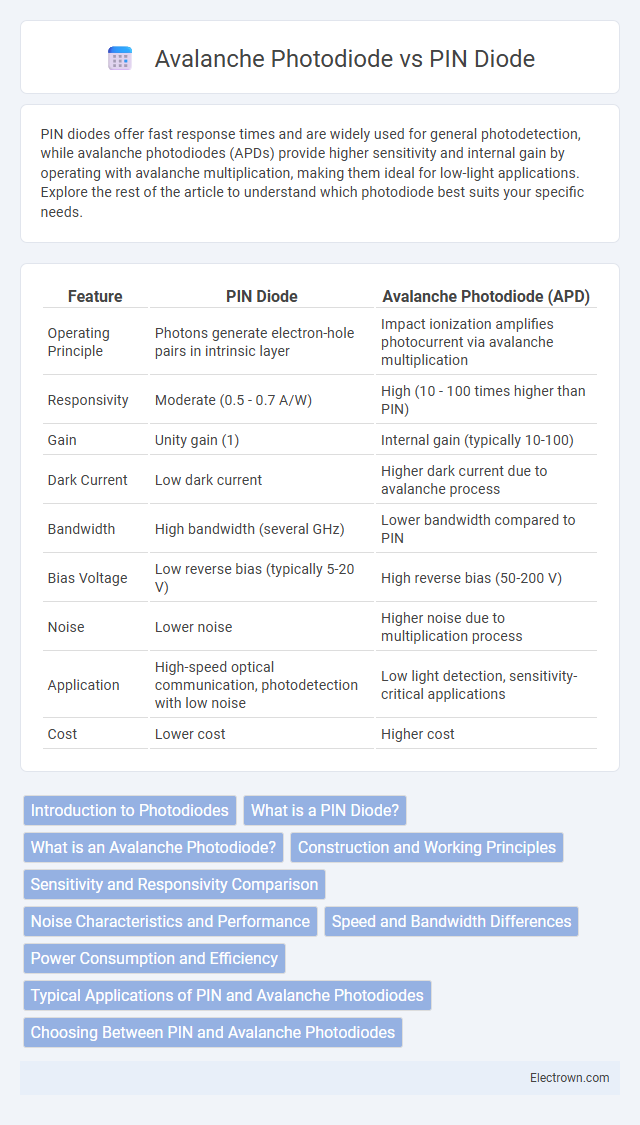
| Feature | PIN Diode | Avalanche Photodiode (APD) |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Photons generate electron-hole pairs in intrinsic layer | Impact ionization amplifies photocurrent via avalanche multiplication |
| Responsivity | Moderate (0.5 - 0.7 A/W) | High (10 - 100 times higher than PIN) |
| Gain | Unity gain (1) | Internal gain (typically 10-100) |
| Dark Current | Low dark current | Higher dark current due to avalanche process |
| Bandwidth | High bandwidth (several GHz) | Lower bandwidth compared to PIN |
| Bias Voltage | Low reverse bias (typically 5-20 V) | High reverse bias (50-200 V) |
| Noise | Lower noise | Higher noise due to multiplication process |
| Application | High-speed optical communication, photodetection with low noise | Low light detection, sensitivity-critical applications |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Photodiodes
Photodiodes are semiconductor devices that convert light into electrical current, essential in optical communication and sensing applications. A PIN diode features a wide intrinsic layer to improve response speed and linearity, making it suitable for high-frequency or moderate sensitivity uses. The Avalanche Photodiode (APD) incorporates internal gain through avalanche multiplication, amplifying weak optical signals with higher sensitivity, ideal for long-distance and low-light detection scenarios.
What is a PIN Diode?
A PIN diode consists of a p-type, intrinsic, and n-type semiconductor layer, designed for high-frequency and photodetection applications. It operates by generating electron-hole pairs in the intrinsic region when exposed to light, enabling efficient photodetection with low noise. Unlike avalanche photodiodes, PIN diodes do not rely on internal gain through impact ionization, resulting in lower sensitivity but faster response times and simpler biasing requirements.
What is an Avalanche Photodiode?
An Avalanche Photodiode (APD) is a highly sensitive semiconductor device designed to convert light into electrical signals with internal gain through avalanche multiplication, enhancing its ability to detect low-intensity optical signals. Unlike PIN diodes, which provide linear response without internal amplification, APDs operate under high reverse-bias voltage to initiate impact ionization, resulting in electron-hole pairs multiplied to amplify the photocurrent. APDs are widely used in fiber-optic communication, LIDAR, and photon-counting applications due to their superior sensitivity and fast response time compared to standard PIN photodiodes.
Construction and Working Principles
PIN diodes consist of an intrinsic layer sandwiched between p-type and n-type semiconductor regions, enabling efficient absorption and swift charge carrier generation for photodetection. Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) feature a similar layered structure but include a high electric field multiplication region that triggers impact ionization, amplifying the photocurrent internally. The PIN diode operates mainly through direct photo-carrier generation without gain, while APDs leverage avalanche multiplication to enhance sensitivity, especially in low-light applications.
Sensitivity and Responsivity Comparison
PIN diodes typically offer moderate sensitivity with responsivity values around 0.5 to 0.7 A/W, making them suitable for standard photodetection applications. Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) provide significantly higher sensitivity due to internal gain mechanisms, achieving responsivity levels up to 10 times greater than PIN diodes, with values often exceeding 5 A/W under optimal bias conditions. Your choice between these devices depends on the required detection sensitivity and signal amplification for applications like optical communication or low-light sensing.
Noise Characteristics and Performance
PIN diodes exhibit lower noise levels compared to avalanche photodiodes (APDs) due to the absence of internal gain mechanisms, resulting in more stable and predictable performance in low-light conditions. Avalanche photodiodes, while offering higher sensitivity and gain through avalanche multiplication, introduce excess noise that can degrade signal quality, especially in high-speed or low-signal environments. Understanding these noise characteristics is crucial for optimizing Your system's performance in applications like optical communication or sensing.
Speed and Bandwidth Differences
PIN diodes offer faster response times with bandwidths typically up to several GHz, making them ideal for high-speed optical communication. Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) provide higher sensitivity but operate with slower response times and narrower bandwidths due to the avalanche multiplication process. Your choice depends on whether speed or sensitivity is the priority in your photodetection application.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
PIN diodes exhibit lower power consumption due to their simple structure and absence of avalanche multiplication, making them suitable for low-energy applications. Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) provide higher efficiency and sensitivity by amplifying weak optical signals through avalanche multiplication, but this process requires higher bias voltages and results in increased power consumption. The trade-off between power consumption and efficiency positions PIN diodes as energy-efficient detectors, while APDs excel in high-sensitivity environments despite their elevated power requirements.
Typical Applications of PIN and Avalanche Photodiodes
PIN photodiodes are commonly used in high-speed optical communication systems, barcode scanners, and medical imaging due to their fast response time and linearity. Avalanche photodiodes excel in low-light detection applications such as LIDAR, fiber optic receivers, and spectroscopy because of their high sensitivity and internal gain mechanism. Your choice between PIN and Avalanche photodiodes depends on whether speed or sensitivity is more critical for your specific application.
Choosing Between PIN and Avalanche Photodiodes
Choosing between PIN and Avalanche photodiodes depends on your application's sensitivity and speed requirements. PIN photodiodes offer lower noise and higher linearity, making them suitable for moderate light detection and high-speed communications. Avalanche photodiodes provide internal gain through avalanche multiplication, enhancing sensitivity in low-light conditions but requiring higher operating voltages and more complex biasing.
PIN diode vs Avalanche photodiode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com