dv/dt protection limits rapid voltage changes to prevent device failure, while snubber protection absorbs voltage spikes and reduces electrical noise in circuits. Explore the article to understand which method best suits your application's needs.
Table of Comparison
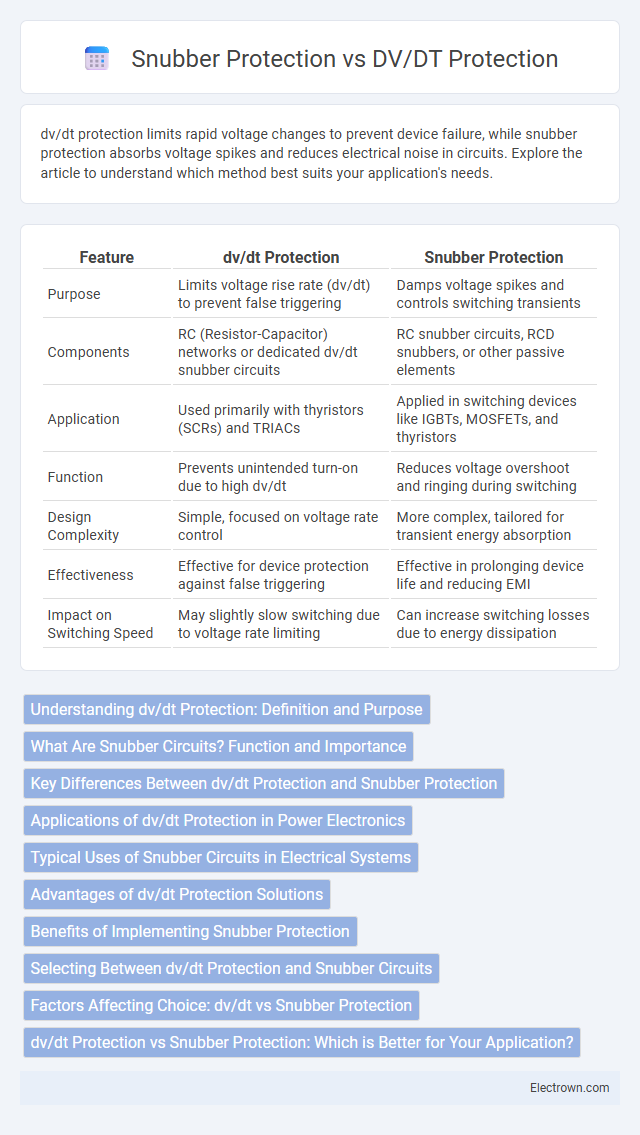
| Feature | dv/dt Protection | Snubber Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Limits voltage rise rate (dv/dt) to prevent false triggering | Damps voltage spikes and controls switching transients |
| Components | RC (Resistor-Capacitor) networks or dedicated dv/dt snubber circuits | RC snubber circuits, RCD snubbers, or other passive elements |
| Application | Used primarily with thyristors (SCRs) and TRIACs | Applied in switching devices like IGBTs, MOSFETs, and thyristors |
| Function | Prevents unintended turn-on due to high dv/dt | Reduces voltage overshoot and ringing during switching |
| Design Complexity | Simple, focused on voltage rate control | More complex, tailored for transient energy absorption |
| Effectiveness | Effective for device protection against false triggering | Effective in prolonging device life and reducing EMI |
| Impact on Switching Speed | May slightly slow switching due to voltage rate limiting | Can increase switching losses due to energy dissipation |
Understanding dv/dt Protection: Definition and Purpose
dv/dt protection is a specialized technique used in power electronics to prevent false triggering of semiconductor devices caused by rapid voltage changes (dv/dt). This protection method ensures device reliability by controlling voltage transients that can induce unintended switching, particularly in insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) and thyristors. Unlike snubber circuits, which absorb and dissipate energy, dv/dt protection primarily targets voltage rate control to maintain safe operating conditions.
