Class G and Class H amplifiers improve efficiency by modulating the power supply voltage to the output stage, reducing energy waste compared to traditional Class AB designs. Learn how these technologies impact audio performance and power consumption to determine which amplifier best suits your needs in the full article.
Table of Comparison
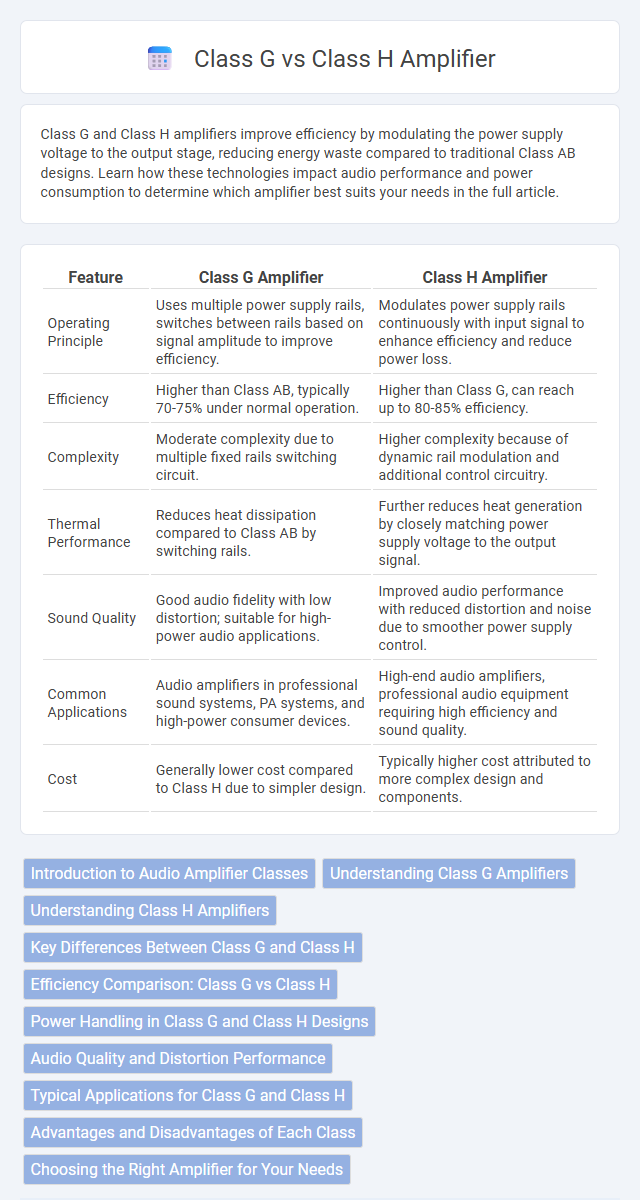
| Feature | Class G Amplifier | Class H Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Uses multiple power supply rails, switches between rails based on signal amplitude to improve efficiency. | Modulates power supply rails continuously with input signal to enhance efficiency and reduce power loss. |
| Efficiency | Higher than Class AB, typically 70-75% under normal operation. | Higher than Class G, can reach up to 80-85% efficiency. |
| Complexity | Moderate complexity due to multiple fixed rails switching circuit. | Higher complexity because of dynamic rail modulation and additional control circuitry. |
| Thermal Performance | Reduces heat dissipation compared to Class AB by switching rails. | Further reduces heat generation by closely matching power supply voltage to the output signal. |
| Sound Quality | Good audio fidelity with low distortion; suitable for high-power audio applications. | Improved audio performance with reduced distortion and noise due to smoother power supply control. |
| Common Applications | Audio amplifiers in professional sound systems, PA systems, and high-power consumer devices. | High-end audio amplifiers, professional audio equipment requiring high efficiency and sound quality. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost compared to Class H due to simpler design. | Typically higher cost attributed to more complex design and components. |
Introduction to Audio Amplifier Classes
Class G amplifiers improve efficiency by switching between multiple power supply rails to reduce power loss, making them ideal for high-power audio applications with moderate distortion tolerance. Class H amplifiers further enhance efficiency through continuous modulation of the power supply rails according to the input signal, enabling better performance and lower heat dissipation in professional audio systems. Both amplifier classes aim to optimize power usage and sound quality compared to traditional Class AB designs, with Class H offering superior efficiency for demanding audio environments.
