A six-port receiver offers enhanced accuracy and simpler hardware for phase and amplitude measurements compared to a traditional heterodyne receiver, which relies on frequency conversion and local oscillators. Discover how these differences impact your signal processing by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
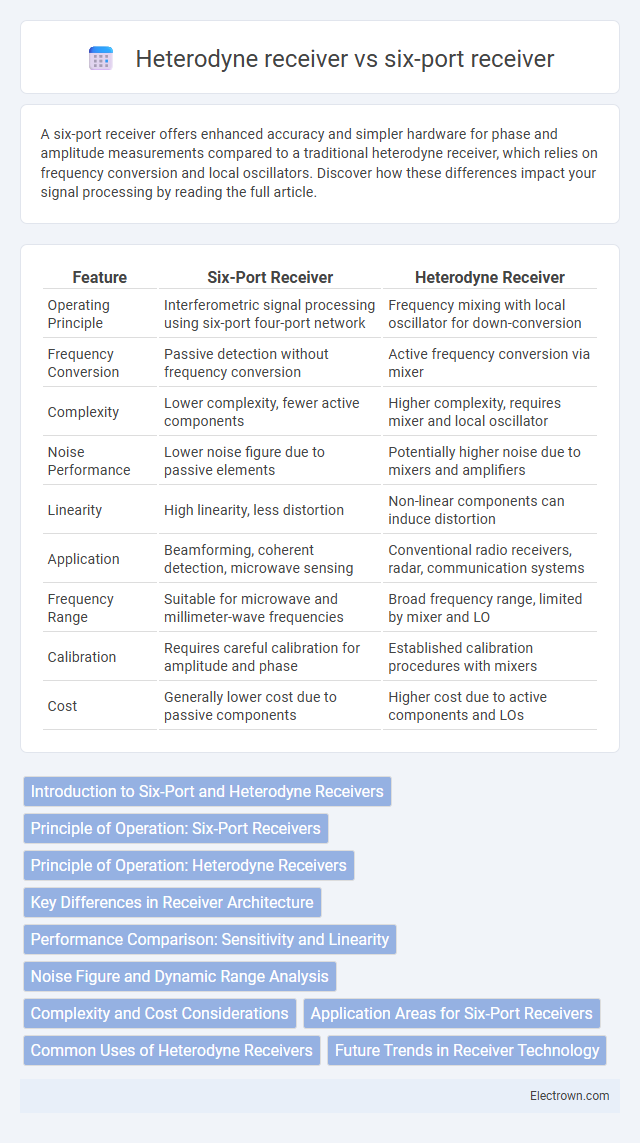
| Feature | Six-Port Receiver | Heterodyne Receiver |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Interferometric signal processing using six-port four-port network | Frequency mixing with local oscillator for down-conversion |
| Frequency Conversion | Passive detection without frequency conversion | Active frequency conversion via mixer |
| Complexity | Lower complexity, fewer active components | Higher complexity, requires mixer and local oscillator |
| Noise Performance | Lower noise figure due to passive elements | Potentially higher noise due to mixers and amplifiers |
| Linearity | High linearity, less distortion | Non-linear components can induce distortion |
| Application | Beamforming, coherent detection, microwave sensing | Conventional radio receivers, radar, communication systems |
| Frequency Range | Suitable for microwave and millimeter-wave frequencies | Broad frequency range, limited by mixer and LO |
| Calibration | Requires careful calibration for amplitude and phase | Established calibration procedures with mixers |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to passive components | Higher cost due to active components and LOs |
Introduction to Six-Port and Heterodyne Receivers
Six-port receivers utilize multiple passive microwave ports to extract amplitude and phase information from a signal, enabling precise vector measurement without the need for local oscillators. Heterodyne receivers operate by mixing an incoming signal with a local oscillator to convert frequencies, allowing for effective signal processing and improved sensitivity. Both technologies play critical roles in modern communication systems, with six-port receivers favored for simplicity and compactness, while heterodyne receivers excel in frequency translation and selectivity.
