RF attenuators reduce signal strength to prevent damage or interference, while RF isolators allow signal flow in one direction and block reflections to protect sensitive components. Discover how understanding these differences can optimize your RF system's performance by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
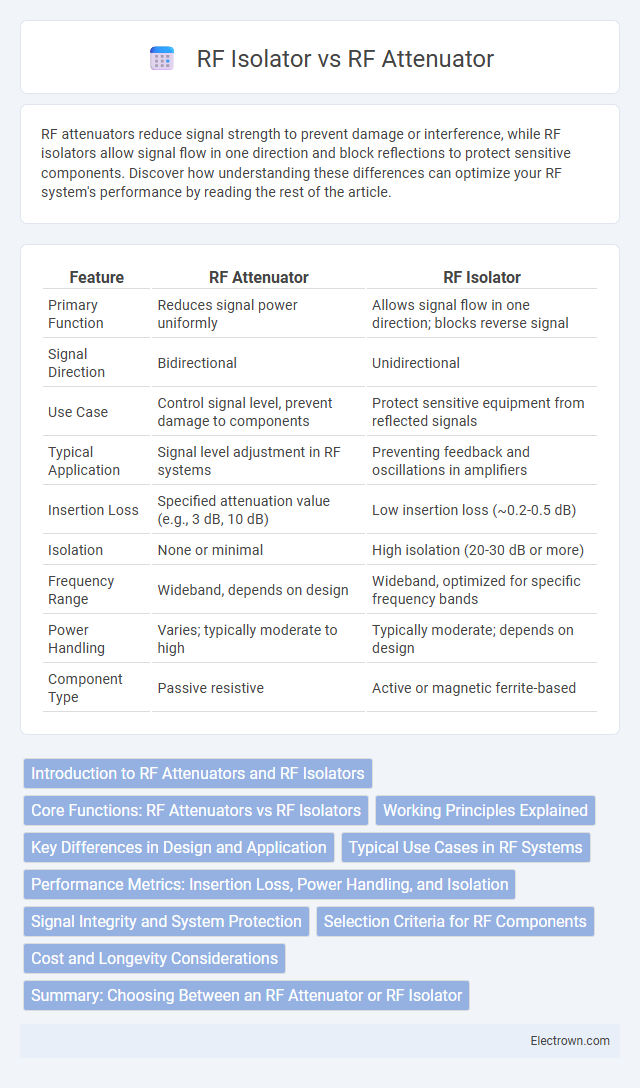
| Feature | RF Attenuator | RF Isolator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces signal power uniformly | Allows signal flow in one direction; blocks reverse signal |
| Signal Direction | Bidirectional | Unidirectional |
| Use Case | Control signal level, prevent damage to components | Protect sensitive equipment from reflected signals |
| Typical Application | Signal level adjustment in RF systems | Preventing feedback and oscillations in amplifiers |
| Insertion Loss | Specified attenuation value (e.g., 3 dB, 10 dB) | Low insertion loss (~0.2-0.5 dB) |
| Isolation | None or minimal | High isolation (20-30 dB or more) |
| Frequency Range | Wideband, depends on design | Wideband, optimized for specific frequency bands |
| Power Handling | Varies; typically moderate to high | Typically moderate; depends on design |
| Component Type | Passive resistive | Active or magnetic ferrite-based |
Introduction to RF Attenuators and RF Isolators
RF attenuators reduce signal power in a controlled manner by providing a fixed or variable loss, ensuring signal levels remain within optimal ranges for electronic components. RF isolators protect sensitive equipment by allowing signals to pass in one direction while absorbing reflections, preventing interference and damage from mismatched impedances. Both components are essential in radio frequency systems to maintain signal integrity and protect circuitry.
Core Functions: RF Attenuators vs RF Isolators
RF attenuators reduce signal strength by a specific amount, ensuring that your equipment operates within safe power levels and preventing signal overload. RF isolators, on the other hand, allow signals to pass in one direction while blocking reflected signals, protecting sensitive components from interference and potential damage. Understanding these core functions helps optimize your RF system for stability and performance by managing signal flow and power levels effectively.
Working Principles Explained
RF attenuators work by reducing signal power through dissipative elements like resistors, providing a controlled decrease in amplitude without altering the signal's frequency. RF isolators rely on non-reciprocal components such as ferrite materials and permanent magnets to allow signal transmission in one direction while blocking reflections, protecting sensitive equipment from interference. Both devices optimize signal integrity but serve different functions: attenuators control signal levels, whereas isolators prevent signal reflection and feedback.
Key Differences in Design and Application
RF attenuators reduce signal strength to prevent receiver overload and improve system linearity, typically offering a fixed or variable attenuation level with minimal signal distortion. RF isolators are designed to allow signal flow in one direction while blocking reflections or interference from the reverse path, protecting sensitive components like amplifiers. Your choice depends on whether you need controlled signal reduction or protection against reflected signals in your RF system.
Typical Use Cases in RF Systems
RF attenuators are commonly used to reduce signal power levels in RF systems to prevent receiver overloads or to match impedance between components, ensuring accurate measurements and protecting sensitive equipment. RF isolators serve to prevent reflected signals from returning to the source, improving stability and minimizing interference, especially in transmission chains involving amplifiers and antennas. Your choice depends on whether you need controlled signal attenuation or directional isolation to maintain signal integrity in your RF setup.
Performance Metrics: Insertion Loss, Power Handling, and Isolation
RF attenuators provide controlled insertion loss to reduce signal power uniformly, ensuring precise power handling without significantly affecting signal integrity. RF isolators offer high isolation by allowing signal flow in one direction while blocking reverse signals, crucial for protecting sensitive components from reflections and interference. Your choice between an attenuator or isolator depends on whether you prioritize consistent signal reduction or prevention of signal reflection in your RF system.
Signal Integrity and System Protection
An RF attenuator reduces signal power uniformly, maintaining signal integrity by preventing distortion and signal overload in sensitive components. An RF isolator provides unidirectional signal flow, protecting your system by preventing reflected signals from damaging the source or interfering with operation. Both devices enhance system protection but serve distinct roles: attenuators control signal levels, while isolators ensure stable and clean signal paths.
Selection Criteria for RF Components
Selection criteria for RF attenuators versus RF isolators center on signal control and system protection needs. RF attenuators are chosen for precise signal level reduction without distortion, ensuring consistent power across components, while RF isolators provide unidirectional signal flow to prevent reflected signals from causing interference or damage. Considerations include insertion loss, isolation value, power handling capacity, and frequency range to match system requirements and maintain signal integrity.
Cost and Longevity Considerations
RF attenuators generally offer a lower cost solution compared to RF isolators due to simpler construction and fewer components. Attenuators tend to have longer lifespans in high-power applications because they dissipate signal energy evenly, reducing stress on components. RF isolators, while more expensive, provide superior protection against signal reflections and system instability, which can extend overall system reliability despite potentially higher maintenance costs.
Summary: Choosing Between an RF Attenuator or RF Isolator
An RF attenuator reduces signal strength by a specified amount to prevent overload and improve system linearity, while an RF isolator protects sensitive components by allowing signal flow in only one direction, minimizing reflections and interference. Your choice depends on whether you need to control signal power levels or ensure signal integrity by blocking unwanted feedback. Selecting the right device optimizes overall RF system performance and reliability.
RF attenuator vs RF isolator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com