Decibel and neper are both logarithmic units used to express ratios of physical quantities, commonly in acoustics and electronics, with decibel relying on a base-10 logarithm while neper uses the natural logarithm. Understanding the difference between decibel and neper can enhance Your grasp of signal measurements and conversions--explore the full article to deepen your insight.
Table of Comparison
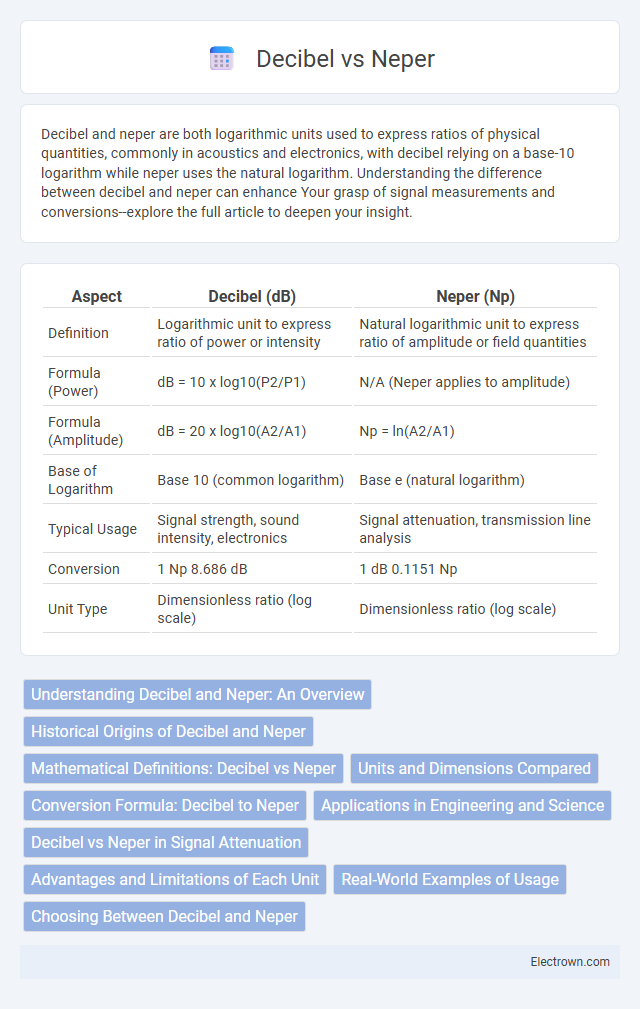
| Aspect | Decibel (dB) | Neper (Np) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Logarithmic unit to express ratio of power or intensity | Natural logarithmic unit to express ratio of amplitude or field quantities |
| Formula (Power) | dB = 10 x log10(P2/P1) | N/A (Neper applies to amplitude) |
| Formula (Amplitude) | dB = 20 x log10(A2/A1) | Np = ln(A2/A1) |
| Base of Logarithm | Base 10 (common logarithm) | Base e (natural logarithm) |
| Typical Usage | Signal strength, sound intensity, electronics | Signal attenuation, transmission line analysis |
| Conversion | 1 Np 8.686 dB | 1 dB 0.1151 Np |
| Unit Type | Dimensionless ratio (log scale) | Dimensionless ratio (log scale) |
Understanding Decibel and Neper: An Overview
Decibel (dB) and Neper (Np) are logarithmic units used to express ratios, commonly in signal processing and acoustics. Decibels quantify power or intensity ratios based on a logarithm of base 10, while Nepers measure amplitude ratios using natural logarithms. Understanding these units helps you accurately interpret signal attenuation or gain in various technical applications.
Historical Origins of Decibel and Neper
The decibel originated from Bell Telephone Laboratories in the early 20th century as a logarithmic unit to measure signal loss and gain in telecommunication systems, reflecting its close association with sound intensity and power ratios. The neper, named after John Napier, the inventor of logarithms, emerged independently as a natural logarithmic unit to quantify ratios of amplitude in fields like acoustics and electrical engineering. Your understanding of these units enhances accurate measurement and comparison of signal strengths across diverse technical applications.
