Choosing between 48kHz and 96kHz sample rates depends on your audio project's needs, as 96kHz offers higher fidelity and better captures high-frequency details, while 48kHz is often sufficient for most professional audio and video applications with smaller file sizes. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these differences impact your audio quality and production workflow.
Table of Comparison
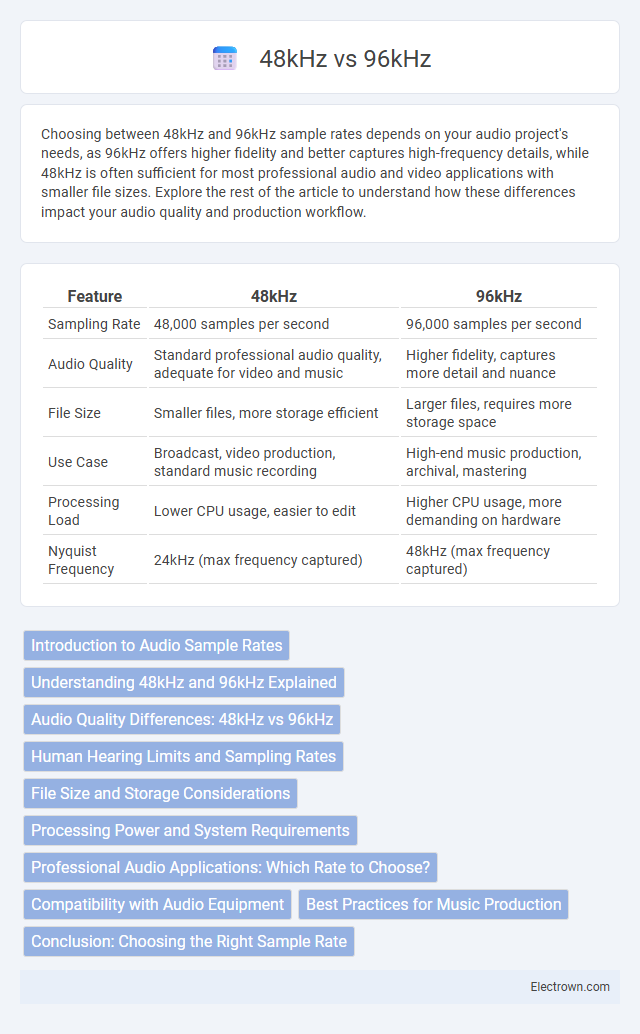
| Feature | 48kHz | 96kHz |
|---|---|---|
| Sampling Rate | 48,000 samples per second | 96,000 samples per second |
| Audio Quality | Standard professional audio quality, adequate for video and music | Higher fidelity, captures more detail and nuance |
| File Size | Smaller files, more storage efficient | Larger files, requires more storage space |
| Use Case | Broadcast, video production, standard music recording | High-end music production, archival, mastering |
| Processing Load | Lower CPU usage, easier to edit | Higher CPU usage, more demanding on hardware |
| Nyquist Frequency | 24kHz (max frequency captured) | 48kHz (max frequency captured) |
Introduction to Audio Sample Rates
Audio sample rates define how many samples of audio are captured per second, with 48kHz and 96kHz being common standards in professional recording and production. A 48kHz sample rate offers a balance between audio quality and file size, commonly used in video production and broadcasting. Choosing 96kHz provides higher audio fidelity with greater detail and dynamic range, ideal for mastering and high-resolution audio projects where preserving sound quality is crucial for Your work.
Understanding 48kHz and 96kHz Explained
Sampling rates of 48kHz and 96kHz determine the audio resolution and frequency range captured during recording, with 48kHz commonly used in video production and 96kHz preferred for high-fidelity music recording. Higher sampling rates like 96kHz provide greater detail and less aliasing, which can improve audio quality when processing or mixing. When choosing between them, consider your project's delivery format and your equipment's capability to handle the increased data rate efficiently.
Audio Quality Differences: 48kHz vs 96kHz
A 96kHz sampling rate captures audio frequencies up to 48kHz, offering greater detail and fidelity compared to 48kHz, which captures up to 24kHz. This higher rate reduces aliasing and allows for more precise editing and processing, benefiting high-resolution audio projects and professional music production. Despite this, audible differences may be subtle for most listeners, as human hearing typically ranges up to 20kHz.
Human Hearing Limits and Sampling Rates
The human hearing range typically spans from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, making a 48 kHz sampling rate sufficient to capture all audible frequencies according to the Nyquist theorem. Sampling at 96 kHz exceeds these limits, allowing for higher frequency data that generally falls outside human perception and often increases file sizes without perceptible audio quality improvement. You should consider whether your equipment and listening environment justify the use of 96 kHz for your audio projects.
File Size and Storage Considerations
Choosing between 48kHz and 96kHz sample rates significantly impacts file size and storage requirements, with 96kHz audio files nearly doubling the data compared to 48kHz. Higher sample rates like 96kHz capture more audio detail but demand increased disk space and longer transfer times, affecting your storage strategy. For applications where storage capacity and bandwidth are limited, 48kHz offers a more efficient balance between quality and file size.
Processing Power and System Requirements
96kHz sampling rate demands significantly higher processing power and storage capacity compared to 48kHz, as it generates twice the amount of audio data per second. Systems with limited CPU power or lower RAM may experience latency or performance issues when handling 96kHz audio streams, impacting real-time audio processing and mixing. For optimal performance, higher-spec hardware and efficient audio interfaces are essential when working with 96kHz to ensure smooth operation and minimal resource bottlenecks.
Professional Audio Applications: Which Rate to Choose?
In professional audio applications, 96kHz sampling rate is preferred for capturing higher frequency details and providing greater headroom during mixing and mastering, resulting in more accurate sound reproduction. However, 48kHz remains a standard for video production and broadcast due to its balance of audio quality and file size efficiency. Choosing between 48kHz and 96kHz depends on the project's requirements for fidelity, processing flexibility, and storage capacity.
Compatibility with Audio Equipment
48kHz is widely supported and compatible with most consumer audio equipment, including headphones, speakers, and digital audio workstations, making it the industry standard for general recording and playback. 96kHz offers higher fidelity and better frequency response, preferred in professional studios and high-end audio systems but may pose compatibility issues with older or less advanced devices. Ensuring your audio equipment can process 96kHz files is crucial to fully benefit from the improved sound quality without playback or conversion problems.
Best Practices for Music Production
Using 48kHz sample rate in music production ensures compatibility with video projects and reduces CPU load, making it ideal for efficient workflows. Choosing 96kHz offers higher audio resolution and greater detail, beneficial for critical mixing and mastering stages where sound fidelity is paramount. Balancing project goals with system resources helps determine the best sample rate, with many professionals opting for 48kHz during recording and switching to 96kHz for final production refinements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Sample Rate
Choosing between 48kHz and 96kHz sample rates depends on your project's needs for audio fidelity and file size. While 96kHz provides higher resolution, 48kHz is often sufficient for most professional recordings and reduces storage and processing demands. Your decision should balance quality requirements with practical considerations like system compatibility and workflow efficiency.
48khz vs 96khz Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com