Double pulse test offers precise insight into semiconductor switching characteristics by applying two controlled pulses, while continuous conduction test measures performance under steady-state current conditions to evaluate device efficiency and thermal behavior. Discover how each testing method impacts your power device analysis by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
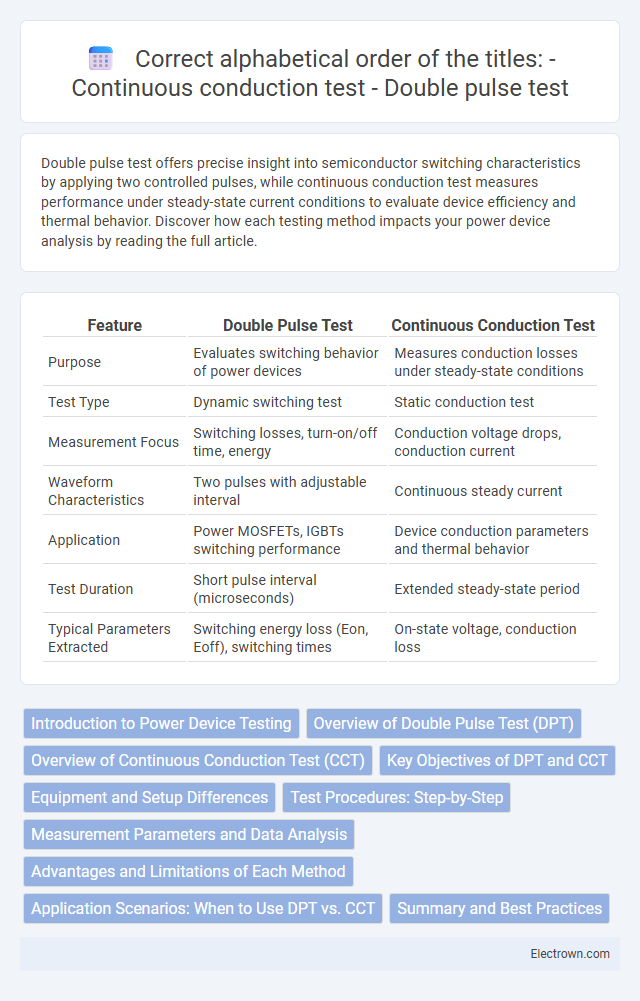
| Feature | Double Pulse Test | Continuous Conduction Test |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluates switching behavior of power devices | Measures conduction losses under steady-state conditions |
| Test Type | Dynamic switching test | Static conduction test |
| Measurement Focus | Switching losses, turn-on/off time, energy | Conduction voltage drops, conduction current |
| Waveform Characteristics | Two pulses with adjustable interval | Continuous steady current |
| Application | Power MOSFETs, IGBTs switching performance | Device conduction parameters and thermal behavior |
| Test Duration | Short pulse interval (microseconds) | Extended steady-state period |
| Typical Parameters Extracted | Switching energy loss (Eon, Eoff), switching times | On-state voltage, conduction loss |
Introduction to Power Device Testing
Power device testing evaluates the performance and reliability of semiconductor components like MOSFETs and IGBTs under different operating conditions. Double pulse tests measure switching losses, transient behavior, and dynamic characteristics by applying two pulses to simulate real switching events. Continuous conduction tests assess conduction losses under steady-state current flow, helping optimize your device's efficiency and thermal management.
Overview of Double Pulse Test (DPT)
The Double Pulse Test (DPT) is a critical method for evaluating the switching behavior and dynamic characteristics of power semiconductor devices, such as IGBTs and MOSFETs. It measures parameters like switching losses, turn-on and turn-off times, and voltage/current waveforms under high-speed conditions. This test provides detailed insights into device performance, enabling optimization of power electronics in converters and inverters.
Overview of Continuous Conduction Test (CCT)
The Continuous Conduction Test (CCT) evaluates the steady-state conduction characteristics of power semiconductor devices under constant current conditions, providing crucial data on on-state voltage drop and conduction losses. Unlike the Double Pulse Test, which focuses on dynamic switching performance and transient behavior, the CCT emphasizes thermal stability and reliability during prolonged conduction. This test is essential for optimizing device parameters in applications requiring sustained current flow, such as power converters and motor drives.
Key Objectives of DPT and CCT
Double Pulse Test (DPT) aims to evaluate the switching behavior and dynamic performance of power semiconductor devices by applying two consecutive pulses to measure parameters like switching losses, turn-on/off times, and transient behaviors. Continuous Conduction Test (CCT) focuses on assessing the device's conduction losses and thermal performance under steady-state current conditions. Your choice between DPT and CCT depends on whether you need detailed switching characteristics or efficient conduction performance analysis.
Equipment and Setup Differences
The Double Pulse Test requires advanced pulse generators and high-speed oscilloscopes to capture transient switching characteristics, while the Continuous Conduction Test typically uses DC power supplies and standard measurement instruments for steady-state analysis. Double Pulse Test setups include complex gate driver circuits and precise timing controls to generate two distinct voltage or current pulses, whereas Continuous Conduction Tests rely on a simpler arrangement to observe continuous current flow through power devices. The specialized equipment in Double Pulse Tests enables detailed dynamic performance evaluation, contrasting the Continuous Conduction Test's focus on thermal and conduction losses under steady operating conditions.
Test Procedures: Step-by-Step
The Double Pulse Test involves applying two controlled voltage pulses to a semiconductor device, allowing you to measure dynamic switching characteristics under real operating conditions. The Continuous Conduction Test requires maintaining a steady load current while measuring conduction losses and voltage drops, providing insight into the device's performance during prolonged operation. Both test procedures emphasize precise timing and accurate measurement setups to ensure reliable data for device evaluation.
Measurement Parameters and Data Analysis
Double pulse test measures switching losses, device turn-on and turn-off times, and transient current behavior by applying two consecutive pulses, enabling detailed analysis of dynamic switching performance. Continuous conduction test evaluates steady-state conduction losses, voltage drop, and thermal characteristics under constant current flow, providing data on device efficiency and thermal stability. Your analysis should compare transient switching parameters from double pulse testing with steady-state conduction metrics from continuous conduction tests for comprehensive device characterization.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
Double pulse test offers precise characterization of switching behavior and dynamic losses in power semiconductor devices, providing detailed insights into turn-on/turn-off transitions and switching overlap. Continuous conduction test enables evaluation of steady-state conduction losses and thermal performance under constant current conditions, ideal for assessing device durability and on-resistance over time. Limitations of double pulse test include its complexity and high test voltages, which may not represent real operating conditions, whereas continuous conduction test lacks dynamic switching information and may overlook transient stress effects.
Application Scenarios: When to Use DPT vs. CCT
Double pulse test (DPT) is ideal for evaluating switching characteristics and dynamic performance of power semiconductor devices in high-frequency applications such as DC-DC converters and inverters. Continuous conduction test (CCT) suits scenarios requiring steady-state analysis of conduction losses and thermal performance under continuous load conditions, common in motor drives and power supplies. Choosing DPT or CCT depends on whether the focus is on transient switching behavior or steady-state conduction evaluation in power electronics systems.
Summary and Best Practices
Double pulse test evaluates switching losses and device behavior under dynamic conditions, making it essential for analyzing transient responses in power electronics. Continuous conduction test measures steady-state conduction losses, offering insight into device efficiency during prolonged operation. For optimal performance, combining both tests provides a comprehensive understanding of your device's switching and conduction characteristics, enabling precise optimization of power electronics systems.
Double pulse test vs Continuous conduction test Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com