Headphone amps and speaker amps are designed to power different types of audio devices, with headphone amps delivering the precise, low-voltage output needed for headphones, while speaker amps provide higher power output to drive speakers efficiently. To understand which amp best suits Your audio setup and ensures optimal sound quality, read on to explore the key differences and applications.
Table of Comparison
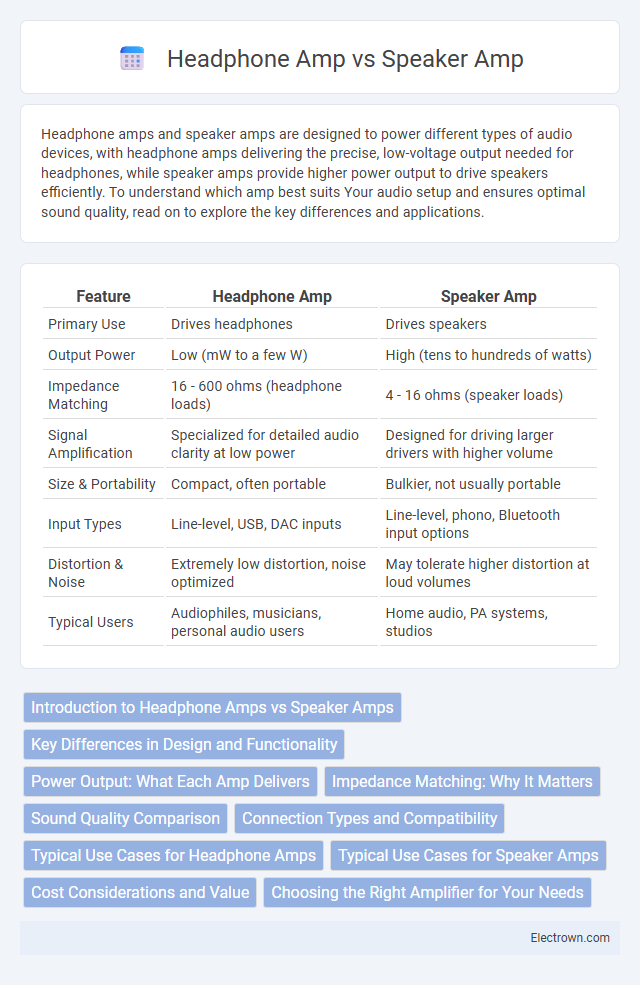
| Feature | Headphone Amp | Speaker Amp |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Drives headphones | Drives speakers |
| Output Power | Low (mW to a few W) | High (tens to hundreds of watts) |
| Impedance Matching | 16 - 600 ohms (headphone loads) | 4 - 16 ohms (speaker loads) |
| Signal Amplification | Specialized for detailed audio clarity at low power | Designed for driving larger drivers with higher volume |
| Size & Portability | Compact, often portable | Bulkier, not usually portable |
| Input Types | Line-level, USB, DAC inputs | Line-level, phono, Bluetooth input options |
| Distortion & Noise | Extremely low distortion, noise optimized | May tolerate higher distortion at loud volumes |
| Typical Users | Audiophiles, musicians, personal audio users | Home audio, PA systems, studios |
Introduction to Headphone Amps vs Speaker Amps
Headphone amps are designed to drive low-impedance headphones, delivering precise audio with minimal distortion and enhanced clarity, while speaker amps provide the higher power necessary to energize larger, higher-impedance speaker drivers. The impedance and power requirements differentiate these amplifiers, with headphone amps typically outputting milliwatts compared to speaker amps that deliver watts. Understanding the electrical demands and intended use cases ensures optimal audio performance and prevents damage to headphones or speakers.
Key Differences in Design and Functionality
Headphone amplifiers are designed to drive low-impedance loads, typically ranging from 16 to 600 ohms, delivering precise audio with minimal distortion for personal listening environments. Speaker amplifiers handle higher power outputs to drive speakers with impedance commonly between 4 to 8 ohms, focusing on delivering broad frequency response and sufficient wattage for room-filling sound. The circuitry of headphone amps emphasizes low noise and compact form factors, while speaker amps prioritize heat dissipation, robust power supply, and protective features to manage the higher electrical demands of loudspeakers.