Mathematical Definitions: Decibel vs Neper
The decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit expressing the ratio of two power quantities, defined as 10 times the base-10 logarithm of their ratio, commonly used in acoustics and electronics. The neper (Np) measures ratios using the natural logarithm, calculated as the natural logarithm of the amplitude ratio, making it particularly suitable for wave propagation and signal attenuation analyses. Your choice between decibel and neper depends on the application's mathematical convenience and the logarithmic base preferred for measuring signal magnitudes.
Units and Dimensions Compared
Decibel (dB) and neper (Np) are logarithmic units used to express ratios of power and amplitude, respectively, with decibels relating to power ratios and nepers to amplitude ratios based on natural logarithms. The decibel is dimensionless but traditionally linked to base-10 logarithms, defined as 10 times the log base 10 of a power ratio or 20 times for amplitude, while the neper is dimensionless and calculated as the natural logarithm (ln) of the amplitude ratio. Conversion between the two involves a constant factor, with 1 neper approximately equal to 8.686 decibels, reflecting their different mathematical bases and usage contexts in fields like acoustics and signal processing.
Conversion Formula: Decibel to Neper
The conversion formula from decibel (dB) to neper (Np) is Np = (dB / 20) x ln(10), where ln(10) 2.3026 represents the natural logarithm of 10. This formula allows precise transformation between logarithmic units commonly used in acoustics and signal processing. Understanding this conversion is essential for interpreting attenuation and gain measurements across different scientific and engineering applications.
Applications in Engineering and Science
Decibels (dB) and nepers (Np) are widely used in engineering and science for measuring signal attenuation and gain in fields such as acoustics, telecommunications, and control systems. Decibels, based on a logarithmic scale with a 10th-power reference, are favored for their simplicity in expressing ratios of power or intensity, while nepers use natural logarithms, offering direct proportionality to amplitude ratios. The choice between dB and Np depends on the specific application requirements, with dB preferred in audio and electronic signal analysis and nepers used in wave propagation and transmission line theory where mathematical convenience is crucial.
Decibel vs Neper in Signal Attenuation
Decibel (dB) and Neper (Np) are logarithmic units used to measure signal attenuation, with decibel expressing the ratio of power or intensity on a base-10 logarithmic scale while Neper uses a natural logarithm scale based on amplitude ratios. In signal processing, attenuation expressed in decibels is calculated as 10 times the logarithm of the power ratio, whereas in nepers it is the natural logarithm of the amplitude ratio, reflecting different but related measurement perspectives. Conversions between the two involve the factor 1 Np 8.686 dB, allowing engineers to switch between units depending on whether the analysis focuses on power or amplitude in communication systems.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Unit
Decibels provide a logarithmic measure favored for its ability to express ratios in a scale that aligns with human perception, making it ideal for audio and signal processing where relative differences matter. Nepers offer a natural mathematical unit derived from the natural logarithm, providing direct linear relation to attenuation or gain, which simplifies certain theoretical analyses in fields like telecommunications and acoustics. While decibels excel in practical measurement and industry standards, they can be less intuitive in pure mathematical formulations where nepers provide clarity, though nepers are less commonly used and understood outside specialized contexts.
Real-World Examples of Usage
Decibel (dB) is commonly used in audio engineering to measure sound intensity, such as in speaker output levels or hearing protection standards, where precise quantification of loudness is crucial. Neper (Np) is often applied in telecommunications and signal processing to express ratios of amplitude or voltage, like in the evaluation of signal attenuation over fiber optic cables or transmission lines. Understanding the practical contexts where your measurements occur helps determine whether decibel or neper provides more intuitive or standardized results.
Choosing Between Decibel and Neper
Choosing between decibel and neper depends on the context of signal measurement and conversion accuracy. Decibels, based on a logarithmic scale with a reference power ratio, are widely used in audio engineering, telecommunications, and acoustics for their intuitive representation of relative power levels. Nepers use a natural logarithm scale, favored in theoretical analysis and signal attenuation calculations due to their direct relation to exponential decay, making them ideal for precise mathematical modeling in physics and engineering.
decibel vs neper Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com