SMD capacitors and MLCCs both serve as surface-mounted capacitors but differ primarily in construction and application; MLCCs are multilayer ceramic capacitors known for high capacitance and reliability in electronic circuits, while SMD capacitors encompass various types beyond just MLCCs, offering versatile options for your specific needs. Explore the article to understand which capacitor type best suits your project's requirements.
Table of Comparison
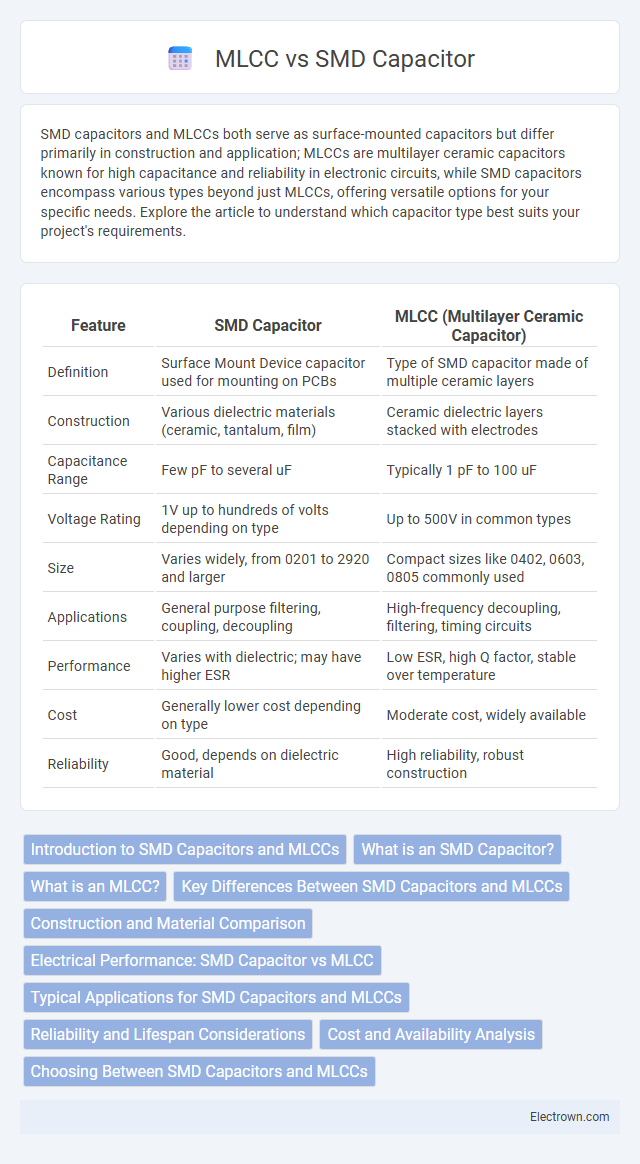
| Feature | SMD Capacitor | MLCC (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Surface Mount Device capacitor used for mounting on PCBs | Type of SMD capacitor made of multiple ceramic layers |
| Construction | Various dielectric materials (ceramic, tantalum, film) | Ceramic dielectric layers stacked with electrodes |
| Capacitance Range | Few pF to several uF | Typically 1 pF to 100 uF |
| Voltage Rating | 1V up to hundreds of volts depending on type | Up to 500V in common types |
| Size | Varies widely, from 0201 to 2920 and larger | Compact sizes like 0402, 0603, 0805 commonly used |
| Applications | General purpose filtering, coupling, decoupling | High-frequency decoupling, filtering, timing circuits |
| Performance | Varies with dielectric; may have higher ESR | Low ESR, high Q factor, stable over temperature |
| Cost | Generally lower cost depending on type | Moderate cost, widely available |
| Reliability | Good, depends on dielectric material | High reliability, robust construction |
Introduction to SMD Capacitors and MLCCs
Surface-Mount Device (SMD) capacitors and Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) are essential components in modern electronic circuits, offering compact size and reliable performance. MLCCs represent a popular type of SMD capacitor, characterized by multiple ceramic dielectric layers that provide high capacitance and stability in a small footprint. Your electronic design benefits from understanding these differences to select the appropriate capacitor for enhanced efficiency and functionality.
What is an SMD Capacitor?
