An ECU (Engine Control Unit) specifically manages engine functions, while a PCM (Powertrain Control Module) oversees both engine and transmission systems to optimize vehicle performance. Discover how understanding these differences can enhance Your vehicle maintenance by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
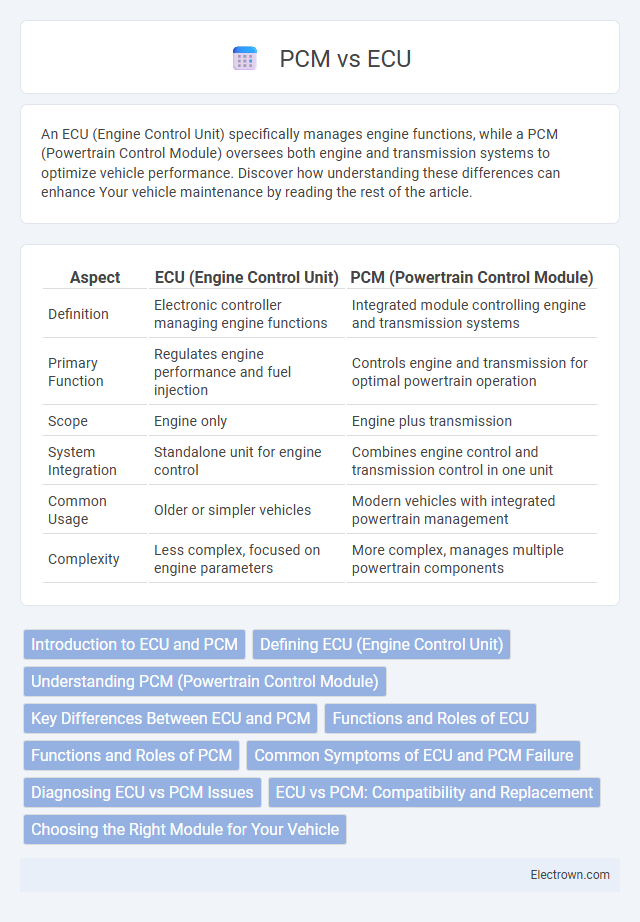
| Aspect | ECU (Engine Control Unit) | PCM (Powertrain Control Module) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electronic controller managing engine functions | Integrated module controlling engine and transmission systems |
| Primary Function | Regulates engine performance and fuel injection | Controls engine and transmission for optimal powertrain operation |
| Scope | Engine only | Engine plus transmission |
| System Integration | Standalone unit for engine control | Combines engine control and transmission control in one unit |
| Common Usage | Older or simpler vehicles | Modern vehicles with integrated powertrain management |
| Complexity | Less complex, focused on engine parameters | More complex, manages multiple powertrain components |
Introduction to ECU and PCM
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) and Powertrain Control Module (PCM) are critical components in modern vehicle engine management, with the ECU primarily focusing on controlling engine functions such as fuel injection and ignition timing. The PCM combines the functionalities of the ECU and Transmission Control Module (TCM), managing both engine and transmission operations to optimize overall powertrain performance. Understanding the distinction between ECU and PCM is essential for diagnostics, repair, and tuning of automotive systems.
Defining ECU (Engine Control Unit)
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) is a critical electronic module in modern vehicles responsible for managing engine functions by processing data from various sensors to optimize fuel injection, ignition timing, and emission controls. It ensures optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions compliance by continuously adjusting parameters based on real-time operating conditions. Unlike the Powertrain Control Module (PCM), which integrates both engine and transmission management, the ECU specifically focuses on controlling engine-related systems.
Understanding PCM (Powertrain Control Module)
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is a critical automotive component that integrates the functions of both the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and the Transmission Control Module (TCM), managing engine performance and transmission operations to optimize fuel efficiency and emissions. PCM processes data from various sensors to control ignition timing, fuel injection, and gear shifts, ensuring smooth and efficient vehicle operation. Understanding your vehicle's PCM can help diagnose performance issues and improve maintenance strategies.
Key Differences Between ECU and PCM
The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) primarily manages specific subsystems such as engine, transmission, or brakes, while the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) integrates control functions for both the engine and transmission into a single unit. ECUs operate independently or as part of a network controlling various vehicle components, whereas the PCM centralizes key powertrain operations to optimize performance and emissions. The PCM typically processes inputs from multiple sensors to provide coordinated control, enhancing fuel efficiency and drivability compared to standalone ECUs.
Functions and Roles of ECU
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) manages crucial functions such as fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and air-fuel mixture optimization to ensure efficient engine performance. It processes data from various sensors to monitor and adjust parameters in real time, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Your vehicle relies on the ECU as the primary controller for engine operation, distinguishing it from the Powertrain Control Module (PCM), which integrates both engine and transmission controls.
Functions and Roles of PCM
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) integrates the functions of both the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and transmission control, managing engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emission systems through precise monitoring and adjustments. It processes data from various sensors to optimize combustion, control idle speed, and regulate transmission shifts for smooth operation. The PCM also plays a crucial role in diagnostics by storing error codes that facilitate troubleshooting and maintenance.
Common Symptoms of ECU and PCM Failure
Common symptoms of ECU failure include engine misfires, stalling, poor fuel efficiency, and difficulty starting the vehicle. PCM failure often causes similar issues but also affects transmission shifting, triggering check engine lights, and erratic engine behavior. Both ECU and PCM malfunctions can result in impaired vehicle performance and diagnostic trouble codes.
Diagnosing ECU vs PCM Issues
Diagnosing ECU vs PCM issues requires understanding that the Engine Control Unit (ECU) primarily manages engine functions, while the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) integrates both engine and transmission controls. Technicians use specialized diagnostic scanners to read error codes stored in the ECU or PCM, pinpointing malfunctions related to sensors, actuators, or communication failures. Accurate diagnosis depends on interpreting these codes alongside live data stream analysis to determine whether the fault lies in the ECU, PCM, wiring, or external components.
ECU vs PCM: Compatibility and Replacement
ECU vs PCM compatibility depends on the specific vehicle make and model, as some cars use ECU (Engine Control Unit) while others use PCM (Powertrain Control Module) to manage engine functions; ensuring you select the correct unit is crucial for proper integration. Replacing an ECU with a PCM or vice versa requires careful consideration of wiring harness connections, software programming, and sensor compatibility to maintain engine performance and avoid diagnostic errors. Your vehicle's repair manual or a professional technician can provide precise recommendations to guarantee a seamless replacement and optimal system functionality.
Choosing the Right Module for Your Vehicle
When choosing the right module for your vehicle, understanding the difference between the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is crucial. The ECU primarily manages engine functions such as fuel injection and ignition timing, while the PCM integrates both engine and transmission controls to optimize overall performance. Selecting the appropriate module depends on your vehicle's specific needs, as PCM offers more comprehensive control for combined systems, whereas ECU targets engine-only management.
ECU vs PCM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com