Tube amplifiers deliver warm, rich tones favored by audiophiles and musicians for their natural harmonic distortion and smooth sound dynamics. Solid-state amplifiers offer reliable, lightweight performance with greater durability and lower maintenance, making them ideal for everyday use--explore the differences further to find the best fit for your audio needs.
Table of Comparison
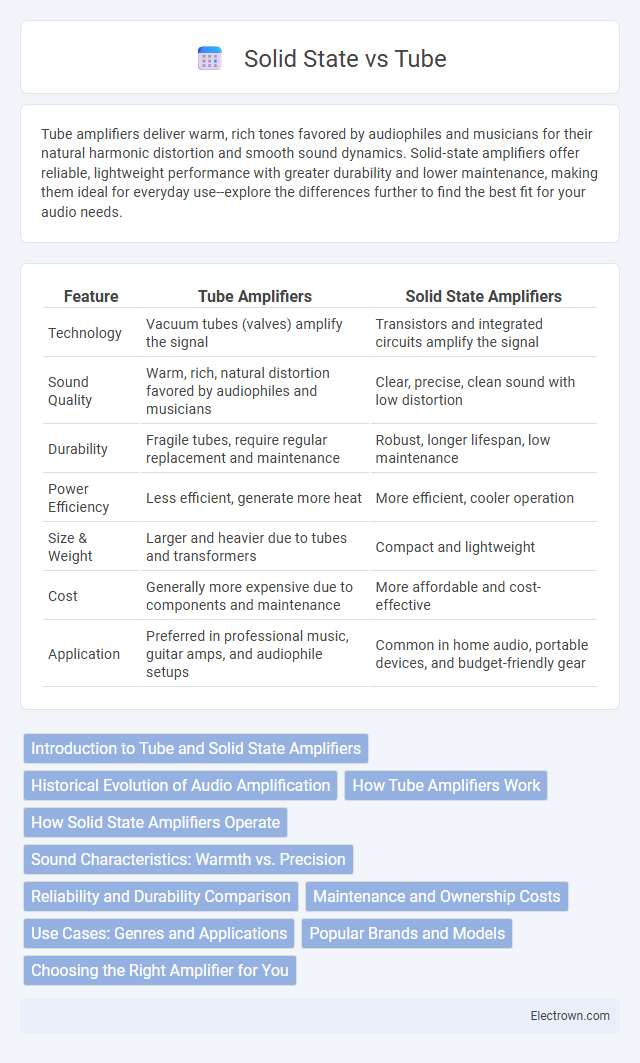
| Feature | Tube Amplifiers | Solid State Amplifiers |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Vacuum tubes (valves) amplify the signal | Transistors and integrated circuits amplify the signal |
| Sound Quality | Warm, rich, natural distortion favored by audiophiles and musicians | Clear, precise, clean sound with low distortion |
| Durability | Fragile tubes, require regular replacement and maintenance | Robust, longer lifespan, low maintenance |
| Power Efficiency | Less efficient, generate more heat | More efficient, cooler operation |
| Size & Weight | Larger and heavier due to tubes and transformers | Compact and lightweight |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to components and maintenance | More affordable and cost-effective |
| Application | Preferred in professional music, guitar amps, and audiophile setups | Common in home audio, portable devices, and budget-friendly gear |
Introduction to Tube and Solid State Amplifiers
Tube amplifiers utilize vacuum tubes to amplify audio signals, delivering warm, rich tones favored in high-fidelity audio and musical instrument amplification. Solid state amplifiers rely on semiconductor devices like transistors, offering greater reliability, compact size, and efficiency with consistent sound quality. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize classic analog warmth or modern, maintenance-free performance.
