SLED (Superluminescent Light Emitting Diodes) emit broad-spectrum, low-coherence light ideal for applications requiring reduced speckle noise, while LED (Light Emitting Diodes) produce narrow-spectrum light commonly used for general illumination and displays. Discover how understanding the differences between SLED and LED can enhance your choice in lighting technology by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
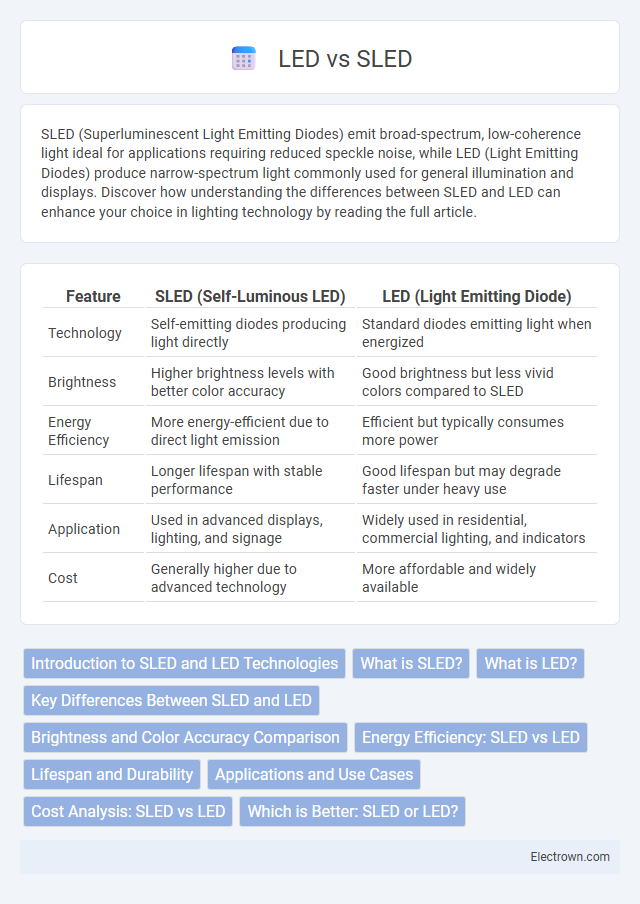
| Feature | SLED (Self-Luminous LED) | LED (Light Emitting Diode) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Self-emitting diodes producing light directly | Standard diodes emitting light when energized |
| Brightness | Higher brightness levels with better color accuracy | Good brightness but less vivid colors compared to SLED |
| Energy Efficiency | More energy-efficient due to direct light emission | Efficient but typically consumes more power |
| Lifespan | Longer lifespan with stable performance | Good lifespan but may degrade faster under heavy use |
| Application | Used in advanced displays, lighting, and signage | Widely used in residential, commercial lighting, and indicators |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced technology | More affordable and widely available |
Introduction to SLED and LED Technologies
SLED (Superluminescent Diode) and LED (Light Emitting Diode) technologies both emit light through semiconductor materials but differ significantly in coherence and spectral output. SLEDs produce a high-brightness, broadband light with low coherence, making them ideal for applications like optical coherence tomography and fiber optic sensing. Your choice between SLED and LED depends on the required spectral width, output power, and spatial coherence for your specific optical system.
What is SLED?
SLED, or Superluminescent Light Emitting Diode, is a semiconductor device that combines the broad emission spectrum of LEDs with the high brightness and coherence of laser diodes. It produces light with low coherence, making it ideal for applications requiring minimal interference, such as optical coherence tomography and fiber optic gyroscopes. Unlike standard LEDs, SLEDs offer higher output power and improved spectral stability, enhancing performance in precision sensing and imaging technologies.
What is LED?
LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it, commonly used in displays, indicators, and lighting applications. You can find LEDs in devices ranging from digital clocks to advanced TV screens due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and compact size. Unlike conventional bulbs, LEDs produce light through electroluminescence, resulting in lower power consumption and higher brightness.
Key Differences Between SLED and LED
SLED (Super Luminescent Diode) and LED (Light Emitting Diode) differ primarily in their light emission characteristics; SLEDs produce broadband, low-coherence light ideal for high-resolution applications like optical coherence tomography, while LEDs emit narrowband light suited for general illumination. SLEDs offer higher brightness and better spectral stability compared to LEDs, which generally have broader spectral widths and lower coherence. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate light source for specialized optical systems or everyday lighting needs.
Brightness and Color Accuracy Comparison
SLED technology offers superior brightness levels compared to traditional LED displays, reaching peak luminance that enhances visibility in high ambient light conditions. Color accuracy in SLED panels is significantly improved due to the precise control of self-emitting pixels, resulting in richer and more vibrant color reproduction. LEDs rely on backlighting, which can cause color bleeding and lower contrast, making SLED a preferred choice for applications demanding sharp and true-to-life visuals.
Energy Efficiency: SLED vs LED
SLED (Surface Light Emitting Diode) technology offers superior energy efficiency compared to traditional LED systems by utilizing advanced phosphor conversion techniques that reduce power consumption while maintaining high luminance levels. Your choice of SLED can result in up to 30% lower energy usage due to its enhanced light extraction efficiency and reduced heat generation. In contrast, standard LEDs, although energy-efficient, often consume more power to achieve similar brightness, making SLED a more sustainable option for long-term energy savings.
Lifespan and Durability
SLED (Surface Light Emitting Diode) technology typically offers enhanced durability through improved heat dissipation compared to conventional LED (Light Emitting Diode) lighting, extending overall lifespan. While standard LEDs generally have a lifespan ranging from 25,000 to 50,000 hours, SLEDs can exceed these figures due to reduced thermal stress and robust encapsulation materials. This increased durability results in lower maintenance costs and longer operational efficiency for applications in harsh or demanding environments.
Applications and Use Cases
SLED technology, with its superior brightness and wider color gamut, excels in large-scale outdoor displays, stadium screens, and commercial advertising where visibility and vividness are critical. LED panels dominate indoor applications such as office lighting, residential fixtures, and digital signage due to their energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and versatility in form factors. Specialized environments like high-performance video walls and immersive visual experiences benefit from integrating SLED displays to enhance image clarity and color accuracy.
Cost Analysis: SLED vs LED
SLED (Super Luminescent Diode) generally has a higher initial cost compared to standard LED (Light Emitting Diode) due to its advanced design and superior performance in applications requiring low coherence and high brightness. Your choice should consider long-term energy savings, as LEDs typically offer better efficiency and longer lifespan, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses. Cost analysis must weigh upfront investment against durability and operational efficiency to determine the most economical solution for specific lighting needs.
Which is Better: SLED or LED?
SLED (Super Luminescent LED) offers higher brightness, better color accuracy, and a more consistent light source compared to traditional LED, making it ideal for applications requiring precision illumination. LED is more cost-effective, energy-efficient, and widely used for general lighting needs. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize performance and color fidelity (SLED) or affordability and energy savings (LED).
SLED vs LED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com