Direct drive inverters connect the motor directly to the load, offering higher efficiency, lower maintenance, and improved performance, while indirect drive inverters use belts or gears, which can introduce energy losses and require more upkeep. Explore the full article to understand which inverter type best suits your needs and how it can optimize Your system's operation.
Table of Comparison
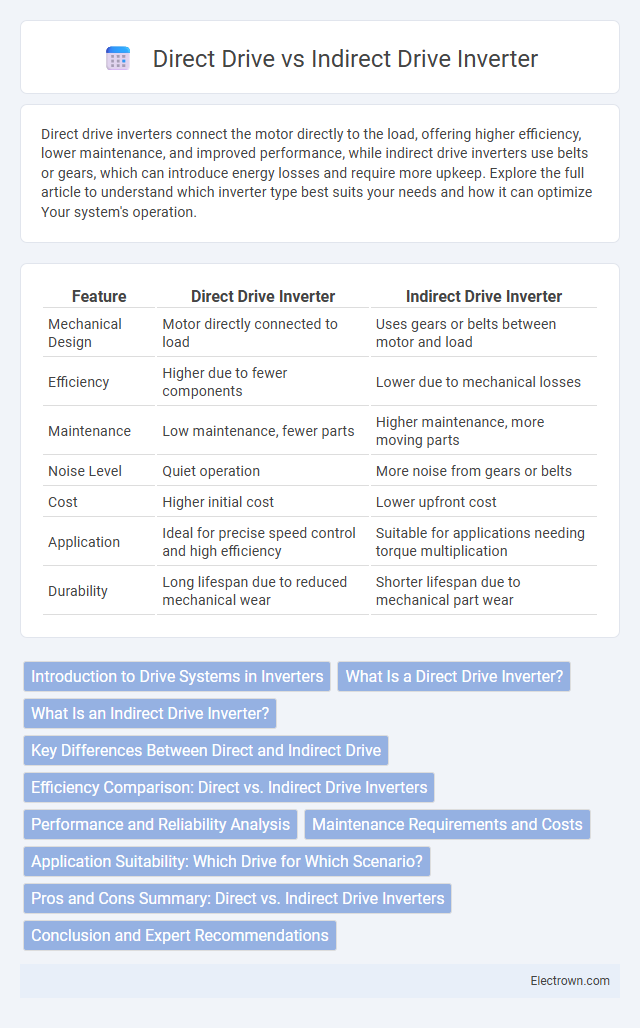
| Feature | Direct Drive Inverter | Indirect Drive Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Design | Motor directly connected to load | Uses gears or belts between motor and load |
| Efficiency | Higher due to fewer components | Lower due to mechanical losses |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, fewer parts | Higher maintenance, more moving parts |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | More noise from gears or belts |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Application | Ideal for precise speed control and high efficiency | Suitable for applications needing torque multiplication |
| Durability | Long lifespan due to reduced mechanical wear | Shorter lifespan due to mechanical part wear |
Introduction to Drive Systems in Inverters
Drive systems in inverters are crucial for controlling the speed and torque of electric motors through precise power conversion. Direct drive inverters connect the motor shaft directly to the load, enhancing efficiency by reducing mechanical losses and maintenance requirements. Indirect drive inverters use intermediary components like belts or gears, offering flexibility in speed and torque adjustments but often at the cost of increased wear and energy loss.
What Is a Direct Drive Inverter?
A direct drive inverter integrates the motor and inverter into a single unit, eliminating the need for additional components like belts or gears found in indirect drive systems. This design enhances energy efficiency, reduces noise, and improves system reliability by minimizing mechanical losses. Your choice of a direct drive inverter can lead to lower maintenance costs and higher overall performance in applications such as HVAC systems and electric vehicles.
What Is an Indirect Drive Inverter?
An indirect drive inverter converts electrical energy to mechanical energy through an additional transmission mechanism, such as gears or belts, to control the output speed and torque. This type of inverter is commonly used in applications requiring variable speeds and flexible torque management, like conveyor belts and HVAC systems. Indirect drive inverters offer advantages in reducing motor wear and enabling precise control but may introduce mechanical losses compared to direct drive systems.
Key Differences Between Direct and Indirect Drive
Direct drive inverters transmit power directly from the motor to the load, resulting in higher efficiency and reduced mechanical losses compared to indirect drive inverters, which use additional components like belts or gears. Direct drive systems offer enhanced reliability and lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts, while indirect drive inverters provide flexibility in motor placement and speed variation through mechanical adjustments. The choice between direct and indirect drive inverters significantly impacts system efficiency, noise levels, and overall operational costs.
Efficiency Comparison: Direct vs. Indirect Drive Inverters
Direct drive inverters typically offer higher efficiency due to the elimination of mechanical transmission losses, as they connect the motor directly to the load, reducing energy waste. Indirect drive inverters involve belts or gears, which introduce friction and slippage, leading to lower overall efficiency compared to direct drive systems. Efficiency ratings for direct drive inverters often exceed 95%, whereas indirect drive systems commonly achieve efficiencies between 85% and 90%.
Performance and Reliability Analysis
Direct drive inverters offer superior performance through reduced mechanical losses and higher energy efficiency, enhancing system reliability by minimizing wear and tear on components. Indirect drive inverters, while generally less efficient due to additional mechanical transmission elements, can provide greater flexibility in system design but often require more maintenance to ensure consistent operation. Reliability in direct drive systems tends to be higher given fewer failure points and improved control precision, making them preferable for applications demanding long-term operational stability.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Direct drive inverters require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts, resulting in lower operational costs over time. Indirect drive inverters involve additional mechanical components like belts or gears that need regular inspection, alignment, and replacement, increasing maintenance complexity and expenses. Lower maintenance frequency and reduced downtime make direct drive systems more cost-effective for long-term applications.
Application Suitability: Which Drive for Which Scenario?
Direct drive inverters excel in applications requiring high precision and efficiency, such as robotics and CNC machines, where minimal mechanical losses and precise control are critical. Indirect drive inverters are better suited for scenarios involving heavy machinery like conveyors and pumps, offering robust performance and easier integration with gearboxes or belts. Selecting the appropriate drive depends on load characteristics, torque requirements, and maintenance preferences, with direct drives favoring high-accuracy tasks and indirect drives ideal for high-torque, lower-precision operations.
Pros and Cons Summary: Direct vs. Indirect Drive Inverters
Direct drive inverters offer higher efficiency and lower maintenance due to fewer mechanical components, making them ideal for applications requiring reliability and reduced energy loss. Indirect drive inverters provide greater flexibility in system design and can handle a wider range of input sources but often involve more complex and costly maintenance. Your choice depends on the priority between operational efficiency and system adaptability.
Conclusion and Expert Recommendations
Direct drive inverters offer higher energy efficiency and reliability by eliminating mechanical transmission losses associated with indirect drive systems. Experts recommend direct drive inverters for applications requiring precise speed control and lower maintenance costs, while indirect drive inverters remain suitable for budget-conscious projects with simpler load demands. Optimal inverter selection should consider specific operational requirements, energy savings potential, and long-term durability.
direct drive vs indirect drive inverter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com