Understanding Class G Amplifiers
Class G amplifiers improve efficiency by using multiple power supply rails that switch according to the input signal level, reducing power waste during low signal conditions. These amplifiers maintain sound quality by operating in Class AB mode within each rail, minimizing distortion while extending battery life in portable audio devices. Your audio system benefits from Class G technology with enhanced performance and lower heat generation compared to traditional Class AB amplifiers.
Understanding Class H Amplifiers
Class H amplifiers improve efficiency by modulating the power supply voltage according to the input signal, reducing power dissipation compared to traditional Class G models, which switch between fixed voltage rails. Your audio system benefits from Class H's ability to minimize heat generation and power wastage, making it ideal for high-power applications where thermal management is crucial. Understanding Class H technology helps optimize amplifier performance with enhanced energy efficiency and extended component longevity.
Key Differences Between Class G and Class H
Class G and Class H amplifiers both enhance efficiency by modulating their power supply voltage, but they differ in complexity and implementation. Class G amplifiers use multiple fixed voltage rails, switching between them to reduce power loss, while Class H amplifiers employ continuous voltage tracking to closely follow the input signal, minimizing distortion and heat generation. Understanding these distinctions can help you select the amplifier that best balances performance and efficiency for your audio applications.
Efficiency Comparison: Class G vs Class H
Class H amplifiers achieve higher efficiency than Class G by modulating the power supply rails in real-time to closely follow the input signal's envelope, reducing power dissipation. Class G amplifiers improve efficiency by switching between multiple fixed voltage rails, optimizing power supply voltage based on signal amplitude but with less precision than Class H. The dynamic rail tracking in Class H results in lower distortion and better power savings, especially at varying output levels, making it more efficient in demanding audio applications.
Power Handling in Class G and Class H Designs
Class G amplifiers improve power handling by switching between multiple power supply rails, reducing power dissipation and increasing efficiency at lower signal levels. Class H designs enhance power handling further with continuous rail tracking, dynamically adjusting the supply voltage to closely follow the input signal amplitude, minimizing voltage drops and heat generation. Your choice between Class G and Class H depends on the desired balance between complexity, cost, and power efficiency for high-performance audio applications.
Audio Quality and Distortion Performance
Class G amplifiers deliver improved audio quality by utilizing multiple power supply rails that reduce power loss and heat, resulting in lower distortion compared to Class AB designs. In contrast, Class H amplifiers employ dynamic rail modulation, which allows for even greater efficiency and tighter control over voltage levels, minimizing crossover distortion and enhancing overall sound clarity. Both classes outperform traditional amplifiers in distortion performance, with Class H offering superior linearity and audio fidelity in high-power applications.
Typical Applications for Class G and Class H
Class G amplifiers are commonly used in audio equipment and portable devices where energy efficiency and reduced heat dissipation are essential, such as in professional sound systems and battery-powered speakers. Class H amplifiers find typical application in high-power audio amplifiers for stadiums, concert venues, and large-scale public address systems where both efficiency and high output power are critical. Your choice between Class G and Class H depends on the specific balance you need between audio quality, power efficiency, and thermal management for your application.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Class
Class G amplifiers offer higher efficiency by utilizing multiple power supply rails that reduce power dissipation, resulting in less heat generation and longer component lifespan, but they can introduce more complexity and potential distortion compared to simpler designs. Class H amplifiers further enhance efficiency by modulating the power supply rails in real-time based on the input signal, providing superior power savings and reduced heat, though this increased design complexity may lead to higher costs and potential reliability concerns. Choosing between Class G and Class H depends on your need for balancing efficiency, audio fidelity, and budget constraints in amplifier applications.
Choosing the Right Amplifier for Your Needs
Class G amplifiers offer improved efficiency by switching between multiple power supply rails, reducing power loss during low to moderate output levels. Class H amplifiers enhance this by continuously modulating the power rails to closely follow the input signal, providing even greater efficiency and lower distortion in high-power applications. Your choice depends on balancing efficiency, sound quality, and complexity, with Class H ideal for demanding professional audio setups and Class G suited for cost-effective, efficient performance.
class g vs class h amplifier Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com