A constant current diode regulates current to a fixed value regardless of voltage changes, making it ideal for protecting circuits from current fluctuations, while a Zener diode primarily maintains a stable reference voltage by operating in reverse breakdown mode. Discover how understanding the differences between these components can enhance your circuit design by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
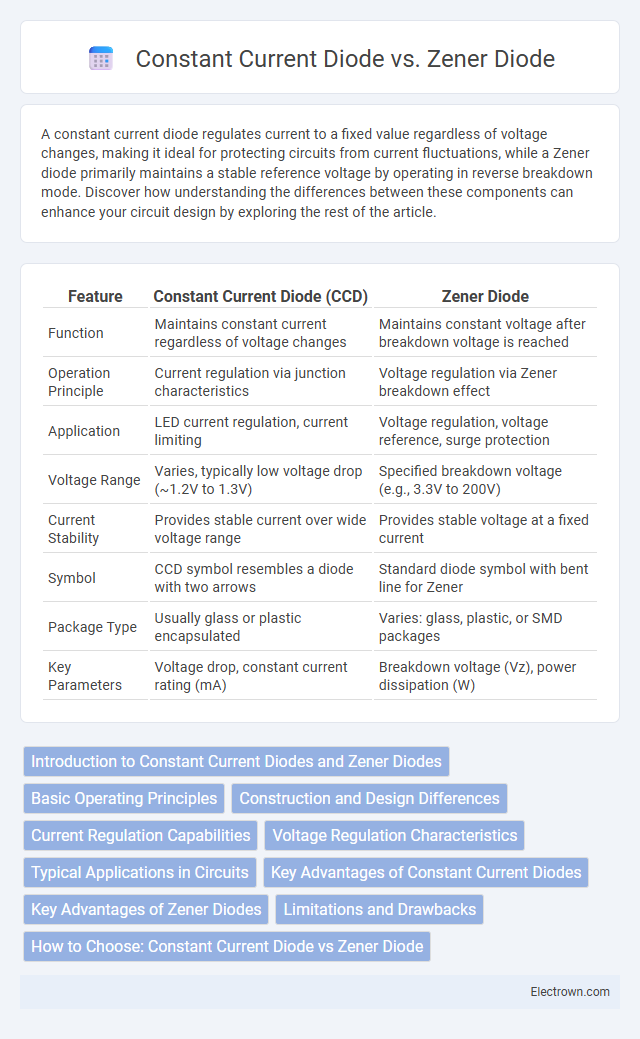
| Feature | Constant Current Diode (CCD) | Zener Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Maintains constant current regardless of voltage changes | Maintains constant voltage after breakdown voltage is reached |
| Operation Principle | Current regulation via junction characteristics | Voltage regulation via Zener breakdown effect |
| Application | LED current regulation, current limiting | Voltage regulation, voltage reference, surge protection |
| Voltage Range | Varies, typically low voltage drop (~1.2V to 1.3V) | Specified breakdown voltage (e.g., 3.3V to 200V) |
| Current Stability | Provides stable current over wide voltage range | Provides stable voltage at a fixed current |
| Symbol | CCD symbol resembles a diode with two arrows | Standard diode symbol with bent line for Zener |
| Package Type | Usually glass or plastic encapsulated | Varies: glass, plastic, or SMD packages |
| Key Parameters | Voltage drop, constant current rating (mA) | Breakdown voltage (Vz), power dissipation (W) |
Introduction to Constant Current Diodes and Zener Diodes
Constant current diodes regulate current flow to maintain a stable current regardless of voltage changes, making them ideal for LED driving and battery charging applications. Zener diodes provide voltage regulation by maintaining a fixed voltage across their terminals when reverse biased, commonly used in voltage reference and protection circuits. Understanding your circuit requirements helps determine whether a constant current diode or a Zener diode is the optimal choice for regulation purposes.
Basic Operating Principles
Constant current diodes regulate current by maintaining a steady current flow regardless of voltage changes, utilizing a semiconductor junction to achieve this stable current. Zener diodes operate by allowing current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific breakdown voltage is reached, providing voltage regulation through a controlled breakdown mechanism. Both devices serve distinct purposes in electronic circuits, with constant current diodes designed for current stabilization and Zener diodes for voltage reference and protection.
Construction and Design Differences
Constant current diodes are constructed with a junction transistor and a resistor to maintain a stable current flow, while Zener diodes incorporate a heavily doped p-n junction designed to regulate voltage via the Zener breakdown effect. The constant current diode's design emphasizes current stabilization regardless of voltage changes, making it ideal for current-sensitive applications. Your choice depends on whether current regulation or voltage regulation is the primary requirement in your circuit.
Current Regulation Capabilities
Constant current diodes maintain a fixed current flow regardless of voltage changes, providing precise current regulation ideal for LED circuits and battery charging. Zener diodes regulate voltage by maintaining a stable reverse breakdown voltage but allow current to vary within limits, making them less effective for constant current applications. For strict current control, constant current diodes outperform Zener diodes due to their inherent current stabilization characteristics.
Voltage Regulation Characteristics
Constant current diodes maintain a stable current flow irrespective of voltage fluctuations, providing linear voltage regulation suited for current stabilization applications. Zener diodes regulate voltage by operating in reverse breakdown region, maintaining a fixed voltage level despite changes in load current, ideal for voltage reference and protection circuits. While Zener diodes offer precise voltage clamping, constant current diodes deliver consistent current regulation, each serving distinct roles in electronic voltage management.
Typical Applications in Circuits
Constant current diodes are commonly utilized in LED driving circuits and battery charging systems to maintain a steady current despite voltage variations, ensuring reliable performance and protecting components. Zener diodes are predominantly used in voltage regulation and overvoltage protection circuits, stabilizing voltage levels by operating in their breakdown region. Both diodes enhance circuit stability but serve distinct purposes--constant current diodes regulate current flow while Zener diodes maintain constant voltage.
Key Advantages of Constant Current Diodes
Constant current diodes provide stable current regulation regardless of voltage variations, ensuring reliable performance in LED circuits and battery chargers. They feature inherent overcurrent protection and simplified circuit design, eliminating the need for complex feedback loops found in Zener diode voltage regulation. Their compact size and lower power dissipation enhance energy efficiency and thermal management compared to conventional Zener diode applications.
Key Advantages of Zener Diodes
Zener diodes provide precise voltage regulation by maintaining a stable reverse breakdown voltage, which protects circuits from voltage spikes and fluctuations. Their ability to operate reliably in reverse bias makes them ideal for reference voltage applications and surge protection in electronic devices. You can benefit from their low cost and simplicity when designing power supplies and voltage stabilization circuits.
Limitations and Drawbacks
Constant current diodes have limitations such as a fixed current value that cannot be adjusted and a restricted operating voltage range, which may not suit applications requiring precise current control across varying voltages. Zener diodes exhibit drawbacks including power dissipation issues at higher currents and limited voltage regulation accuracy under fluctuating load conditions. Understanding these constraints helps you select the appropriate diode for voltage stabilization or current regulation tasks.
How to Choose: Constant Current Diode vs Zener Diode
Choosing between a constant current diode and a Zener diode depends on your circuit's requirements for voltage regulation and current control. A constant current diode is ideal when maintaining a steady current regardless of voltage fluctuations is critical, commonly used in LED circuits and battery charging applications. Your selection favors a Zener diode when voltage stabilization at a specific value is necessary, especially in voltage reference and protection circuits.
Constant current diode vs Zener diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com