Historical Evolution of Audio Amplification
The historical evolution of audio amplification began with tube amplifiers, which dominated the early 20th century due to their warm sound quality and high voltage capabilities, essential for radio and early hi-fi systems. The advent of solid-state amplifiers in the 1960s introduced semiconductor transistors, offering greater durability, lower heat output, and more efficient power consumption, revolutionizing consumer electronics. Despite the shift, tube amplifiers remain prized in audiophile and professional settings for their distinct harmonic distortion and tonal warmth.
How Tube Amplifiers Work
Tube amplifiers operate by using vacuum tubes to amplify audio signals, where electrons flow through a vacuum between heated cathodes and anodes, creating a warm and rich sound characteristic. The tubes' ability to introduce subtle harmonic distortion and natural compression provides a dynamic, musical quality that many audiophiles prefer over solid-state models. Your listening experience benefits from the unique tonal warmth and organic response that tube amplifiers deliver, making them ideal for high-fidelity audio systems.
How Solid State Amplifiers Operate
Solid state amplifiers operate using semiconductor devices such as transistors to amplify audio signals with high efficiency and reliability. Their operation relies on the movement of electrons through silicon-based components, producing less heat and requiring less maintenance than tube amplifiers. Solid state technology offers precise tone control and consistent performance across varying environmental conditions.
Sound Characteristics: Warmth vs. Precision
Tube amplifiers deliver a warm, rich sound with natural harmonic distortion that enhances musicality and depth, creating a more organic listening experience. Solid-state amplifiers provide precise, clean, and consistent audio with higher fidelity and less coloration, ideal for accurate sound reproduction. Your choice depends on whether you prefer the soulful warmth of tubes or the detailed clarity of solid-state technology.
Reliability and Durability Comparison
Tube amplifiers tend to have shorter lifespans due to their vacuum tubes, which require periodic replacement and can be sensitive to heat and physical shock, reducing overall reliability. Solid-state amplifiers use semiconductor components that offer greater durability and consistent performance under various conditions, making them more reliable over time. In terms of maintenance and operational lifespan, solid-state devices generally provide enhanced reliability and lower repair costs compared to tube-based systems.
Maintenance and Ownership Costs
Tube amplifiers demand frequent maintenance due to the limited lifespan of vacuum tubes, which need regular replacement and occasional bias adjustments, leading to higher ongoing costs. Solid-state amplifiers offer greater reliability and lower maintenance expenses since their components are more durable and less prone to wear over time. When considering long-term ownership, your total cost of maintaining a tube amplifier will generally exceed that of a solid-state model due to parts and servicing requirements.
Use Cases: Genres and Applications
Tube amplifiers excel in blues, jazz, and classic rock genres due to their warm, harmonically rich sound favored by studio recordings and live performances. Solid-state amplifiers provide clean, reliable tones ideal for genres like pop, metal, and punk, making them suitable for high-gain distortion and consistent sound reinforcement in large venues. Musicians often choose tube amps for expressive, dynamic playing and solid-state amps for durability and budget-friendly applications in practice and recording settings.
Popular Brands and Models
Popular tube amplifier brands include Marshall, Fender, and Vox, known for models like the Marshall JCM800, Fender Twin Reverb, and Vox AC30, which deliver warm, rich tones favored in rock and blues genres. Solid-state amplifiers from brands like Roland, Line 6, and Boss offer reliable, low-maintenance options with models such as the Roland JC-120, Line 6 Spider V, and Boss Katana, prized for versatility and crisp, clean sounds. Choosing your amplifier depends on whether you prioritize the classic, organic sound of tube amps or the durability and modern features of solid-state units.
Choosing the Right Amplifier for You
Tube amplifiers offer warm, rich tones favored by guitarists seeking vintage sound characteristics, while solid state amps provide reliable, lightweight performance with clean, precise audio ideal for diverse musical styles. Consider your playing environment and tonal preferences: tube amps often excel in live settings with natural distortion, whereas solid state models deliver consistent volume and lower maintenance for studio use. Choosing the right amplifier depends on your desired sound quality, portability, and reliability to match your musical needs.
tube vs solid state Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com