A frequency synthesizer generates a range of frequencies from a single reference frequency, while a PLL (Phase-Locked Loop) is used to lock the output frequency to a reference signal, ensuring stability and accuracy. Understanding the differences between these two technologies will help you optimize your RF design and signal processing; continue reading to explore their unique applications and advantages.
Table of Comparison
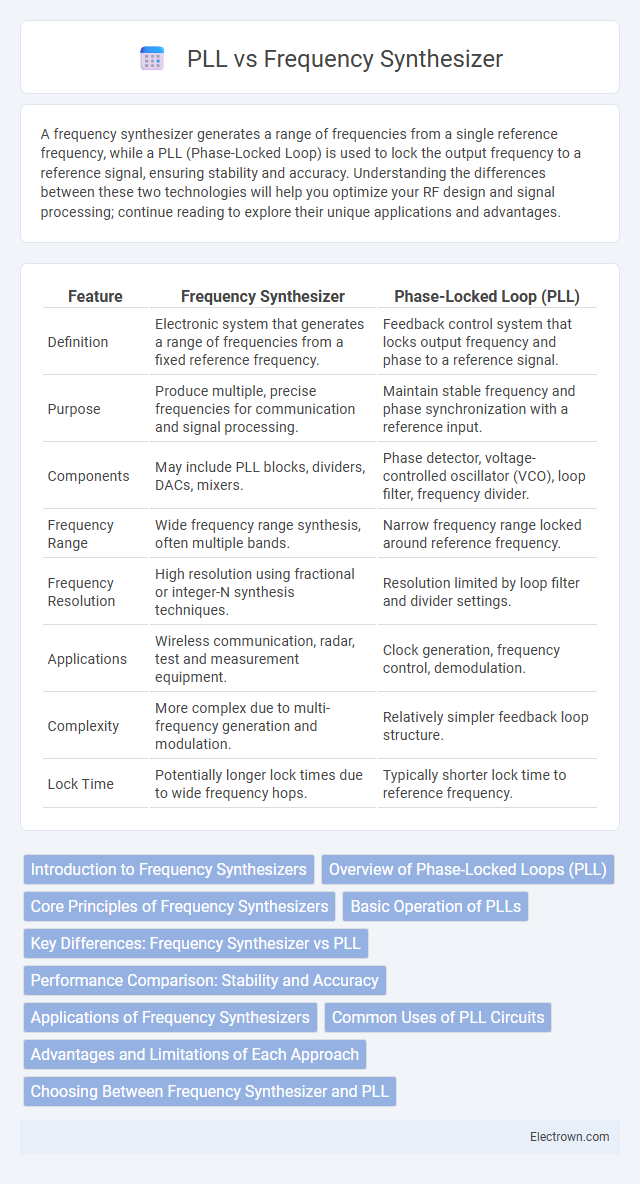
| Feature | Frequency Synthesizer | Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electronic system that generates a range of frequencies from a fixed reference frequency. | Feedback control system that locks output frequency and phase to a reference signal. |
| Purpose | Produce multiple, precise frequencies for communication and signal processing. | Maintain stable frequency and phase synchronization with a reference input. |
| Components | May include PLL blocks, dividers, DACs, mixers. | Phase detector, voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), loop filter, frequency divider. |
| Frequency Range | Wide frequency range synthesis, often multiple bands. | Narrow frequency range locked around reference frequency. |
| Frequency Resolution | High resolution using fractional or integer-N synthesis techniques. | Resolution limited by loop filter and divider settings. |
| Applications | Wireless communication, radar, test and measurement equipment. | Clock generation, frequency control, demodulation. |
| Complexity | More complex due to multi-frequency generation and modulation. | Relatively simpler feedback loop structure. |
| Lock Time | Potentially longer lock times due to wide frequency hops. | Typically shorter lock time to reference frequency. |
Introduction to Frequency Synthesizers
Frequency synthesizers generate precise output frequencies by combining multiple oscillators and dividers, enabling versatile signal generation across wide frequency ranges. Unlike basic Phase-Locked Loops (PLLs), frequency synthesizers often integrate PLLs within their architecture to achieve high stability and rapid frequency switching. They are essential in modern communication systems, radar, and signal processing applications where accurate frequency control is critical.
