A monostable multivibrator generates a single output pulse when triggered, ideal for timing applications requiring a precise pulse, while an astable multivibrator continuously oscillates between two states, producing a square wave without any external trigger. Discover how your choice between these circuits impacts your electronic project by exploring the full comparison below.
Table of Comparison
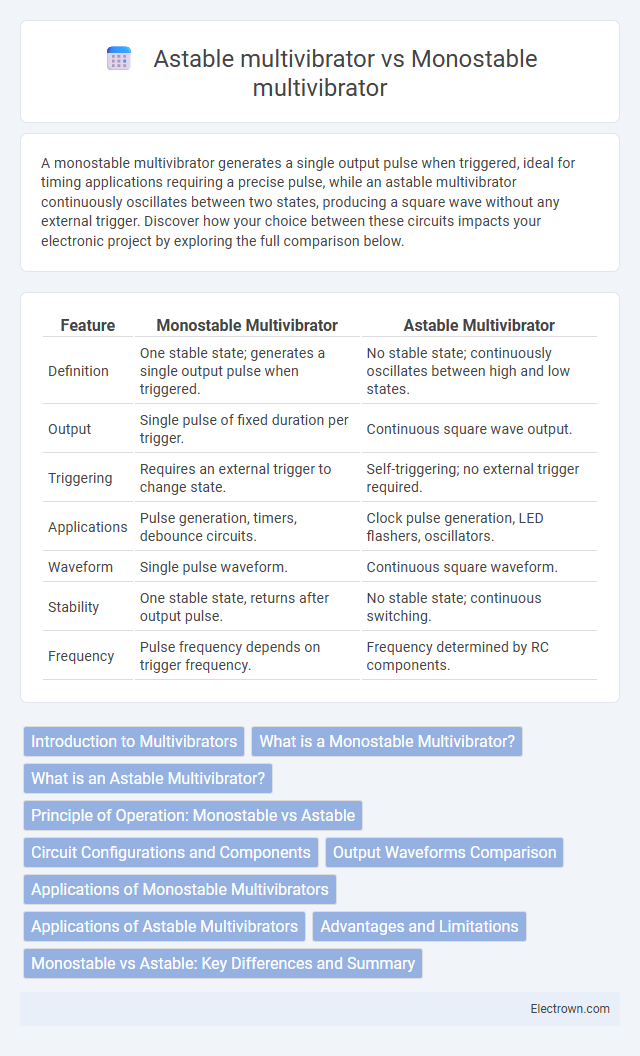
| Feature | Monostable Multivibrator | Astable Multivibrator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One stable state; generates a single output pulse when triggered. | No stable state; continuously oscillates between high and low states. |
| Output | Single pulse of fixed duration per trigger. | Continuous square wave output. |
| Triggering | Requires an external trigger to change state. | Self-triggering; no external trigger required. |
| Applications | Pulse generation, timers, debounce circuits. | Clock pulse generation, LED flashers, oscillators. |
| Waveform | Single pulse waveform. | Continuous square waveform. |
| Stability | One stable state, returns after output pulse. | No stable state; continuous switching. |
| Frequency | Pulse frequency depends on trigger frequency. | Frequency determined by RC components. |
Introduction to Multivibrators
Multivibrators are fundamental electronic circuits used to generate square, pulse, or timing waveforms. Monostable multivibrators produce a single stable output pulse in response to an input trigger, ideal for one-shot timer applications, while astable multivibrators continuously oscillate between two unstable states, generating a free-running square wave without external input. Your choice between these depends on whether you need a single timed output or continuous oscillation for tasks like clock generation or pulse modulation.
What is a Monostable Multivibrator?
A Monostable Multivibrator is an electronic circuit that generates a single output pulse of a specific duration in response to an external trigger signal, making it a one-shot pulse generator. It has one stable state and one quasi-stable state, returning to the stable state after the pulse duration elapses. Common applications include timer circuits, pulse width modulation, and switch debouncing.
What is an Astable Multivibrator?
An astable multivibrator is an electronic oscillator circuit that continuously switches between its two unstable states, generating a square wave without requiring any external trigger input. It is widely used for clock pulses, timing signals, and waveform generation in applications such as timers, blinkers, and pulse width modulation. Unlike a monostable multivibrator, which has one stable state and produces a single output pulse when triggered, the astable multivibrator produces a free-running oscillation.
Principle of Operation: Monostable vs Astable
A monostable multivibrator generates a single output pulse of fixed duration in response to an input trigger, returning to its stable state afterward. An astable multivibrator continuously oscillates between two states without requiring an external trigger, producing a square wave output. The monostable relies on a timing component like a resistor-capacitor (RC) network to define pulse width, while the astable uses feedback and RC timing to sustain free-running oscillations.
Circuit Configurations and Components
Monostable multivibrators feature one stable state and utilize components such as a resistor, capacitor, and a single transistor or IC to generate a single output pulse upon triggering. Astable multivibrators lack a stable state, relying on two transistors or ICs paired with resistors and capacitors to produce a continuous square wave oscillation. The primary difference in circuit configurations is that monostable circuits include a trigger input for pulse initiation, whereas astable circuits operate autonomously without external triggering.
Output Waveforms Comparison
Monostable multivibrators generate a single pulse of fixed duration in response to a triggering input, producing a single output waveform per trigger event. Astable multivibrators continuously oscillate between high and low states, generating a square wave output without any external trigger. The monostable output is a one-time pulse, while the astable output is a repetitive waveform with a frequency determined by circuit components such as resistors and capacitors.
Applications of Monostable Multivibrators
Monostable multivibrators serve as reliable pulse generators in timing circuits, enabling precise control of pulse duration in applications like timers, pulse-width modulation, and switch debouncing. These circuits are essential in triggering devices where a single output pulse is required in response to an input signal, such as in digital logic and communication systems. Your projects benefit from monostable multivibrators by ensuring stable, timed responses critical for accurate event detection and signal processing.
Applications of Astable Multivibrators
Astable multivibrators, known for generating continuous square wave oscillations without external triggering, are widely used in clock pulse generation for digital circuits. Your projects can benefit from their applications in LED flashers, tone generators, and pulse-width modulation (PWM) controllers, where stable, repetitive timing signals are crucial. Unlike monostable multivibrators, which produce a single output pulse when triggered, astable multivibrators provide continuous output, making them ideal for clock and timing-related applications.
Advantages and Limitations
Monostable multivibrators offer precise single pulse generation with stable pulse width, ideal for timing applications, but are limited by their inability to produce continuous waveforms. Astable multivibrators generate continuous square waves without external triggering, making them suitable for clock pulses and oscillators, but their frequency stability depends heavily on component tolerances. Both types face challenges in accuracy and stability when operating under variable temperature or power supply conditions, impacting their performance in high-precision circuits.
Monostable vs Astable: Key Differences and Summary
Monostable multivibrators generate a single output pulse of fixed duration in response to an input trigger, making them ideal for timer and pulse generation applications. Astable multivibrators continuously oscillate between high and low output states without an external trigger, functioning as free-running oscillators or clock pulse generators. Your choice depends on whether you need a one-shot pulse (monostable) or a continuous square wave signal (astable).
Monostable multivibrator vs astable multivibrator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com