Absorptive switches minimize signal reflection by absorbing the energy of the input signal when in the off state, ensuring better impedance matching and reducing signal degradation in RF systems. Understanding the differences between absorptive and reflective switches can help you choose the right component for your specific application; keep reading to explore their advantages and use cases.
Table of Comparison
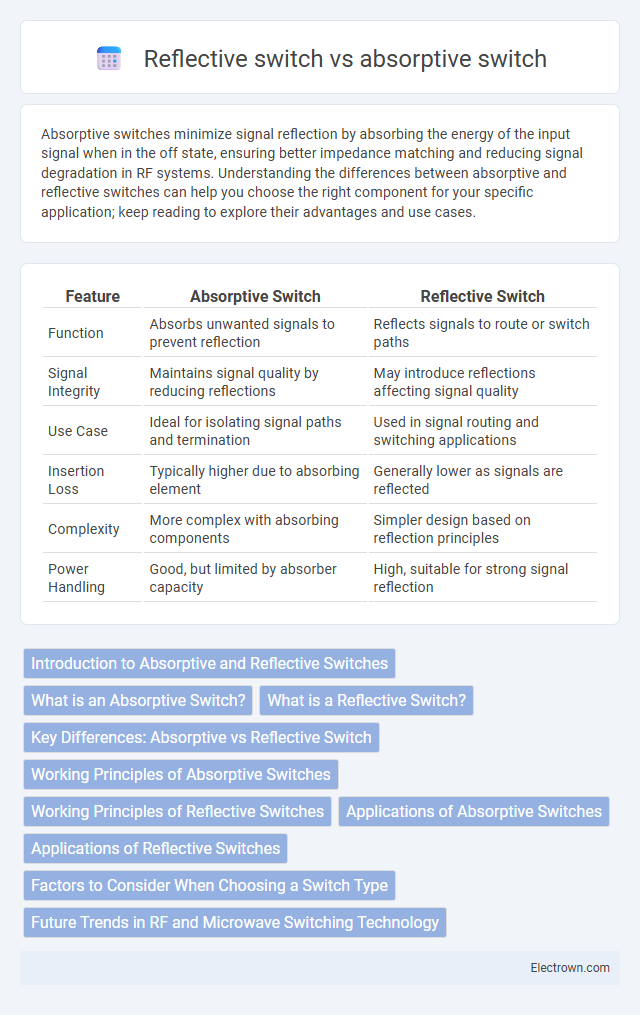
| Feature | Absorptive Switch | Reflective Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Absorbs unwanted signals to prevent reflection | Reflects signals to route or switch paths |
| Signal Integrity | Maintains signal quality by reducing reflections | May introduce reflections affecting signal quality |
| Use Case | Ideal for isolating signal paths and termination | Used in signal routing and switching applications |
| Insertion Loss | Typically higher due to absorbing element | Generally lower as signals are reflected |
| Complexity | More complex with absorbing components | Simpler design based on reflection principles |
| Power Handling | Good, but limited by absorber capacity | High, suitable for strong signal reflection |
Introduction to Absorptive and Reflective Switches
Absorptive switches maintain a constant impedance by absorbing the signal when in the off state, preventing reflections and ensuring signal integrity in RF and microwave circuits. Reflective switches, in contrast, reflect the signal back when off, causing potential interference and standing waves in transmission lines. Your choice between absorptive and reflective switches directly impacts system performance, especially in applications requiring precise signal control and minimal loss.
What is an Absorptive Switch?
An absorptive switch is a type of RF switch designed to absorb the signal power when in the off state, minimizing reflections and preventing signal interference. It offers improved isolation and better impedance matching compared to reflective switches, which reflect the signal back to the source. Absorptive switches are commonly used in applications requiring low insertion loss and high isolation, such as in communication systems and test equipment.
What is a Reflective Switch?
A reflective switch directs an incoming signal back toward its source, reflecting energy instead of absorbing it, which contrasts with an absorptive switch that dissipates the signal as heat to prevent reflections. Reflective switches are commonly used in RF and microwave systems to test or isolate components by reflecting signals for measurement purposes. Your choice between these switches depends on whether signal reflection or absorption is more beneficial for accurate system performance.
Key Differences: Absorptive vs Reflective Switch
Absorptive switches maintain signal integrity by matching impedance and absorbing unwanted reflections, minimizing signal loss and distortion in high-frequency applications. Reflective switches, in contrast, reflect signals back toward the source when off, causing potential interference and signal degradation. Your choice between absorptive and reflective switches depends on the need for clean signal paths versus cost and design complexity.
Working Principles of Absorptive Switches
Absorptive switches operate by routing an input signal to an output while simultaneously dissipating power from the isolated port, ensuring minimal signal reflection and maintaining impedance matching. These switches use PIN diodes or FETs configured to absorb the signal energy when in the "off" state, preventing signal interference and improving isolation performance. The absorption mechanism enhances system linearity and reduces insertion loss compared to reflective switches, which reflect isolated signals back to the source.
Working Principles of Reflective Switches
Reflective switches operate by directing the incoming signal back towards the source or to a different port based on the control signal, utilizing changes in impedance or resonance within the switch's internal structure. These switches rely on materials or components that alter their reflective properties, such as ferrite or MEMS mirrors, to achieve fast and efficient signal routing without significant insertion loss. The working principle is grounded in wave interference and impedance mismatch, enabling precise control over signal reflection paths in RF and microwave systems.
Applications of Absorptive Switches
Absorptive switches are primarily used in RF and microwave communication systems for signal routing and isolation, providing minimal reflection and maintaining impedance matching to prevent interference. They are ideal in phased array antennas, radar systems, and test instrumentation where signal integrity and low insertion loss are critical. Their capability to absorb signals in the off state enhances overall system performance by reducing unwanted reflections and improving signal quality.
Applications of Reflective Switches
Reflective switches are extensively used in microwave and photonic circuits where precise signal routing and isolation are critical, including phased array antennas and optical communication systems. Their ability to reflect signals without absorption makes them ideal for applications requiring signal integrity and low insertion loss. These switches also enhance performance in radar systems and signal modulation by efficiently managing signal reflection paths.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Switch Type
When choosing between an absorptive switch and a reflective switch, consider factors such as insertion loss, isolation, and power handling capabilities because absorptive switches minimize signal reflections, making them ideal for sensitive RF applications. Reflective switches are typically preferred for high-power applications due to their simpler design and lower cost but may introduce signal reflections that affect system performance. Evaluate the application's sensitivity to VSWR, the required switching speed, and thermal management needs to determine the optimal switch type for reliable and efficient operation.
Future Trends in RF and Microwave Switching Technology
Future trends in RF and microwave switching technology emphasize increased integration of absorptive and reflective switches to enhance signal integrity and minimize loss in advanced communication systems. Absorptive switches are evolving with improved isolation and linearity, making them ideal for dynamic and adaptive applications, while reflective switches continue to provide cost-effective solutions for simpler architectures. Your choice will depend on the need for performance versus complexity as these technologies converge in next-generation 5G and beyond networks.
Absorptive switch vs reflective switch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com