Metal-ceramic tube RF amplifiers offer high power and robust performance in high-frequency applications, but solid-state RF amplifiers provide greater efficiency, reliability, and smaller size for modern communication systems. Discover which technology best suits your needs by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
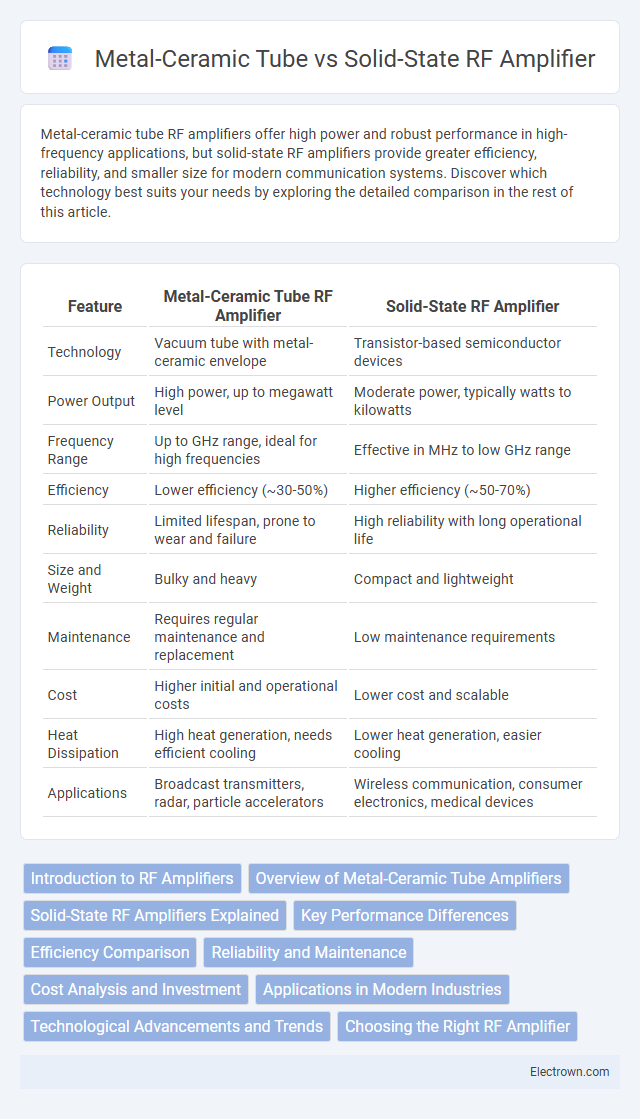
| Feature | Metal-Ceramic Tube RF Amplifier | Solid-State RF Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Vacuum tube with metal-ceramic envelope | Transistor-based semiconductor devices |
| Power Output | High power, up to megawatt level | Moderate power, typically watts to kilowatts |
| Frequency Range | Up to GHz range, ideal for high frequencies | Effective in MHz to low GHz range |
| Efficiency | Lower efficiency (~30-50%) | Higher efficiency (~50-70%) |
| Reliability | Limited lifespan, prone to wear and failure | High reliability with long operational life |
| Size and Weight | Bulky and heavy | Compact and lightweight |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and replacement | Low maintenance requirements |
| Cost | Higher initial and operational costs | Lower cost and scalable |
| Heat Dissipation | High heat generation, needs efficient cooling | Lower heat generation, easier cooling |
| Applications | Broadcast transmitters, radar, particle accelerators | Wireless communication, consumer electronics, medical devices |
Introduction to RF Amplifiers
Metal-ceramic tube RF amplifiers utilize vacuum tube technology with robust metal-ceramic construction to deliver high power and reliability in demanding radio frequency applications. Solid-state RF amplifiers rely on semiconductor devices such as transistors, offering greater efficiency, smaller size, and improved linearity for modern communication systems. Both amplifier types play crucial roles in RF transmission, with metal-ceramic tubes favored in high-power, high-frequency scenarios and solid-state amplifiers widely adopted for their durability and compact design.