Overview of Phase-Locked Loops (PLL)
Phase-Locked Loops (PLLs) are essential components in frequency synthesis, enabling precise frequency control by locking the output signal phase to a reference frequency. The core elements include a phase detector, a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), and a loop filter, which work synchronously to minimize phase error and maintain frequency stability. PLLs provide fast frequency acquisition and low phase noise, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate frequency generation and modulation.
Core Principles of Frequency Synthesizers
Frequency synthesizers generate a range of frequencies from a single reference frequency using techniques like direct digital synthesis (DDS) or phase-locked loops (PLLs). Core principles involve a stable reference oscillator, a frequency divider, and a control mechanism to produce precise, adjustable output frequencies. PLL-based synthesizers lock the output phase to the reference signal, minimizing frequency drift and enabling high spectral purity.
Basic Operation of PLLs
A Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) operates by continuously adjusting the phase of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) to match the phase of a reference signal, effectively locking the output frequency to the desired value. The PLL consists of three main components: a phase detector, a low-pass filter, and a VCO, which work together to minimize the phase difference and stabilize the output frequency. Understanding the basic operation of PLLs is essential when comparing them to frequency synthesizers, as PLLs provide precise frequency control and stability through feedback mechanisms.
Key Differences: Frequency Synthesizer vs PLL
Frequency synthesizers generate multiple frequencies from a single reference frequency using techniques like direct digital synthesis or phase locking, while PLLs (Phase-Locked Loops) primarily maintain frequency stability by locking the output phase to a reference. Frequency synthesizers provide higher frequency resolution and flexibility compared to PLLs, which excel in maintaining signal coherence and reducing phase noise. Understanding these key differences helps you select the right solution for applications requiring either dynamic frequency generation or precise frequency control.
Performance Comparison: Stability and Accuracy
Frequency synthesizers offer superior frequency stability and accuracy by directly generating precise output frequencies through digital techniques, minimizing phase noise and jitter. PLLs rely on a feedback loop that adjusts a voltage-controlled oscillator, which can introduce more phase noise and slower response times, potentially reducing stability. Your choice depends on application needs, with frequency synthesizers favored for high-precision, low-noise environments and PLLs suitable for simpler, cost-effective frequency control.
Applications of Frequency Synthesizers
Frequency synthesizers are extensively used in wireless communication systems for generating precise and stable frequencies essential for signal modulation and demodulation. They are integral in instrumentation, radar systems, and radio transmitters where multiple frequency outputs are required. Unlike PLLs, frequency synthesizers offer greater frequency range and faster switching speeds, making them ideal for modern multi-band and multi-standard applications.
Common Uses of PLL Circuits
PLL circuits are commonly used in frequency synthesizers for generating stable and precise frequencies in communication systems, radio transmitters, and signal processing. They enable frequency modulation, demodulation, and clock recovery, making them essential in wireless devices, GPS modules, and microprocessors. Your electronic designs benefit from PLL circuits by improving signal integrity and minimizing phase noise in complex frequency synthesis tasks.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
Frequency synthesizers offer precise frequency generation with high stability and low phase noise, making them ideal for communication systems requiring multiple frequencies. Phase-Locked Loops (PLLs) provide fast frequency locking and simpler design, but may suffer from higher phase noise and limited frequency resolution. Your choice depends on the application's need for frequency accuracy versus speed and complexity constraints.
Choosing Between Frequency Synthesizer and PLL
Choosing between a frequency synthesizer and a phase-locked loop (PLL) depends on your specific application requirements such as frequency stability, output signal purity, and tuning speed. Frequency synthesizers offer greater flexibility and accuracy for generating a wide range of frequencies, while PLLs provide simplicity and low phase noise for stable frequency generation. Your decision should consider factors like system complexity, cost, and the required frequency resolution to achieve optimal performance.
Frequency Synthesizer vs PLL Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com