Filter capacitors smooth out voltage fluctuations in power supplies by reducing ripple voltage, while bypass capacitors stabilize voltage levels by shunting high-frequency noise to ground. Understanding the distinct roles of these capacitors can significantly improve your circuit's performance; explore the article for a deeper insight.
Table of Comparison
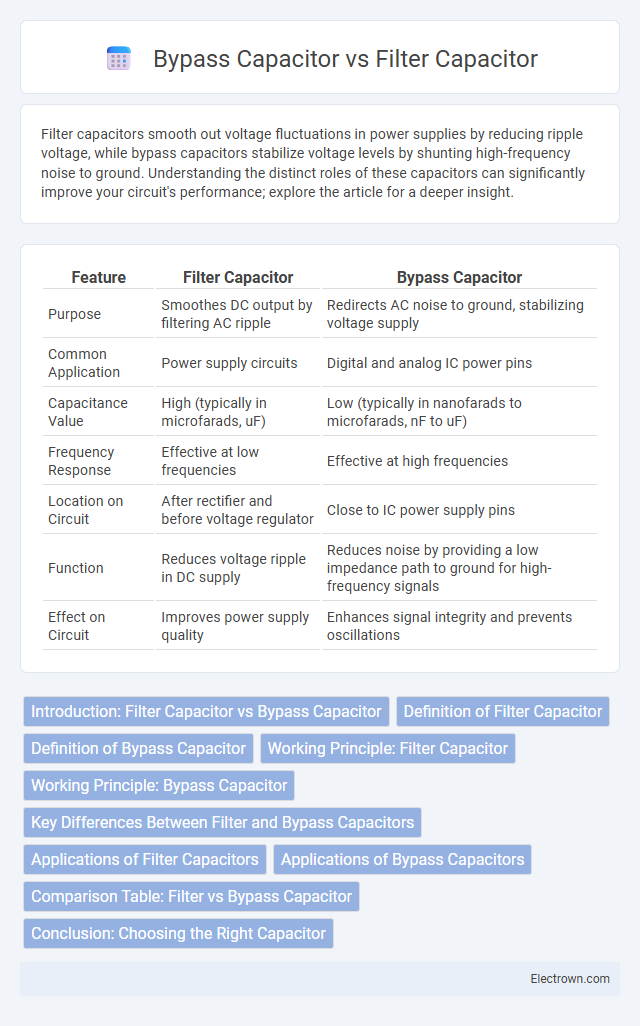
| Feature | Filter Capacitor | Bypass Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Smoothes DC output by filtering AC ripple | Redirects AC noise to ground, stabilizing voltage supply |
| Common Application | Power supply circuits | Digital and analog IC power pins |
| Capacitance Value | High (typically in microfarads, uF) | Low (typically in nanofarads to microfarads, nF to uF) |
| Frequency Response | Effective at low frequencies | Effective at high frequencies |
| Location on Circuit | After rectifier and before voltage regulator | Close to IC power supply pins |
| Function | Reduces voltage ripple in DC supply | Reduces noise by providing a low impedance path to ground for high-frequency signals |
| Effect on Circuit | Improves power supply quality | Enhances signal integrity and prevents oscillations |
Introduction: Filter Capacitor vs Bypass Capacitor
Filter capacitors smooth rectified AC voltage by reducing ripples in power supplies, ensuring stable DC output for electronic circuits. Bypass capacitors, placed close to active components, shunt high-frequency noise to ground, enhancing signal integrity and reducing electromagnetic interference. Understanding the distinct roles of filter capacitors and bypass capacitors optimizes your circuit's performance and reliability.
Definition of Filter Capacitor
A filter capacitor is an electronic component designed to smooth the output of power supplies by reducing voltage ripple and noise in DC signals. Unlike bypass capacitors that primarily shunt high-frequency noise to ground, filter capacitors store and release electrical energy to stabilize voltage levels. Your circuits rely on filter capacitors to maintain consistent power delivery and enhance overall performance.
Definition of Bypass Capacitor
A bypass capacitor is a small-value capacitor connected in parallel with a power supply pin of an active device to filter out high-frequency noise and provide a stable voltage supply. Unlike filter capacitors, which smooth out low-frequency ripple in power supplies, bypass capacitors target high-frequency noise reduction by shunting AC signals to ground. Your circuit's stability and signal integrity depend on the proper use of bypass capacitors to maintain clean power rails.
Working Principle: Filter Capacitor
A filter capacitor smooths the output of rectified AC voltage by storing and releasing electrical energy, effectively reducing voltage ripple. It charges to the peak voltage of the rectified signal and discharges when the voltage falls, maintaining a more constant DC level. This energy storage capability stabilizes the power supply output in electronic circuits.
Working Principle: Bypass Capacitor
A bypass capacitor works by providing a low impedance path to ground for high-frequency noise, effectively filtering out unwanted signals from the power supply. It stabilizes voltage levels by shunting transient currents away from sensitive components, ensuring smooth and reliable operation in electronic circuits. Your circuit's performance improves as the bypass capacitor minimizes voltage spikes and electromagnetic interference.
Key Differences Between Filter and Bypass Capacitors
Filter capacitors primarily smooth out voltage fluctuations in power supplies by removing ripple signals, while bypass capacitors stabilize voltage by shunting high-frequency noise to ground in electronic circuits. Filter capacitors typically have larger capacitance values and are positioned after rectifiers, whereas bypass capacitors are smaller and placed close to integrated circuits for noise suppression. Understanding these key differences helps optimize your circuit's performance and reliability.
Applications of Filter Capacitors
Filter capacitors are primarily used in power supply circuits to smooth out the rectified output, reducing ripple voltage and providing a stable DC voltage for electronic devices. They are essential in applications like audio equipment, DC power supplies, and voltage regulation systems, where maintaining clean and consistent voltage is critical. Your circuit's performance improves significantly by minimizing noise and fluctuations through effective filtering of AC components.
Applications of Bypass Capacitors
Bypass capacitors are primarily used in electronic circuits to reduce noise and stabilize voltage supply by shunting high-frequency interference away from sensitive components like microcontrollers and amplifiers. Common applications include decoupling power supply lines in digital circuits, improving signal integrity in RF communication devices, and minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI) in audio and video equipment. Their placement close to integrated circuits ensures efficient filtering of transient voltage spikes, enhancing overall circuit performance and reliability.
Comparison Table: Filter vs Bypass Capacitor
Filter capacitors primarily smooth out voltage fluctuations in power supplies by storing and releasing energy to reduce ripple voltage, whereas bypass capacitors provide a low impedance path to ground for high-frequency noise, stabilizing voltage in electronic circuits. Filter capacitors typically have larger capacitance values (microfarads to millifarads) and are used in DC power supply circuits, while bypass capacitors have smaller values (picofarads to microfarads) and are placed close to IC power pins to suppress high-frequency noise. The main difference lies in their application: filter capacitors manage bulk voltage stabilization and ripple reduction, and bypass capacitors handle localized noise filtering and signal integrity enhancement.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Capacitor
Selecting the right capacitor depends on your circuit requirements: filter capacitors smooth out voltage fluctuations in power supplies by reducing ripple, while bypass capacitors stabilize voltage by shunting noise to ground in high-frequency applications. Filter capacitors typically have larger capacitance values to handle lower-frequency signals, whereas bypass capacitors use smaller values optimized for high-frequency noise suppression. Understanding these functional differences ensures your design maintains optimal performance and reliability.
filter capacitor vs bypass capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com