Spurious responses often contain irrelevant or misleading information, while image responses are designed to accurately interpret and describe visual content. Discover how understanding these differences can improve Your interaction with AI by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
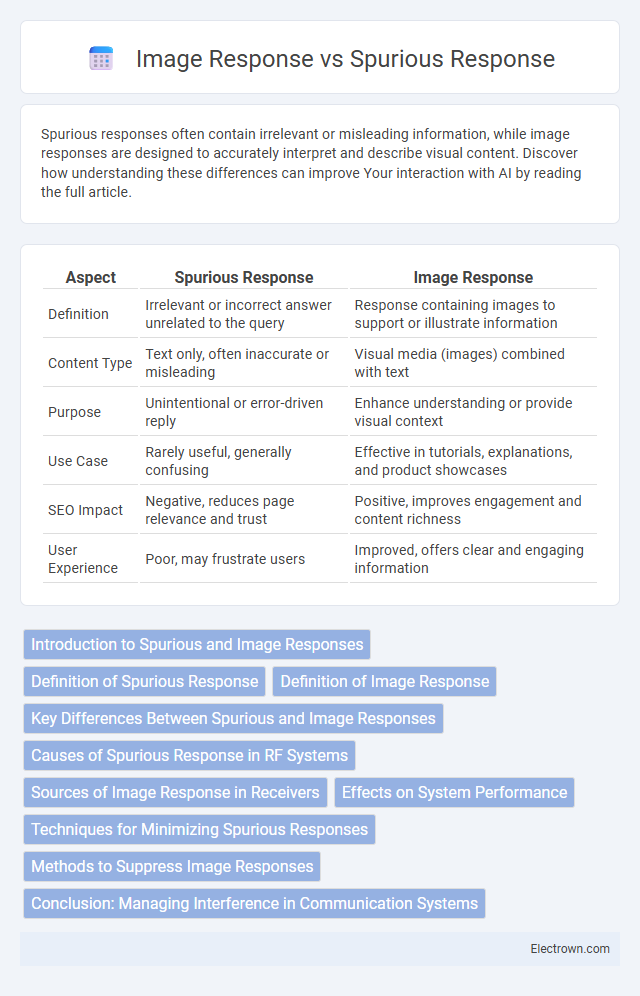
| Aspect | Spurious Response | Image Response |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Irrelevant or incorrect answer unrelated to the query | Response containing images to support or illustrate information |
| Content Type | Text only, often inaccurate or misleading | Visual media (images) combined with text |
| Purpose | Unintentional or error-driven reply | Enhance understanding or provide visual context |
| Use Case | Rarely useful, generally confusing | Effective in tutorials, explanations, and product showcases |
| SEO Impact | Negative, reduces page relevance and trust | Positive, improves engagement and content richness |
| User Experience | Poor, may frustrate users | Improved, offers clear and engaging information |
Introduction to Spurious and Image Responses
Spurious responses occur when unwanted signals generate false outputs in radio frequency systems, often caused by nonlinearities in components like mixers and amplifiers. Image responses arise from the frequency conversion process in mixers, producing a mirrored frequency that interferes with the desired signal. Understanding these artifacts is crucial for designing filters and circuits that enhance signal clarity and system performance.
Definition of Spurious Response
Spurious response refers to unwanted signals generated by a receiver that do not correspond to the intended input frequency, often caused by nonlinearities or internal mixing products within the system. This differs from image response, which is a specific type of interference originating from the mirror frequency in a superheterodyne receiver. Understanding the definition of spurious response helps you design filters and circuits that minimize signal distortion and improve overall receiver performance.
Definition of Image Response
Image response refers to an unwanted signal component generated in a receiver when mixing frequencies create mirror-frequency outputs, causing interference in the intended signal path. It occurs due to inadequate filtering or non-ideal mixing, producing spurious frequencies identical in amplitude but inverted in spectrum relative to the desired signal. Your system's performance depends on minimizing image response to enhance signal clarity and reduce distortion in communication devices.
Key Differences Between Spurious and Image Responses
Spurious responses arise from non-linearities within a system causing unwanted signals at unexpected frequencies, whereas image responses result from signals mirrored around a local oscillator frequency during frequency conversion in receivers. Spurious responses typically degrade signal integrity by introducing interference from harmonics or mixing products, while image responses create ambiguity by producing duplicate frequency components that can confuse signal demodulation. Understanding these key differences helps you design more effective filters and mixers to minimize interference and improve overall system performance.
Causes of Spurious Response in RF Systems
Spurious response in RF systems primarily occurs due to nonlinearities in mixers and amplifiers, causing unwanted signals at frequencies that are combinations of input frequencies. Other causes include local oscillator harmonics, intermodulation distortion, and poor filtering, which generate frequencies outside the desired signal band. Understanding these factors helps you minimize spurious responses and improve the accuracy of your RF system.
Sources of Image Response in Receivers
Image response in receivers originates primarily from the mixing of the incoming signal with the local oscillator frequency's image frequency, which lies symmetrically around the local oscillator. This undesired signal arises due to imperfect filtering before the mixer stage, allowing signals at the image frequency to be downconverted to the same intermediate frequency as the desired signal. Your receiver's selectivity and image rejection ratio are critical parameters in minimizing these sources of image response.
Effects on System Performance
Spurious responses generate unwanted signals that interfere with the desired output, causing increased noise levels and reduced signal clarity, which degrade overall system performance. Image responses arise from imperfect filtering and mixer nonlinearity, producing mirror-frequency signals that can distort or mask the intended signal, leading to erroneous data processing. Minimizing both spurious and image responses is crucial to maintaining signal integrity and ensuring your system operates at peak efficiency.
Techniques for Minimizing Spurious Responses
Techniques for minimizing spurious responses include using high-quality filters, precise frequency tuning, and advanced signal processing algorithms to enhance signal clarity and reduce interference. Employing image rejection mixers and careful circuit design further suppresses unwanted image responses by improving selectivity and reducing noise. Your system's performance benefits significantly from integrating these methods to ensure accurate signal detection and enhanced communication reliability.
Methods to Suppress Image Responses
Methods to suppress image responses involve implementing precise filtering techniques such as front-end bandpass filters and double-balanced mixers to enhance selectivity and reduce unwanted signals. Utilizing image-reject mixers or employing frequency planning strategies also helps to minimize spurious responses by eliminating frequencies that overlap with image frequencies. Your system's performance improves significantly through careful tuning and design adjustments targeting these suppression methods, ensuring clearer signal reception.
Conclusion: Managing Interference in Communication Systems
Managing interference in communication systems requires understanding the differences between spurious response and image response to optimize signal clarity and system performance. Spurious response arises from non-linearities producing unwanted frequencies, while image response results from imperfect filtering of mirror frequencies in receivers. Your effective interference mitigation depends on precise filtering techniques and adaptive signal processing to minimize these degradation sources.
Spurious Response vs Image Response Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com