Principle of Operation: Six-Port Receivers
Six-port receivers operate on the principle of measuring the interference of multiple signals combined at six distinct ports, allowing the extraction of amplitude and phase information through power measurements only. This technique enables the determination of complex signal parameters without the need for conventional mixers or local oscillators as used in heterodyne receivers. The passive six-port network simplifies the architecture, providing robust and accurate vector measurements critical for applications in radar, wireless communication, and signal analysis.
Principle of Operation: Heterodyne Receivers
Heterodyne receivers operate by mixing the incoming radio frequency (RF) signal with a stable local oscillator (LO) signal to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) that is easier to process and amplify. This frequency conversion enables improved selectivity and sensitivity in signal detection by shifting the spectrum without losing the information content. The heterodyne principle effectively separates the signal of interest from noise and interference by exploiting the difference frequency generated during mixing.
Key Differences in Receiver Architecture
The Six-port receiver features a passive microwave front-end with multiple ports for signal mixing, enabling direct detection of signal parameters such as phase and amplitude through power measurements. In contrast, the heterodyne receiver employs active mixing between the incoming RF signal and a local oscillator to convert the frequency to an intermediate frequency (IF) for further amplification and processing. The Six-port architecture offers simpler hardware with fewer mixer components and no need for a local oscillator frequency selection, while the heterodyne design provides higher selectivity and sensitivity due to frequency downconversion and IF filtering stages.
Performance Comparison: Sensitivity and Linearity
Six-port receivers exhibit higher sensitivity due to their ability to measure complex signal parameters directly, minimizing conversion losses and noise figure compared to heterodyne receivers. Heterodyne receivers often provide better linearity by utilizing frequency translation and established mixer designs, which handle strong signal environments with less distortion. Sensitivity improvements in six-port receivers make them ideal for low-power applications, whereas heterodyne receivers excel in scenarios demanding robust linearity and dynamic range.
Noise Figure and Dynamic Range Analysis
Six-port receivers typically exhibit lower noise figures compared to heterodyne receivers due to their passive mixing architecture, which minimizes active components contributing to noise. The dynamic range of six-port receivers is often superior, benefiting from better linearity and reduced intermodulation distortion, making them suitable for high-sensitivity applications. Your choice between these receivers should consider the trade-off between noise figure and dynamic range based on application requirements.
Complexity and Cost Considerations
Six-port receivers offer a simpler architecture with fewer components compared to heterodyne receivers, resulting in lower manufacturing and maintenance costs. Their reduced circuit complexity enhances reliability and makes them highly suitable for cost-sensitive applications. Your choice depends on balancing performance needs against budget constraints, where six-port receivers often provide an economical yet efficient solution.
Application Areas for Six-Port Receivers
Six-port receivers are widely used in radar systems, wireless communication, and microwave measurement due to their compact design, low cost, and ability to provide accurate phase and amplitude information without complex mixers. They excel in scenarios requiring real-time signal processing and channel estimation, such as satellite communications and radio frequency identification (RFID) systems. Unlike heterodyne receivers, six-port receivers offer simplified architectures ideal for broadband and multiband applications, making them valuable in emerging 5G and IoT technologies.
Common Uses of Heterodyne Receivers
Heterodyne receivers are commonly used in radio communications, radar systems, and signal processing due to their ability to convert high-frequency signals to a lower intermediate frequency for easier analysis. These receivers achieve high sensitivity and selectivity, making them ideal for satellite communications, wireless networks, and broadcast receivers. You will find heterodyne receivers widely implemented in applications requiring precise frequency tuning and noise reduction.
Future Trends in Receiver Technology
Six-port receivers offer enhanced signal processing speed and simplified architecture, making them ideal for next-generation communication systems demanding high data rates and low latency. Heterodyne receivers, known for their frequency conversion precision, continue to evolve with advanced components but face limitations in integration and power consumption compared to six-port designs. Your choice will largely depend on future trends emphasizing miniaturization, energy efficiency, and integration with digital signal processing in receiver technology.
Six-port receiver vs heterodyne receiver Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com