High pass filters allow frequencies above a certain cutoff to pass while attenuating lower frequencies, making them ideal for removing unwanted bass or low-frequency noise. Low pass filters do the opposite by allowing frequencies below the cutoff to pass and reducing higher frequencies, which is useful for smoothing signals or reducing high-frequency noise; discover how these filters impact Your audio and signal processing applications by reading the rest of the article.
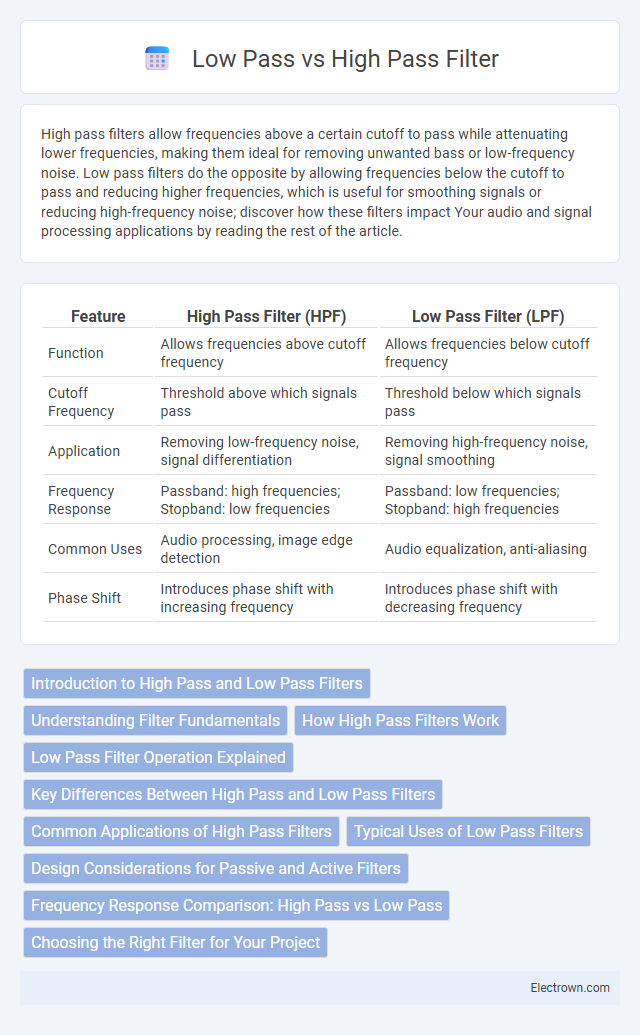
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High Pass Filter (HPF) | Low Pass Filter (LPF) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Allows frequencies above cutoff frequency | Allows frequencies below cutoff frequency |
| Cutoff Frequency | Threshold above which signals pass | Threshold below which signals pass |
| Application | Removing low-frequency noise, signal differentiation | Removing high-frequency noise, signal smoothing |
| Frequency Response | Passband: high frequencies; Stopband: low frequencies | Passband: low frequencies; Stopband: high frequencies |
| Common Uses | Audio processing, image edge detection | Audio equalization, anti-aliasing |
| Phase Shift | Introduces phase shift with increasing frequency | Introduces phase shift with decreasing frequency |
Introduction to High Pass and Low Pass Filters
High pass and low pass filters are essential components in signal processing that control the frequency content of your signals. A high pass filter allows frequencies above a specific cutoff frequency to pass while attenuating lower frequencies, making it ideal for removing unwanted low-frequency noise. In contrast, a low pass filter permits frequencies below its cutoff frequency, effectively smoothing signals by reducing high-frequency components.
Understanding Filter Fundamentals
High pass filters allow frequencies above a specified cutoff to pass while attenuating lower frequencies, making them ideal for removing unwanted low-frequency noise. Low pass filters do the opposite by permitting frequencies below the cutoff to pass through, effectively smoothing signals and eliminating high-frequency interference. Understanding these filter fundamentals helps you select the right filter type to optimize signal clarity in audio, communication, and data processing applications.
How High Pass Filters Work
High pass filters work by allowing frequencies higher than a specified cutoff frequency to pass through while attenuating lower frequencies. They achieve this by using capacitors and resistors or inductors that impede low-frequency signals and permit high-frequency signals to pass with minimal attenuation. This selective frequency response is essential in applications like audio processing and signal conditioning to remove unwanted low-frequency noise.
Low Pass Filter Operation Explained
Low pass filters allow signals with frequencies below a specified cutoff frequency to pass while attenuating higher frequencies, making them essential in removing high-frequency noise from audio and communication signals. The operation relies on components such as resistors and capacitors arranged in configurations like RC or active filters, where the capacitor's frequency-dependent impedance blocks high-frequency signals. This selective frequency response is quantified by the filter's -3 dB cutoff point, determining the transition zone between the passband and the attenuation region.
Key Differences Between High Pass and Low Pass Filters
High pass filters allow frequencies higher than a specified cutoff frequency to pass while attenuating lower frequencies, making them ideal for removing low-frequency noise or isolating high-frequency signals. Low pass filters pass frequencies below the cutoff frequency and attenuate higher frequencies, commonly used in audio applications to smooth signals or reduce high-frequency noise. The key difference lies in their frequency response: high pass filters emphasize high-frequency components, whereas low pass filters emphasize low-frequency components.
Common Applications of High Pass Filters
High pass filters are commonly used in audio processing to remove low-frequency noise and hum, enhancing the clarity of vocals and instruments. They play a crucial role in communication systems by blocking unwanted low-frequency signals while allowing higher-frequency data to pass through. In imaging and signal processing, high pass filters emphasize edges and fine details by attenuating smooth, low-frequency background information.
Typical Uses of Low Pass Filters
Low pass filters are commonly used in audio processing to remove high-frequency noise and retain the desired low-frequency signals, enhancing sound clarity and warmth. They play a critical role in smoothing signals in analog and digital communications by eliminating rapid fluctuations and interference. These filters are also essential in image processing to blur images and reduce fine texture details, aiding in noise reduction and image enhancement.
Design Considerations for Passive and Active Filters
Design considerations for passive and active high pass and low pass filters include component selection, frequency response, and power handling capabilities. Passive filters rely on resistors, capacitors, and inductors, offering simplicity and no power source but limited gain and potential insertion loss. Active filters incorporate operational amplifiers to provide gain, improved signal integrity, and precise control over cutoff frequencies while requiring a power supply and careful stability design.
Frequency Response Comparison: High Pass vs Low Pass
High pass filters allow frequencies above a defined cutoff point to pass while attenuating lower frequencies, resulting in a frequency response that rises sharply after the cutoff frequency. Low pass filters, conversely, permit frequencies below the cutoff frequency to pass and attenuate higher frequencies, showing a frequency response that gradually decreases past the cutoff. The transition band and steepness of the slope determine the effectiveness in selectively filtering desired frequency ranges in both high pass and low pass filters.
Choosing the Right Filter for Your Project
High pass filters allow frequencies above a specific cutoff frequency to pass while attenuating lower frequencies, ideal for removing unwanted low-frequency noise or emphasizing high-frequency components in audio and signal processing. Low pass filters, conversely, permit frequencies below the cutoff frequency, effectively smoothing signals and reducing high-frequency interference, commonly used in applications like audio bass enhancement or sensor data stabilization. Your choice between a high pass and low pass filter depends on the frequency range critical to your project's goals and the type of noise or signal characteristics you aim to preserve or eliminate.
high pass vs low pass filter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com