An SMD capacitor is a surface-mount device designed for automatic placement on printed circuit boards, offering compact size and reliable performance. MLCC, or Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor, is a common type of SMD capacitor known for its high capacitance in a small form factor, excellent stability, and low ESR. Your choice depends on the specific electronic application's needs for size, capacitance, and frequency characteristics.
What is an MLCC?
An MLCC (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor) is a type of SMD (Surface-Mount Device) capacitor composed of multiple ceramic dielectric layers stacked between metal electrodes. These capacitors provide high capacitance in a compact size, making them ideal for high-frequency applications and modern electronic circuits. MLCCs exhibit low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and superior temperature stability compared to other SMD capacitors.
Key Differences Between SMD Capacitors and MLCCs
SMD capacitors encompass various types, including ceramic, tantalum, and electrolytic, whereas MLCCs (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors) specifically refer to ceramic capacitors with multiple dielectric layers. MLCCs offer higher capacitance values in a smaller size due to their multilayer construction, providing superior performance in high-frequency applications compared to some other SMD capacitor types. Choosing the right component for your circuit depends on factors like capacitance, voltage rating, and frequency response, with MLCCs often preferred for compact, high-reliability designs.
Construction and Material Comparison
SMD capacitors primarily consist of a metal case with internal electrodes separated by a dielectric, often using tantalum or aluminum materials for stable capacitance and high volumetric efficiency. MLCCs (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors) feature multiple layers of ceramic dielectric and metal electrodes stacked together, offering high capacitance density and low ESR, with materials like barium titanate for enhanced performance. The ceramic dielectric in MLCCs provides superior temperature and frequency stability compared to the electrolytic dielectrics used in many SMD capacitors, influencing their suitability for different electronic applications.
Electrical Performance: SMD Capacitor vs MLCC
SMD capacitors, including MLCCs (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors), offer distinct electrical performance characteristics, with MLCCs excelling in high capacitance stability, low equivalent series resistance (ESR), and superior frequency response. MLCCs provide excellent insulation resistance and minimal leakage current, making them ideal for high-frequency applications and filtering circuits. Comparatively, other SMD capacitors like tantalum or film capacitors may offer higher capacitance values but generally exhibit higher ESR and less stability under temperature variations.
Typical Applications for SMD Capacitors and MLCCs
SMD capacitors, widely used in automotive electronics, telecommunications, and consumer devices, offer flexibility in capacitance values and voltage ratings for power supply smoothing and signal filtering. MLCCs (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors) dominate high-frequency applications such as RF circuits, smartphones, and computer motherboards due to their low ESR, high capacitance density, and reliability under thermal stress. Both components are crucial in compact electronic designs, with MLCCs favored for decoupling and noise reduction, while SMD capacitors suit general-purpose bypass and timing circuits.
Reliability and Lifespan Considerations
SMD capacitors, particularly multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), offer high reliability due to their solid construction, minimal electrolyte leakage, and resistance to environmental stress. MLCCs typically exhibit longer lifespans compared to other SMD capacitor types because of their stable dielectric materials such as X7R or C0G, which maintain capacitance under varying temperatures and voltages. Reliability in high-frequency and high-temperature applications is enhanced by MLCCs' low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and robust mechanical properties, making them ideal for modern electronics requiring durability.
Cost and Availability Analysis
SMD capacitors generally offer a broader range of cost options and are widely available across various electronic component suppliers, making them accessible for diverse project budgets. MLCCs, a specific type of SMD capacitor, tend to have competitive pricing due to mass production but face occasional shortages impacting availability and price stability in high-demand sectors like automotive and telecom. Evaluating your project's cost constraints and supply chain reliability is crucial when choosing between general SMD capacitors and MLCCs to ensure optimal procurement efficiency.
Choosing Between SMD Capacitors and MLCCs
Choosing between SMD capacitors and MLCCs depends on your circuit's performance requirements and space constraints. SMD capacitors offer a variety of types including tantalum and electrolytic, while MLCCs are ceramic-based with high reliability and low equivalent series resistance (ESR). Your selection should consider factors like capacitance stability, voltage rating, and frequency response to optimize device functionality.
SMD capacitor vs MLCC Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com