Overview of Metal-Ceramic Tube Amplifiers
Metal-ceramic tube amplifiers use vacuum tubes encased in durable metal-ceramic envelopes, ensuring excellent thermal stability and high power handling capabilities for RF amplification. These amplifiers are ideal for high-frequency applications requiring robust performance, such as radio broadcasting and radar systems, where their linearity and power efficiency outperform many solid-state options. Your choice of metal-ceramic tube amplifiers guarantees reliable operation in demanding environments with superior power output compared to solid-state RF amplifiers.
Solid-State RF Amplifiers Explained
Solid-state RF amplifiers use semiconductor devices such as transistors to amplify radio frequency signals with high efficiency, reliability, and compact size compared to metal-ceramic tube amplifiers. These amplifiers offer better thermal management and longer operational lifespan due to their solid-state components, reducing the need for frequent maintenance. The transition from metal-ceramic tube technology to solid-state RF amplifiers marks significant advancements in power handling, linearity, and integration within modern communication systems.
Key Performance Differences
Metal-ceramic tube RF amplifiers deliver higher power output and superior linearity, making them ideal for high-frequency applications requiring precise signal amplification. Solid-state RF amplifiers offer greater reliability, longer lifespan, and more compact size due to semiconductor technology, but may have limitations in maximum power handling compared to metal-ceramic tubes. Your choice depends on prioritizing power capacity or durability for specific radio frequency amplification needs.
Efficiency Comparison
Metal-ceramic tube RF amplifiers typically achieve efficiencies between 40% and 60%, benefitting from robust thermal management and high power handling capabilities. Solid-state RF amplifiers often deliver slightly lower efficiencies around 30% to 50%, but improvements in semiconductor technology have narrowed this gap while offering greater reliability and smaller form factors. The choice between metal-ceramic tubes and solid-state amplifiers depends on specific application power demands and efficiency priorities.
Reliability and Maintenance
Metal-ceramic tube RF amplifiers offer high reliability due to their robust construction, but they require periodic maintenance such as tube replacement and cooling system checks. Solid-state RF amplifiers provide greater reliability with minimal maintenance needs, benefiting from fewer moving components and longer operational lifespans. Your choice will impact downtime and service costs, with solid-state options generally offering lower maintenance frequency and quicker recovery times.
Cost Analysis and Investment
Metal-ceramic tube RF amplifiers typically involve higher initial capital expenditures due to their intricate vacuum tube manufacturing processes and costly materials like specialized ceramics and metals. Solid-state RF amplifiers offer lower upfront costs coupled with reduced maintenance expenses, driven by advancements in semiconductor technologies such as GaN and LDMOS, which enhance durability and efficiency. Over the long term, solid-state amplifiers deliver superior return on investment through increased reliability, smaller footprints, and energy savings despite potentially higher operational power consumption.
Applications in Modern Industries
Metal-ceramic tube amplifiers excel in high-power broadcasting and radar systems due to their robust thermal management and durability under extreme conditions. Solid-state RF amplifiers dominate telecommunications, satellite communications, and medical imaging for their compact size, energy efficiency, and reliability. The choice between these technologies hinges on specific industry needs, balancing power output with integration demands.
Technological Advancements and Trends
Metal-ceramic tube RF amplifiers have historically provided high power output and robust performance in harsh environments, driven by advancements in ceramic materials and vacuum tube design. Solid-state RF amplifiers now dominate due to rapid improvements in semiconductor technology, including GaN and LDMOS transistors, which offer higher efficiency, smaller size, and greater reliability. Emerging trends prioritize integration, thermal management innovations, and digital control techniques to enhance performance and scalability in communication and radar systems.
Choosing the Right RF Amplifier
Choosing the right RF amplifier depends on application requirements such as power output, efficiency, and durability. Metal-ceramic tube amplifiers excel in high-power, high-frequency applications due to their robust thermal handling and linearity, making them ideal for radar and broadcast transmitters. Solid-state RF amplifiers provide greater reliability, compact size, and improved efficiency for moderate power levels while offering easier maintenance and longer operational lifespans in communication and industrial systems.
Metal-ceramic tube vs solid-state RF amplifier Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com