Power Output: What Each Amp Delivers
Headphone amps deliver power optimized for low-impedance, high-sensitivity headphones, typically ranging from a few milliwatts to around 2 watts, ensuring clear, distortion-free sound at safe listening levels. Speaker amps provide significantly higher power output, often from 20 watts to several hundred watts per channel, designed to drive larger, passive speakers that require more current to produce robust, room-filling sound. Understanding these power output differences helps you choose the right amplifier to match your audio equipment and achieve optimal performance.
Impedance Matching: Why It Matters
Impedance matching is crucial for both headphone amps and speaker amps to ensure optimal audio performance and prevent damage to equipment. Headphone amps typically handle impedances ranging from 16 to 600 ohms, requiring precise matching to deliver clear sound and adequate power without distortion. Speaker amps usually drive lower impedance loads, such as 4 to 8 ohms, and improper matching can lead to reduced efficiency and potential overheating.
Sound Quality Comparison
Headphone amps are designed to deliver precise audio detail and controlled impedance, enhancing clarity and dynamic range for personal listening, while speaker amps provide higher power output to drive larger drivers, emphasizing volume and robust soundstage. The sound quality of headphone amps often reveals subtle nuances and depth that speaker amps may not reproduce due to their focus on power over finesse. Choosing the correct amp depends on matching impedance and ensuring optimal signal-to-noise ratio for the intended listening device, guaranteeing superior audio fidelity.
Connection Types and Compatibility
Headphone amps typically use 3.5mm or 1/4-inch headphone jacks to connect directly to headphones, ensuring impedance matching and optimal audio quality, while speaker amps utilize binding posts or spring clips designed for connecting speaker cables capable of handling higher power output. Compatibility depends on the impedance and power requirements; headphone amps cater to low-impedance headphones (usually 16-600 ohms), whereas speaker amps are built to drive speakers with lower impedance ratings (4-8 ohms) and higher wattage demands. Using the correct connection types and matching impedance levels is crucial to prevent damage and achieve the best sound performance from both amps.
Typical Use Cases for Headphone Amps
Headphone amps are specifically designed to deliver precise audio amplification tailored for personal listening through headphones, enhancing sound quality and driving high-impedance headphones that standard devices cannot efficiently power. They are commonly used in professional audio production, audiophile setups, and portable music players to ensure clear, distortion-free sound at various volume levels. Unlike speaker amps, headphone amps focus on low power output optimized for individual ears, making them ideal for private listening environments rather than room-filling sound projection.
Typical Use Cases for Speaker Amps
Speaker amplifiers primarily power loudspeakers in home audio systems, public address setups, and musical instrument amplification, delivering high wattage to drive larger speaker drivers efficiently. They are designed to handle higher impedance and power loads, making them ideal for producing sound in open or large spaces where volume and clarity over distance are essential. Unlike headphone amps, speaker amps are optimized for lower frequency ranges and robust output, enabling immersive room-filling sound experiences.
Cost Considerations and Value
Headphone amps typically cost less than speaker amps due to lower power output requirements and simpler circuitry, making them more accessible for personal audio setups. Value in headphone amps is often judged by audio clarity, noise reduction, and impedance matching, while speaker amps emphasize wattage, build robustness, and speaker compatibility for larger sound setups. Budget-conscious buyers should evaluate the intended use and performance needs to balance cost against the audio quality benefits each amp type delivers.
Choosing the Right Amplifier for Your Needs
Selecting the right amplifier depends on whether you need a headphone amp or a speaker amp, as headphone amps deliver precise, low-power signals tailored for headphones, ensuring clear audio without distortion. Speaker amps provide higher wattage to drive larger speaker drivers, offering sufficient power for room-filling sound and optimal performance. Matching the amplifier's output impedance and power rating to your headphones or speakers ensures maximum audio quality and prevents damage.
headphone amp vs speaker amp Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com