Log detectors measure signal amplitude on a logarithmic scale, providing a wide dynamic range ideal for analyzing signals with large variations, while RMS detectors calculate the root mean square value to accurately represent the signal's true power, essential for assessing average signal strength. Explore the rest of the article to understand which detector suits your specific application and how their differences impact signal measurement accuracy.
Table of Comparison
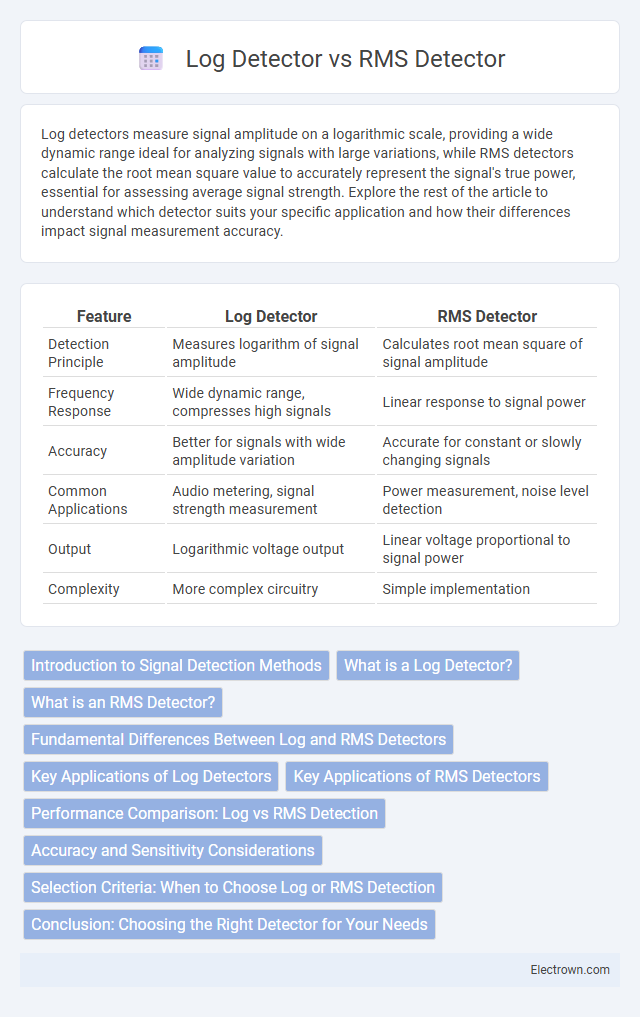
| Feature | Log Detector | RMS Detector |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Principle | Measures logarithm of signal amplitude | Calculates root mean square of signal amplitude |
| Frequency Response | Wide dynamic range, compresses high signals | Linear response to signal power |
| Accuracy | Better for signals with wide amplitude variation | Accurate for constant or slowly changing signals |
| Common Applications | Audio metering, signal strength measurement | Power measurement, noise level detection |
| Output | Logarithmic voltage output | Linear voltage proportional to signal power |
| Complexity | More complex circuitry | Simple implementation |
Introduction to Signal Detection Methods
Log detectors convert signal amplitude to a logarithmic scale, enabling efficient handling of wide dynamic ranges in communication systems. RMS detectors calculate the root mean square value, providing accurate power measurement in varying signal conditions. Your choice between these methods depends on the signal type and the precision required for measurement and analysis.
What is a Log Detector?
A Log Detector is a type of signal detector that measures the logarithm of the input signal's amplitude, providing a wide dynamic range and improved sensitivity for varying signal strengths. It converts input signals into a logarithmic scale, making it especially useful in applications like RF measurements and audio signal processing where large variations in amplitude occur. Unlike an RMS detector, which calculates the root mean square value representing the effective power of a signal, the Log Detector offers a more linear response to changes in signal level over a broad range.
What is an RMS Detector?
An RMS detector measures the root mean square value of a signal, providing an accurate representation of its power by calculating the square root of the average of the squared input values. This makes RMS detectors ideal for audio signal processing and power measurement, as they capture both the amplitude and energy content of complex waveforms. Your choice between a log detector and an RMS detector depends on whether you need precise power measurement (RMS) or rapid amplitude approximation (log).
Fundamental Differences Between Log and RMS Detectors
Log detectors and RMS detectors differ fundamentally in their signal processing approaches, with log detectors converting input signals to a logarithmic scale to measure signal power over a wide dynamic range, while RMS detectors calculate the root mean square of the signal amplitude to accurately represent its effective power. The logarithmic transformation in log detectors enables better handling of signals with large amplitude variations, making them suitable for applications requiring wide dynamic range measurements. Your choice between these detectors depends on the required precision in power measurement and the nature of the input signal's amplitude characteristics.
Key Applications of Log Detectors
Log detectors are commonly used in RF and microwave communication systems to measure signal power over a wide dynamic range, making them ideal for applications like signal strength monitoring, automatic gain control, and spectrum analysis. They excel in scenarios requiring accurate power detection of varying signal amplitudes, enabling precise control in transmitters and receivers. Your measurement setup benefits from the log detector's fast response and logarithmic compression, which simplifies power calculations compared to RMS detectors.
Key Applications of RMS Detectors
RMS detectors are crucial in audio engineering for accurately measuring the effective power of signals, ensuring consistent sound levels in both recording and playback environments. They are widely used in telecommunications to monitor signal strength without distortion, improving the clarity and reliability of communication channels. Your audio processing systems benefit from RMS detectors by providing precise level control, essential for dynamic range management and noise reduction applications.
Performance Comparison: Log vs RMS Detection
Log detectors excel in measuring signals with wide dynamic ranges due to their logarithmic response, making them ideal for applications requiring precise amplitude tracking of weak and strong signals. RMS detectors provide accurate true power measurements by calculating the root mean square value, ensuring reliable performance in systems where power estimation and noise immunity are critical. Your choice between log and RMS detection impacts measurement accuracy and signal fidelity depending on whether amplitude dynamic range or true power representation is more important.
Accuracy and Sensitivity Considerations
Log detectors provide higher sensitivity for low-level signals, making them ideal for applications requiring precise detection of weak signals, while RMS detectors excel in accuracy for measuring the actual signal power regardless of waveform shape. RMS detectors deliver consistent accuracy over a wide dynamic range by averaging the square of the signal, which is essential for signals with varying amplitude and complex modulation types. Sensitivity trade-offs favor log detectors for rapid detection of small signal variations, whereas RMS detectors prioritize accurate representation of true power in environments with fluctuating signal strengths.
Selection Criteria: When to Choose Log or RMS Detection
Select a log detector when signal amplitude spans several orders of magnitude or when rapid changes in signal strength require precise, wide dynamic range measurement. Choose an RMS detector for accurate representation of energy content in varying signal waveforms, especially in audio, RF, or power measurement applications where consistent output relative to signal power is critical. Your choice depends on the specific needs for dynamic range, accuracy, and the nature of the measured signal.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Detector for Your Needs
Log detectors excel at measuring signals over a wide dynamic range, making them ideal for applications like spectrum analyzers and RF power monitoring where accurate detection of both low and high signal levels is critical. RMS detectors provide precise measurements of the actual power content in complex waveforms, which is essential for audio signal processing and communications equipment requiring true power assessment. Selecting between a log detector and an RMS detector depends on whether the priority is dynamic range handling or accurate power representation of varying waveforms.
Log detector vs RMS detector Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com