Air core inductors offer low core losses and high-frequency performance, making them ideal for RF circuits, while ferrite core inductors provide higher inductance values and better magnetic coupling in compact sizes suitable for power electronics. Discover which inductor type best fits your application by exploring the detailed comparisons in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
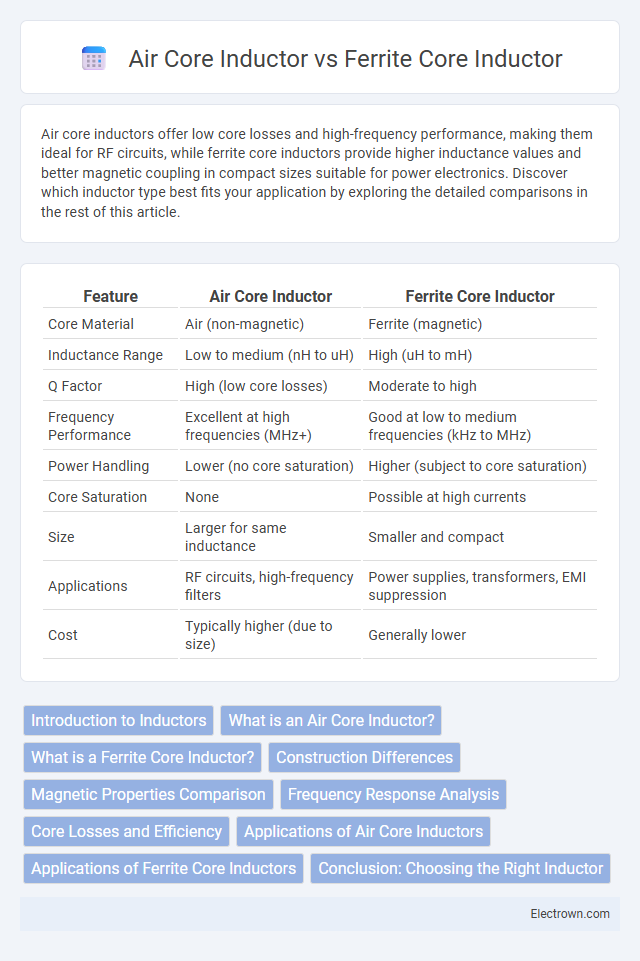
| Feature | Air Core Inductor | Ferrite Core Inductor |
|---|---|---|
| Core Material | Air (non-magnetic) | Ferrite (magnetic) |
| Inductance Range | Low to medium (nH to uH) | High (uH to mH) |
| Q Factor | High (low core losses) | Moderate to high |
| Frequency Performance | Excellent at high frequencies (MHz+) | Good at low to medium frequencies (kHz to MHz) |
| Power Handling | Lower (no core saturation) | Higher (subject to core saturation) |
| Core Saturation | None | Possible at high currents |
| Size | Larger for same inductance | Smaller and compact |
| Applications | RF circuits, high-frequency filters | Power supplies, transformers, EMI suppression |
| Cost | Typically higher (due to size) | Generally lower |
Introduction to Inductors
Air core inductors utilize a non-magnetic core, resulting in lower inductance but higher frequency response and minimal core losses ideal for RF applications. Ferrite core inductors incorporate a magnetic ferrite core, providing higher inductance and greater energy storage efficiency, commonly used in power supply and noise suppression circuits. The choice between air core and ferrite core inductors depends on frequency, inductance requirements, and application-specific magnetic properties.
What is an Air Core Inductor?
An air core inductor consists of a coil of wire wound without a magnetic core, relying solely on the air to provide inductance. Unlike a ferrite core inductor, which uses a ferrite material to concentrate magnetic flux and increase inductance, air core inductors offer higher linearity and lower core losses, making them ideal for high-frequency applications. Your choice of an air core inductor can improve signal integrity in RF circuits by minimizing distortion caused by core saturation.
What is a Ferrite Core Inductor?
A ferrite core inductor uses a core made of ferrite material, which is a magnetic ceramic compound consisting of iron oxide combined with other metals, enhancing inductance and minimizing core losses. Ferrite cores provide high magnetic permeability, enabling smaller inductor sizes with improved efficiency in high-frequency applications. You can rely on ferrite core inductors for better performance in circuits requiring compact, low-loss components compared to air core inductors, which lack a magnetic core and generally offer lower inductance values.
Construction Differences
Air core inductors feature a coil wound around a non-magnetic material like plastic or air, resulting in negligible core losses and high-frequency performance. Ferrite core inductors use a ferrite magnetic core, which increases inductance by concentrating the magnetic flux, but introduces core losses especially at higher frequencies. The key construction difference lies in the presence of a ferrite core that enhances inductance in the ferrite core inductor, while air core inductors prioritize low loss and linearity with no magnetic core material.
Magnetic Properties Comparison
Air core inductors exhibit negligible magnetic permeability, resulting in low core losses and minimal magnetic hysteresis, making them ideal for high-frequency applications where signal integrity is crucial. Ferrite core inductors possess high magnetic permeability and can store more magnetic energy, which enhances inductance but introduces core losses and potential saturation under high current conditions. Your choice between these depends on the desired trade-off between frequency response and inductance stability under varying load conditions.
Frequency Response Analysis
Air core inductors exhibit superior frequency response with minimal core losses, making them ideal for high-frequency applications above 10 MHz. Ferrite core inductors offer high inductance values with low DC resistance but suffer from core losses and saturation at elevated frequencies, typically effective up to a few MHz. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize broad frequency range performance or higher inductance with compact size.
Core Losses and Efficiency
Air core inductors exhibit minimal core losses due to the absence of magnetic material, resulting in higher efficiency at high frequencies and reduced heat generation. Ferrite core inductors, while offering increased inductance and size reduction, experience core losses primarily from hysteresis and eddy currents within the ferrite material, which can reduce overall efficiency. Selecting between air core and ferrite core inductors depends on the application's frequency range and efficiency requirements, with air cores preferred for low-loss high-frequency circuits and ferrite cores suitable for compact, lower-frequency designs.
Applications of Air Core Inductors
Air core inductors are widely used in high-frequency applications such as RF circuits, oscillators, and wireless communication systems due to their low core losses and minimal signal distortion. They are ideal in precision tuning circuits and broadband filters where maintaining signal integrity is critical. Their non-magnetic core eliminates core saturation, making them suitable for transient and high-power pulse applications.
Applications of Ferrite Core Inductors
Ferrite core inductors are widely used in high-frequency applications such as power supplies, RF circuits, and EMI suppression due to their high magnetic permeability and low core losses. Their ability to handle higher inductance values in compact sizes makes them ideal for switching regulators and signal filtering in communications equipment. You can rely on ferrite core inductors for efficient energy storage and noise reduction in sensitive electronic devices.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Inductor
Air core inductors offer low core losses and high-frequency performance, making them ideal for RF applications where signal purity is crucial. Ferrite core inductors provide higher inductance and better magnetic coupling, suited for power electronics requiring compact size and efficiency. Evaluate your circuit's frequency, size constraints, and power requirements to select the right inductor for your needs.
air core inductor vs ferrite core inductor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com