Zener diodes are designed to allow current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific breakdown voltage is reached, making them ideal for voltage regulation, while Schottky diodes offer fast switching speeds and low forward voltage drops, suitable for high-efficiency power applications. Discover how choosing the right diode can impact Your electronic circuit's performance by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
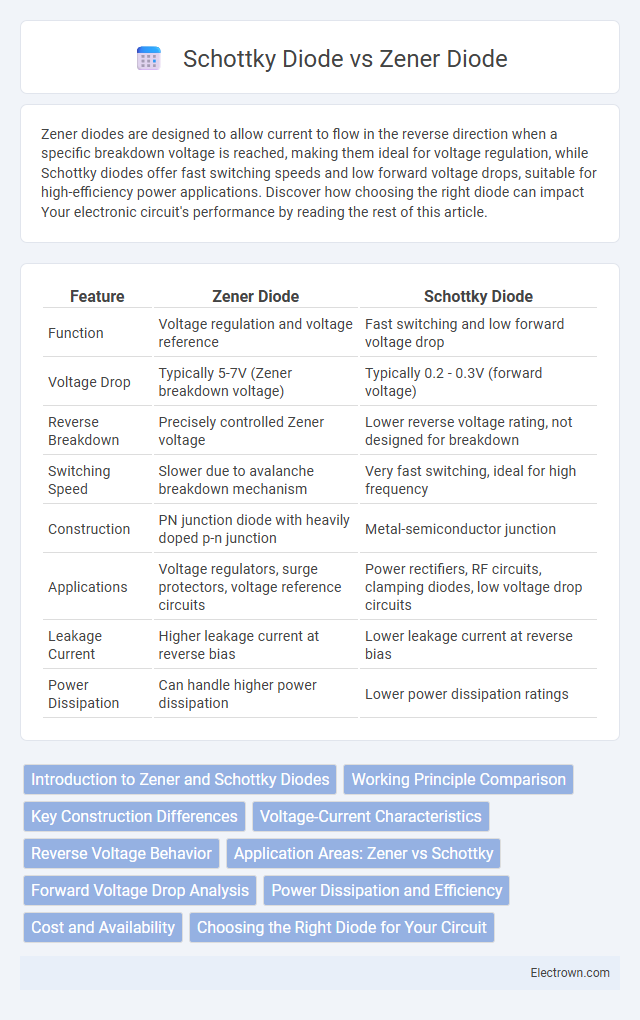
| Feature | Zener Diode | Schottky Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Voltage regulation and voltage reference | Fast switching and low forward voltage drop |
| Voltage Drop | Typically 5-7V (Zener breakdown voltage) | Typically 0.2 - 0.3V (forward voltage) |
| Reverse Breakdown | Precisely controlled Zener voltage | Lower reverse voltage rating, not designed for breakdown |
| Switching Speed | Slower due to avalanche breakdown mechanism | Very fast switching, ideal for high frequency |
| Construction | PN junction diode with heavily doped p-n junction | Metal-semiconductor junction |
| Applications | Voltage regulators, surge protectors, voltage reference circuits | Power rectifiers, RF circuits, clamping diodes, low voltage drop circuits |
| Leakage Current | Higher leakage current at reverse bias | Lower leakage current at reverse bias |
| Power Dissipation | Can handle higher power dissipation | Lower power dissipation ratings |
Introduction to Zener and Schottky Diodes
Zener diodes are designed to regulate voltage by allowing current to flow in reverse once a specific breakdown voltage is reached, making them ideal for voltage stabilization applications. Schottky diodes feature a metal-semiconductor junction that offers low forward voltage drop and fast switching speeds, commonly used in high-frequency and power efficiency circuits. Both diodes serve distinct functions in electronics, with Zener diodes focusing on voltage regulation and Schottky diodes excelling in rectification and switching tasks.
