RF baluns and transformers both serve to transfer radio frequency signals, but baluns specifically convert between balanced and unbalanced lines while transformers primarily focus on impedance matching and isolation. Understanding your circuit's requirements for signal conversion and impedance will help you decide which component suits your needs--read on to explore their differences and applications in detail.
Table of Comparison
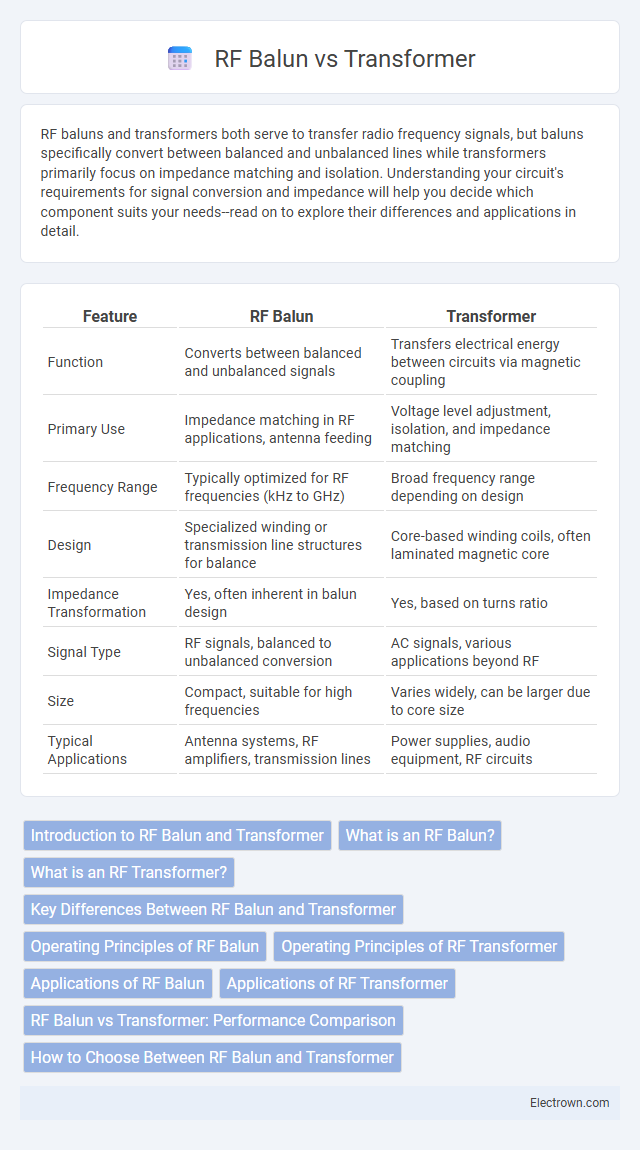
| Feature | RF Balun | Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts between balanced and unbalanced signals | Transfers electrical energy between circuits via magnetic coupling |
| Primary Use | Impedance matching in RF applications, antenna feeding | Voltage level adjustment, isolation, and impedance matching |
| Frequency Range | Typically optimized for RF frequencies (kHz to GHz) | Broad frequency range depending on design |
| Design | Specialized winding or transmission line structures for balance | Core-based winding coils, often laminated magnetic core |
| Impedance Transformation | Yes, often inherent in balun design | Yes, based on turns ratio |
| Signal Type | RF signals, balanced to unbalanced conversion | AC signals, various applications beyond RF |
| Size | Compact, suitable for high frequencies | Varies widely, can be larger due to core size |
| Typical Applications | Antenna systems, RF amplifiers, transmission lines | Power supplies, audio equipment, RF circuits |
Introduction to RF Balun and Transformer
RF baluns and transformers are critical components in radio frequency circuits, serving distinct roles in impedance matching and signal conversion. An RF balun (balanced to unbalanced transformer) converts between balanced and unbalanced signals, ensuring proper signal transmission without interference. Transformers primarily transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction, often providing voltage transformation and isolation in RF applications.
What is an RF Balun?
An RF balun is a device that converts between balanced and unbalanced radio frequency signals, enabling efficient transmission in RF systems. It maintains impedance matching while minimizing signal loss and electromagnetic interference. Unlike traditional transformers, RF baluns are specifically designed for high-frequency applications, ensuring optimal performance in antenna feeds and transmission lines.
What is an RF Transformer?
An RF transformer is a passive electrical device designed to transfer radio frequency signals between circuits while providing impedance matching and isolation. It consists of two or more coupled inductors (coils) wound on a magnetic core, enabling efficient energy transfer at high frequencies with minimal loss. Understanding your specific signal requirements helps optimize RF transformer selection for applications such as impedance matching and signal coupling.
Key Differences Between RF Balun and Transformer
RF baluns and transformers both function to transfer signals, but key differences lie in their specific applications and impedance characteristics. RF baluns convert between balanced and unbalanced signals, optimizing signal integrity in antenna systems, while transformers primarily provide impedance matching and isolation without necessarily altering signal symmetry. Your choice depends on whether balanced signal conversion or impedance transformation is the primary requirement in your RF design.
Operating Principles of RF Balun
RF baluns operate by converting between balanced and unbalanced signals through electromagnetic coupling, utilizing coils or transmission lines to maintain signal integrity and impedance matching. The balanced output delivers symmetrical signals, minimizing noise and interference, essential in RF applications like antennas and mixers. Your system's performance can benefit from a balun's ability to isolate and efficiently transfer RF energy compared to traditional transformers.
Operating Principles of RF Transformer
RF transformers operate by transferring energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction using a magnetic core and windings, enabling impedance matching and signal isolation in high-frequency applications. Unlike a balun, which converts between balanced and unbalanced signals, an RF transformer maintains the signal type while stepping voltage or current up or down. Your design's performance depends on core material, winding technique, and frequency range to minimize losses and ensure efficient power transfer.
Applications of RF Balun
RF baluns are primarily used in radio frequency systems to convert between balanced and unbalanced signals, enabling seamless integration of antennas with transmission lines or devices. Their applications include impedance matching in dipole antennas, feeding differential inputs of RF amplifiers, and reducing common-mode noise in communication transceivers. Baluns improve signal integrity and minimize electromagnetic interference in RF front-end circuits for wireless communication, broadcasting, and radar systems.
Applications of RF Transformer
RF transformers are essential in impedance matching and signal isolation across wireless communication systems, including transmitters, receivers, and amplifiers. They enable efficient power transfer and minimize signal loss in RF circuits for cellular networks, radar systems, and broadband devices. Their ability to handle wide frequency ranges with low insertion loss makes them pivotal in RF filter design and antenna feed networks.
RF Balun vs Transformer: Performance Comparison
RF baluns and transformers both serve to match impedance and balance signals in RF circuits, but baluns excel in converting between balanced and unbalanced signals with minimal phase distortion. Transformers typically provide higher isolation and power handling capabilities but may introduce more insertion loss and bandwidth limitations compared to high-quality RF baluns. Performance comparison reveals that RF baluns offer superior signal symmetry and lower common-mode interference, making them preferable for applications requiring precise balanced-to-unbalanced transitions.
How to Choose Between RF Balun and Transformer
Choosing between an RF balun and transformer depends on the specific application requirements such as impedance matching, signal type, and frequency range. RF baluns excel in converting between balanced and unbalanced signals while maintaining isolation and minimizing signal distortion, making them ideal for antenna systems and balanced line interfaces. Transformers offer broader voltage transformation capabilities and are better suited for power applications and impedance matching in low-frequency circuits where isolation and signal integrity are less critical.
RF balun vs transformer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com