A PFC circuit enhances power factor by reducing reactive power, improving efficiency and reducing energy loss, while a harmonic filter specifically mitigates harmonic distortion caused by nonlinear loads to protect equipment and ensure power quality. Discover how understanding the differences between these two can optimize Your electrical systems in the following article.
Table of Comparison
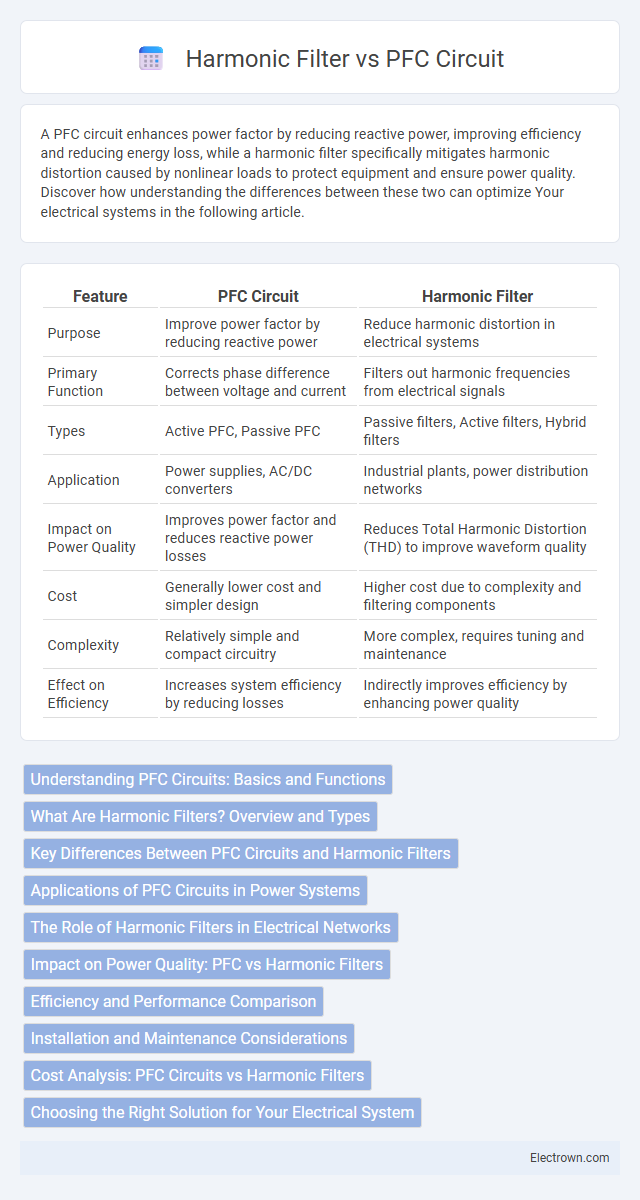
| Feature | PFC Circuit | Harmonic Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Improve power factor by reducing reactive power | Reduce harmonic distortion in electrical systems |
| Primary Function | Corrects phase difference between voltage and current | Filters out harmonic frequencies from electrical signals |
| Types | Active PFC, Passive PFC | Passive filters, Active filters, Hybrid filters |
| Application | Power supplies, AC/DC converters | Industrial plants, power distribution networks |
| Impact on Power Quality | Improves power factor and reduces reactive power losses | Reduces Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) to improve waveform quality |
| Cost | Generally lower cost and simpler design | Higher cost due to complexity and filtering components |
| Complexity | Relatively simple and compact circuitry | More complex, requires tuning and maintenance |
| Effect on Efficiency | Increases system efficiency by reducing losses | Indirectly improves efficiency by enhancing power quality |
Understanding PFC Circuits: Basics and Functions
PFC circuits enhance the power quality by reducing harmonics and improving power factor, ensuring more efficient energy consumption in electrical systems. These circuits control the input current to follow the input voltage waveform, minimizing reactive power and lowering energy losses. Your system benefits from PFC circuits by achieving compliance with regulatory standards and reducing stress on electrical infrastructure compared to standard harmonic filters.