Working Principle Comparison
Zener diodes operate by exploiting the Zener breakdown phenomenon in reverse bias to maintain a stable voltage across electronic circuits, making them ideal for voltage regulation. Schottky diodes function through metal-semiconductor junctions, allowing for fast switching speeds and low forward voltage drops due to majority carrier conduction. The Zener diode's mechanism centers on controlled avalanche breakdown, while the Schottky diode's operation relies on majority carrier flow that minimizes storage time and enhances efficiency in high-speed applications.
Key Construction Differences
Zener diodes feature a heavily doped p-n junction designed to operate in reverse breakdown mode, allowing precise voltage regulation. Schottky diodes consist of a metal-semiconductor junction, typically between metal and n-type silicon, resulting in lower forward voltage drop and faster switching speeds. Your choice between these diodes depends on whether voltage stability or efficiency in high-speed applications is more critical.
Voltage-Current Characteristics
Zener diodes exhibit a sharp breakdown voltage allowing them to maintain a stable voltage in reverse bias, making them ideal for voltage regulation. Schottky diodes feature a low forward voltage drop (typically 0.2 to 0.3 volts) and fast switching due to their metal-semiconductor junction, resulting in higher efficiency in power applications. The voltage-current characteristics of Zener diodes show a distinct knee at the Zener voltage, while Schottky diodes display a smoother forward voltage drop and negligible reverse recovery time.
Reverse Voltage Behavior
Zener diodes exhibit a well-defined reverse breakdown voltage, allowing them to regulate voltage precisely when the reverse voltage exceeds this threshold. Schottky diodes, however, have a lower reverse breakdown voltage and tend to conduct small leakage currents under reverse bias, making them less ideal for voltage regulation. The sharp reverse voltage characteristic of Zener diodes makes them preferred for voltage stabilization, while Schottky diodes are favored for fast switching applications due to their low forward voltage drop.
Application Areas: Zener vs Schottky
Zener diodes are primarily used in voltage regulation and reference circuits due to their ability to maintain a stable output voltage. Schottky diodes excel in high-speed switching, power rectification, and low forward voltage drop applications, making them ideal for power supplies and RF circuits. While Zener diodes provide precise voltage clamping, Schottky diodes improve efficiency in high-frequency and low-voltage drop scenarios.
Forward Voltage Drop Analysis
Zener diodes typically exhibit a forward voltage drop around 0.7 volts, similar to standard silicon diodes, whereas Schottky diodes have a significantly lower forward voltage drop, ranging from 0.15 to 0.45 volts, due to their metal-semiconductor junction. The lower forward voltage drop of Schottky diodes results in higher efficiency and reduced power loss, especially in low-voltage, high-speed switching applications. This characteristic makes Schottky diodes preferable for power-sensitive circuits, while Zener diodes are primarily used for voltage regulation and reference purposes.
Power Dissipation and Efficiency
Zener diodes exhibit higher power dissipation due to their voltage regulation characteristics, often resulting in increased heat generation under load, which can reduce overall efficiency in voltage stabilization circuits. Schottky diodes, with their lower forward voltage drop and faster switching speeds, enhance efficiency by minimizing power loss and thermal stress in high-frequency or low-voltage applications. Choosing the appropriate diode based on your circuit's power dissipation and efficiency requirements directly impacts performance and thermal management.
Cost and Availability
Zener diodes typically offer lower cost and wider availability due to their long-standing use in voltage regulation across various electronic applications. Schottky diodes, though generally more expensive, provide faster switching speeds and lower forward voltage drops, making them valuable in high-frequency circuits but less abundant than Zener diodes. For your project, choosing between them depends on balancing the cost-effectiveness of Zener diodes with the specialized performance benefits of Schottky diodes.
Choosing the Right Diode for Your Circuit
Selecting between a Zener diode and a Schottky diode depends on the specific circuit requirements, as Zener diodes excel at voltage regulation by maintaining a stable reference voltage under reverse breakdown conditions. Schottky diodes offer low forward voltage drop and fast switching speeds, making them ideal for power rectification and high-frequency applications. Evaluating factors such as voltage stability, forward voltage, switching speed, and power dissipation helps ensure optimal diode performance in your electronic design.
zener diode vs schottky diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com