Analog mixers offer tactile controls and warm sound characteristics favored by many audio professionals, while digital mixers provide advanced features like onboard effects, scene recall, and flexible routing. To explore which mixer suits Your audio needs best, continue reading the detailed comparison in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
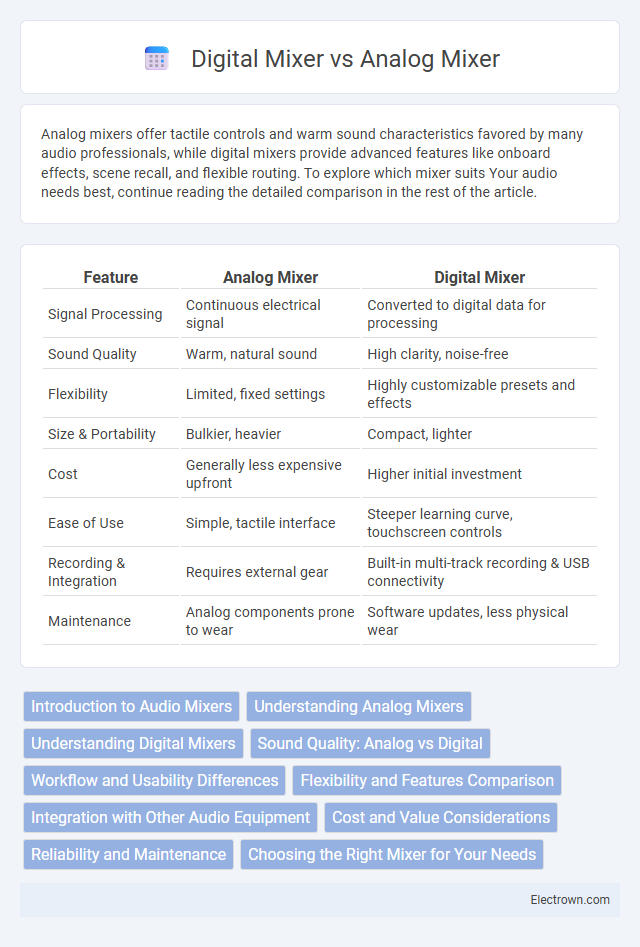
| Feature | Analog Mixer | Digital Mixer |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Processing | Continuous electrical signal | Converted to digital data for processing |
| Sound Quality | Warm, natural sound | High clarity, noise-free |
| Flexibility | Limited, fixed settings | Highly customizable presets and effects |
| Size & Portability | Bulkier, heavier | Compact, lighter |
| Cost | Generally less expensive upfront | Higher initial investment |
| Ease of Use | Simple, tactile interface | Steeper learning curve, touchscreen controls |
| Recording & Integration | Requires external gear | Built-in multi-track recording & USB connectivity |
| Maintenance | Analog components prone to wear | Software updates, less physical wear |
Introduction to Audio Mixers
Audio mixers, essential for combining multiple audio signals, come in two main types: analog and digital. Analog mixers process sound using physical circuitry, offering tactile controls and a warm, natural sound preferred by many audio professionals. Your choice between analog and digital mixers depends on factors like workflow preferences, available features, and integration with digital audio workstations (DAWs).
Understanding Analog Mixers
Analog mixers process audio signals through physical circuitry, allowing real-time tactile control over sound with dedicated knobs and faders for each channel. They deliver warm, natural sound characteristics favored by many audio engineers for live performances and recording studios. Understanding analog mixers involves recognizing their straightforward signal flow and the absence of digital effects or recall features found in digital mixers.
Understanding Digital Mixers
Digital mixers offer advanced features like built-in effects, scene recall, and precise automation that enhance your sound control and workflow efficiency. Unlike analog mixers, digital mixers process audio signals through software, providing greater flexibility and easier integration with modern recording setups. Understanding digital mixers allows you to leverage their intuitive touchscreens and customizable interfaces for professional-quality mixing in both live and studio environments.
Sound Quality: Analog vs Digital
Analog mixers deliver warmth and natural sound with smooth harmonic distortion favored by audiophiles, while digital mixers provide precise signal processing, offering cleaner audio with lower noise floors and extensive EQ, compression, and effects capabilities. Analog circuitry often results in subtle coloration that enhances musical character, whereas digital mixers boast transparent sound reproduction and flexible routing options for complex mixes. The choice depends on preference for vintage tonal qualities versus modern clarity and versatility in sound shaping.
Workflow and Usability Differences
Analog mixers provide tactile control with physical knobs and faders, allowing for immediate, hands-on adjustments that many users find intuitive for live performances and quick setups. Digital mixers offer customizable layouts, scene recall, and built-in effects, streamlining complex workflows and enabling precise automation that enhances efficiency in studio and live environments. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize straightforward, real-time manipulation or advanced features that optimize session management and sound processing.
Flexibility and Features Comparison
Digital mixers offer superior flexibility with programmable settings, scene recall, and onboard effects that allow precise customization for various audio environments. Analog mixers provide tactile control and simplicity, favored for real-time adjustments and straightforward signal routing without latency. Digital units often integrate USB interfaces and remote control capabilities, enhancing workflow efficiency and feature versatility compared to analog mixers.
Integration with Other Audio Equipment
Analog mixers typically provide straightforward, tactile connections such as XLR and TRS inputs and outputs, allowing seamless integration with traditional studio gear like outboard compressors, equalizers, and microphones. Digital mixers feature USB, Ethernet, and MIDI interfaces that enable enhanced compatibility with computers, digital audio workstations (DAWs), and networked audio systems, streamlining complex setups and remote control. Integration efficiency in digital mixers supports automation, preset recall, and multi-channel recording, which analog mixers generally lack.
Cost and Value Considerations
Analog mixers generally have lower upfront costs and provide tactile control that many audio professionals value for hands-on mixing. Digital mixers often come with higher price points but offer extensive features, presets, and integration options that can enhance workflow and post-production efficiency. Your choice depends on whether immediate budget constraints or long-term functional value aligns best with your audio mixing needs.
Reliability and Maintenance
Analog mixers offer robust reliability with fewer software dependencies, making them less prone to digital glitches and easier to troubleshoot on-site. Digital mixers require regular firmware updates and can experience software-related failures, but benefit from advanced diagnostics and remote maintenance capabilities. Maintenance for analog mixers often involves replacing physical components, whereas digital mixers may need firmware optimization and hardware compatibility checks to ensure optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Mixer for Your Needs
Selecting the right mixer depends on your specific audio requirements and workflow preferences. Analog mixers offer tactile control and warm sound quality favored in live performances and traditional studio settings. Digital mixers provide advanced features like onboard effects, recallable settings, and compact design, making them ideal for complex productions and remote mixing scenarios.
analog vs digital mixer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com