Noise floor represents the baseline level of background noise in a system, while sensitivity measures the minimum signal strength a device can detect above that noise. Understanding these key differences helps you optimize audio or communication equipment performance; read on to explore their impact in detail.
Table of Comparison
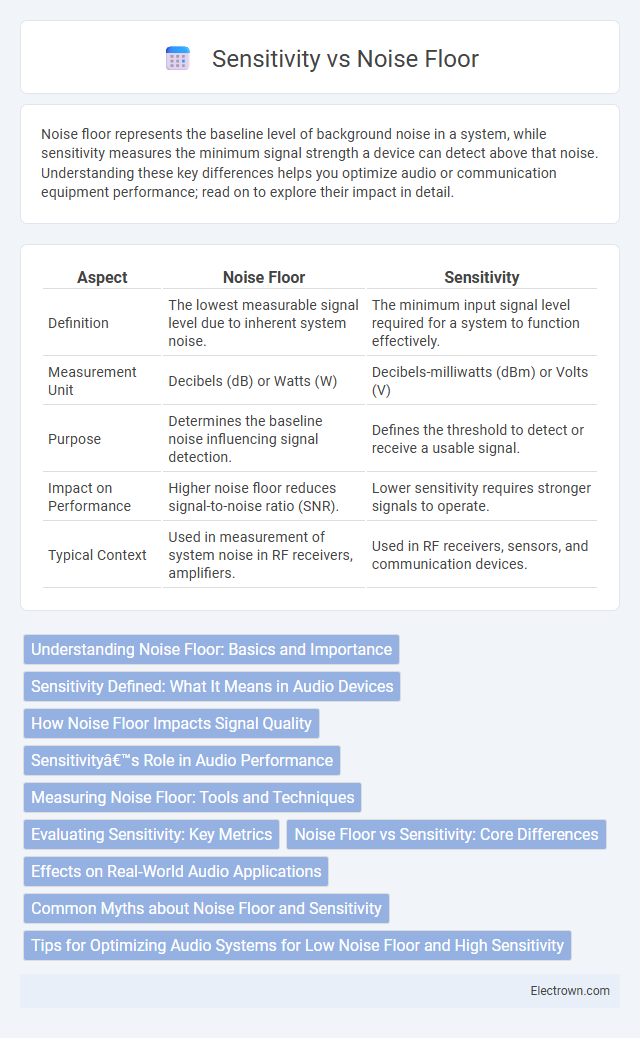
| Aspect | Noise Floor | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The lowest measurable signal level due to inherent system noise. | The minimum input signal level required for a system to function effectively. |
| Measurement Unit | Decibels (dB) or Watts (W) | Decibels-milliwatts (dBm) or Volts (V) |
| Purpose | Determines the baseline noise influencing signal detection. | Defines the threshold to detect or receive a usable signal. |
| Impact on Performance | Higher noise floor reduces signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). | Lower sensitivity requires stronger signals to operate. |
| Typical Context | Used in measurement of system noise in RF receivers, amplifiers. | Used in RF receivers, sensors, and communication devices. |
Understanding Noise Floor: Basics and Importance
The noise floor represents the level of background noise inherent in a system, setting the baseline limit for detecting signals. Understanding the noise floor is crucial because it determines the minimum signal strength that can be distinguished from noise, directly impacting device sensitivity. Lowering the noise floor enhances sensitivity, enabling better performance in communication systems, sensors, and audio equipment.
Sensitivity Defined: What It Means in Audio Devices
Sensitivity in audio devices refers to the minimum input signal level required for the device to produce a specified output level, directly impacting its ability to detect faint sounds. It is measured in decibels (dB) and indicates how efficiently an audio device converts input signals into output signals. A higher sensitivity rating means the device can capture quieter sounds, making it crucial for microphones, headphones, and other audio equipment used in detailed sound recording or playback.
How Noise Floor Impacts Signal Quality
The noise floor sets the baseline level of unwanted electrical signals in a system, directly affecting the detectability of weak signals and overall signal quality. A higher noise floor reduces the dynamic range, causing potential signal distortion and loss of critical information in communication and audio devices. Minimizing the noise floor enhances sensitivity, allowing systems to distinguish and accurately process low-level signals amidst background noise.
Sensitivity’s Role in Audio Performance
Sensitivity in audio performance determines how effectively a microphone or speaker converts sound into electrical signals or vice versa, directly impacting clarity and detail in the output. A higher sensitivity allows for capturing softer sounds with greater precision, enhancing the audio experience in both recording and playback environments. Balancing sensitivity with an appropriate noise floor ensures optimal sound quality by minimizing unwanted background noise while preserving signal fidelity.
Measuring Noise Floor: Tools and Techniques
Measuring noise floor involves using spectrum analyzers and sound level meters to accurately detect the base level of background noise in electronic systems or acoustic environments. Techniques such as averaging multiple measurements and utilizing signal analyzers with high dynamic range improve the precision of noise floor assessment. Ensuring your measurement tools have low internal noise and proper calibration is essential for reliable sensitivity analysis.
Evaluating Sensitivity: Key Metrics
Evaluating sensitivity involves measuring the minimum signal level a device can reliably detect above its noise floor, expressed in decibels (dB). Key metrics include the noise figure (NF), which quantifies the degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio, and the minimum detectable signal (MDS), representing the lowest power level discernible without error. Precise sensitivity assessment requires analyzing these parameters in conjunction with the system's noise floor to ensure optimal performance in communication receivers.
Noise Floor vs Sensitivity: Core Differences
Noise floor represents the minimum level of background noise present in a system, while sensitivity measures the lowest signal strength that a device can detect above this noise. The core difference lies in noise floor being an inherent environmental or electronic limitation, whereas sensitivity reflects the device's capability to discern signals despite this noise. Understanding these concepts is crucial for optimizing signal detection and improving overall system performance in communication and audio equipment.
Effects on Real-World Audio Applications
A low noise floor enhances audio sensitivity by allowing devices to detect quieter signals without distortion, crucial in real-world applications like live performances and studio recordings. High sensitivity combined with a minimal noise floor improves the clarity and detail of captured sound, reducing unwanted background noise and enabling superior dynamic range. This balance ensures audio equipment delivers accurate sound reproduction, essential for critical listening environments and professional audio production.
Common Myths about Noise Floor and Sensitivity
Noise floor and sensitivity are often misunderstood, with common myths claiming higher sensitivity always means better performance and that a lower noise floor guarantees clearer signals. In reality, sensitivity indicates the minimum signal strength your device can detect, while noise floor represents the background interference level affecting signal clarity. Understanding the distinction helps you optimize device settings for accurate signal reception without being misled by these oversimplifications.
Tips for Optimizing Audio Systems for Low Noise Floor and High Sensitivity
Maintain a low noise floor by using high-quality microphones with proper impedance matching and positioning them away from electronic interference sources. Enhance sensitivity by selecting components designed for high dynamic range and ensuring clean power supply to minimize signal degradation. You can optimize your audio system further by employing shielded cables and keeping gain levels balanced to prevent distortion while preserving clarity.
Noise Floor vs Sensitivity Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com