What Are Harmonic Filters? Overview and Types
Harmonic filters are electrical devices designed to mitigate harmonic distortion caused by non-linear loads in power systems, improving power quality and preventing equipment damage. Common types include passive filters, which use inductors, capacitors, and resistors to block specific harmonic frequencies, and active filters, which dynamically inject compensating currents to cancel harmonics. Hybrid filters combine passive and active elements for enhanced performance across a wider range of harmonics and load conditions.
Key Differences Between PFC Circuits and Harmonic Filters
PFC circuits primarily improve power factor by correcting the phase angle between voltage and current, reducing reactive power and enhancing energy efficiency in electrical systems. Harmonic filters target the reduction of harmonic distortion caused by nonlinear loads, protecting equipment from overheating and ensuring compliance with power quality standards. Your choice depends on whether the focus is on power factor correction or mitigating harmonic interference in the electrical network.
Applications of PFC Circuits in Power Systems
PFC circuits are essential in power systems to improve power factor, reducing reactive power and enhancing energy efficiency in industrial motors, lighting systems, and renewable energy inverters. These circuits help minimize utility penalties by aligning the phase between voltage and current, leading to lower electricity costs and improved equipment lifespan. Your power system benefits from PFC implementation by achieving compliance with regulatory standards and reducing harmonic distortion that affects system stability.
The Role of Harmonic Filters in Electrical Networks
Harmonic filters play a crucial role in electrical networks by mitigating voltage and current distortions caused by non-linear loads, ensuring power quality and compliance with standards such as IEEE 519. Unlike PFC circuits that primarily correct power factor by adjusting the phase angle between voltage and current, harmonic filters specifically target and reduce harmonics that can cause overheating, equipment malfunction, and increased losses. Your electrical system benefits from improved efficiency and extended equipment lifespan when harmonic filters are properly integrated to manage harmonic distortion effectively.
Impact on Power Quality: PFC vs Harmonic Filters
Power Factor Correction (PFC) circuits improve power quality by reducing reactive power and enhancing voltage stability, resulting in lower energy losses and improved efficiency of electrical systems. Harmonic filters specifically target and mitigate harmonic distortions caused by nonlinear loads, thereby reducing electrical noise, heating, and damage to sensitive equipment. Your choice between PFC and harmonic filters depends on whether the primary goal is to correct power factor or to control harmonic distortion for optimal power quality.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
PFC circuits improve power factor by controlling input current, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing losses in electrical systems. Harmonic filters target the attenuation of specific harmonic frequencies, improving power quality and protecting sensitive equipment from distortion. Your choice between a PFC circuit and a harmonic filter depends on whether efficiency or harmonic mitigation is the primary performance requirement.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
PFC circuits typically require relatively simple installation, integrating directly with power supplies and demanding minimal space, whereas harmonic filters often involve larger components and more complex wiring to shape system harmonic profiles. Maintenance for PFC circuits centers on periodic inspection of capacitors and inductors to ensure performance, while harmonic filters necessitate regular tuning and replacement of parts like reactors and capacitors to maintain effective harmonic suppression. Proper sizing and environmental conditions significantly impact the longevity and efficiency of both PFC circuits and harmonic filters in industrial applications.
Cost Analysis: PFC Circuits vs Harmonic Filters
PFC circuits generally incur lower initial costs and simpler installation expenses compared to harmonic filters, which require higher upfront investment due to complex components and design. However, harmonic filters offer long-term savings by reducing penalties from utility companies for harmonic distortions and improving power quality, potentially lowering energy bills. Evaluating your energy consumption profile and utility rates is essential to determine the most cost-effective solution for your power management needs.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Electrical System
Selecting between a PFC circuit and a harmonic filter depends on your electrical system's specific power quality issues and efficiency goals. PFC circuits primarily improve power factor and reduce reactive power, enhancing energy efficiency and lowering utility costs. Harmonic filters target distortion caused by non-linear loads, protecting sensitive equipment and ensuring compliance with power quality standards for reliable system operation.
pfc circuit vs harmonic filter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com