What Are Snubber Circuits? Function and Importance
Snubber circuits are electrical components designed to suppress voltage transients and limit dv/dt rates in power semiconductor devices, preventing damage caused by rapid voltage changes. These circuits typically consist of resistors, capacitors, and sometimes diodes, strategically placed to absorb or dissipate the induced energy during switching events. Their importance lies in enhancing device reliability, reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI), and improving overall circuit performance in applications involving inductive loads or high-speed switching.
Key Differences Between dv/dt Protection and Snubber Protection
dv/dt protection limits the rate of voltage change across power semiconductor devices to prevent false triggering and reduce stress, while snubber protection absorbs voltage spikes and controls transient energy to protect devices from voltage overshoot and ringing. dv/dt protection typically involves specific circuit components like dv/dt filters or snubber networks tailored to slow voltage transitions, whereas snubbers often include resistor-capacitor (RC) or resistor-capacitor-diode (RCD) configurations designed to dissipate energy. Understanding these key differences helps you select the right approach for enhancing device reliability and system stability under high switching speed conditions.
Applications of dv/dt Protection in Power Electronics
dv/dt protection is crucial in power electronics to prevent false triggering of semiconductor devices such as thyristors and IGBTs caused by rapid voltage changes. Your power converters and motor drives benefit from dv/dt protection by enhancing system reliability and reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI). Unlike snubber circuits that primarily absorb transient energy, dv/dt protection specifically limits voltage rise time, ensuring stable switching and prolonging device lifespan.
Typical Uses of Snubber Circuits in Electrical Systems
Snubber circuits are commonly used in electrical systems to suppress voltage spikes caused by rapid switching events in power semiconductor devices like IGBTs and MOSFETs. These circuits protect components by limiting dv/dt rates, reducing electromagnetic interference, and enhancing overall system reliability in motor drives, inverters, and power converters. They are essential in improving transient response and preventing device failure due to high voltage stress.
Advantages of dv/dt Protection Solutions
dv/dt protection solutions provide superior insulation of sensitive power electronics from voltage spikes caused by rapid voltage changes, significantly reducing the risk of device failure. These protections enhance system reliability by minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and reducing stress on switching devices, thereby extending their operational lifespan. Your equipment benefits from improved switching performance and lowered maintenance costs compared to traditional snubber protection methods.
Benefits of Implementing Snubber Protection
Snubber protection effectively limits voltage spikes and reduces dv/dt stress on power electronic devices, enhancing their reliability and lifespan. You benefit from improved circuit stability and minimized electromagnetic interference, which are critical in high-speed switching applications. Implementing snubbers also helps prevent false triggering in sensitive components, ensuring consistent performance under varying load conditions.
Selecting Between dv/dt Protection and Snubber Circuits
Selecting between dv/dt protection and snubber circuits depends on the specific application requirements such as voltage spikes and switching frequency. dv/dt protection is ideal for limiting the rate of voltage change to prevent false triggering in power devices like thyristors and IGBTs. Snubber circuits provide energy dissipation and voltage spike suppression, making them suitable for protecting switches from transient overvoltages and improving overall system reliability.
Factors Affecting Choice: dv/dt vs Snubber Protection
Choice between dv/dt protection and snubber protection depends on switching device sensitivity, system voltage levels, and transient rise time requirements. dv/dt protection is preferred for semiconductor devices like IGBTs to prevent false triggering caused by rapid voltage changes, while snubber circuits are chosen to control voltage spikes and reduce switching losses in power electronics. Factors such as switching frequency, device voltage rating, and thermal management also influence the selection of the appropriate protection method.
dv/dt Protection vs Snubber Protection: Which is Better for Your Application?
dv/dt protection devices effectively prevent voltage spikes by controlling the rate of voltage change, reducing stress on semiconductor switches and improving system reliability. Snubber circuits absorb transient energy and limit voltage overshoot, but often require careful design and component sizing to optimize performance. Your choice depends on specific application requirements such as switching frequency, load conditions, and cost constraints, with dv/dt protection favored for precise control and snubbers preferred for simplicity and energy absorption.
dv/dt protection vs snubber protection Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com