24-bit audio offers greater dynamic range and finer detail compared to 16-bit audio, enhancing the clarity and depth of sound recordings. Discover how this difference impacts Your listening experience and recording quality by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
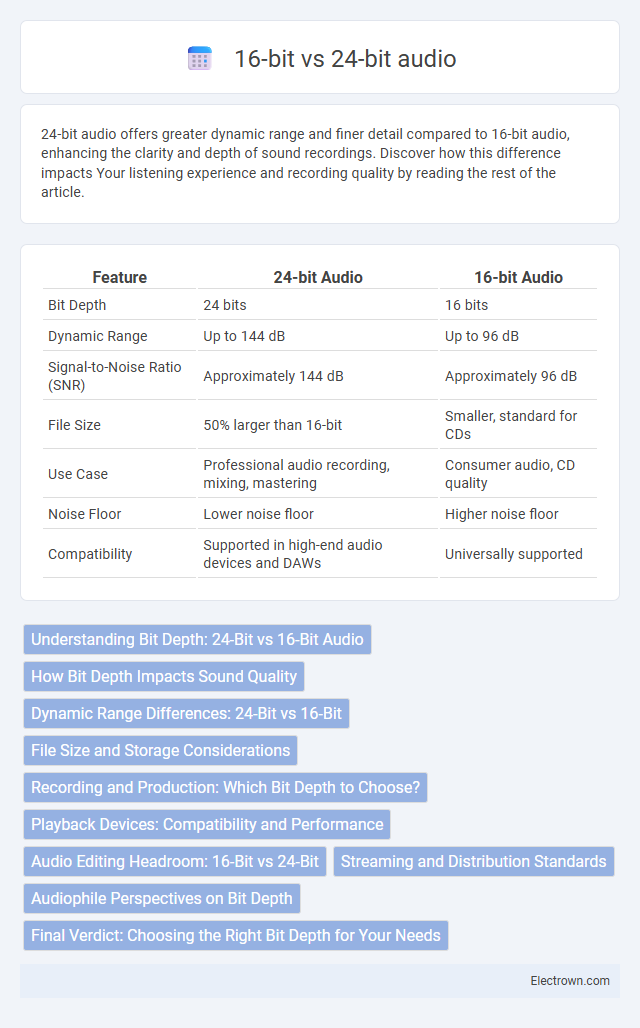
| Feature | 24-bit Audio | 16-bit Audio |
|---|---|---|
| Bit Depth | 24 bits | 16 bits |
| Dynamic Range | Up to 144 dB | Up to 96 dB |
| Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) | Approximately 144 dB | Approximately 96 dB |
| File Size | 50% larger than 16-bit | Smaller, standard for CDs |
| Use Case | Professional audio recording, mixing, mastering | Consumer audio, CD quality |
| Noise Floor | Lower noise floor | Higher noise floor |
| Compatibility | Supported in high-end audio devices and DAWs | Universally supported |
Understanding Bit Depth: 24-Bit vs 16-Bit Audio
Bit depth in audio refers to the number of bits used to represent each audio sample, directly affecting dynamic range and noise floor. A 24-bit audio file offers a dynamic range of 144 dB, compared to 16-bit audio's 96 dB, allowing for greater detail and less quantization noise. Understanding bit depth helps you choose the right audio quality for your recording or playback needs, ensuring optimal sound fidelity.
How Bit Depth Impacts Sound Quality
Bit depth in audio determines the dynamic range and noise floor, with 24-bit audio providing a theoretical dynamic range of 144 dB compared to 96 dB in 16-bit audio. Higher bit depth allows for more precise amplitude representation, resulting in finer detail, reduced quantization noise, and better sound fidelity, especially in quiet passages. Consequently, 24-bit audio captures greater nuance and clarity, making it the preferred choice for professional recording and high-resolution playback.
Dynamic Range Differences: 24-Bit vs 16-Bit
24-bit audio offers a dynamic range of approximately 144 dB, significantly surpassing the 96 dB dynamic range of 16-bit audio, enabling finer gradations between the quietest and loudest sounds. This increased dynamic range in 24-bit audio reduces quantization noise, providing clearer and more detailed sound reproduction, especially in professional audio recording and mixing environments. The superior precision of 24-bit audio allows for more headroom during processing, minimizing distortion and preserving audio fidelity.
File Size and Storage Considerations
24-bit audio offers higher dynamic range and better sound quality but results in significantly larger file sizes compared to 16-bit audio, often consuming nearly 50% more storage space. When managing Your audio library or projects, balancing quality with available storage is crucial, as 16-bit files are more space-efficient and suitable for most consumer audio applications. For archival or professional use where fidelity is paramount, investing in additional storage for 24-bit files may be necessary.
Recording and Production: Which Bit Depth to Choose?
Choosing between 24-bit and 16-bit audio for recording and production hinges on dynamic range and noise floor considerations. 24-bit audio offers a theoretical dynamic range of 144 dB, providing greater headroom and lower noise, crucial for capturing subtle details and maintaining quality during mixing and mastering. Conversely, 16-bit audio, with a 96 dB dynamic range, may suffice for final distribution but lacks the flexibility and fidelity needed during the production stages.
Playback Devices: Compatibility and Performance
24-bit audio delivers higher resolution sound compared to 16-bit, offering greater dynamic range and finer detail, which enhances playback quality on compatible devices. However, many common playback devices, such as standard headphones and consumer speakers, often do not fully exploit the benefits of 24-bit audio, making 16-bit audio sufficient for everyday listening. Your choice should consider whether your playback equipment supports true 24-bit processing to experience the superior performance and improved sound fidelity it provides.
Audio Editing Headroom: 16-Bit vs 24-Bit
24-bit audio offers significantly greater headroom during audio editing compared to 16-bit, providing 144 dB of dynamic range versus 96 dB, which reduces the risk of distortion and allows for more precise adjustments. Your edits will retain higher fidelity with less noise and quantization errors, making 24-bit the preferred format for professional mixing and mastering. This increased bit depth enables smoother volume automation and detailed processing without compromising the original sound quality.
Streaming and Distribution Standards
Streaming platforms predominantly use 16-bit audio due to its balance between sound quality and data efficiency, aligning with CD-quality standards at 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz sample rates. However, emerging high-resolution streaming services support 24-bit audio files, offering superior dynamic range and detail for audiophiles and professional distribution. The adoption of 24-bit streaming is limited by bandwidth constraints and device compatibility, making 16-bit audio the standard for widespread distribution.
Audiophile Perspectives on Bit Depth
Audiophiles often prefer 24-bit audio for its superior dynamic range and lower noise floor compared to 16-bit, enabling finer detail and greater sonic clarity in high-fidelity recordings. The increased bit depth enhances subtle nuances in music, capturing extended harmonic content and providing a more immersive listening experience. Despite the theoretical benefits, the audible difference may be minimal on standard playback systems, making 24-bit most advantageous in professional production and high-end audio setups.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Bit Depth for Your Needs
Choosing between 24-bit and 16-bit audio depends on your specific needs for dynamic range and sound quality. 24-bit audio offers a greater dynamic range of up to 144 dB, reducing noise and allowing more detailed recordings, making it ideal for professional music production. For everyday listening or casual use, 16-bit audio provides sufficient quality with lower file sizes and compatibility across most playback devices.
24-bit vs 16-bit audio Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com