Power inverters change direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), enabling your devices to run on battery or solar power, while power converters adjust voltage levels within AC or DC circuits to match device requirements. Explore the detailed differences and applications of these essential electrical components to optimize your power solutions.
Table of Comparison
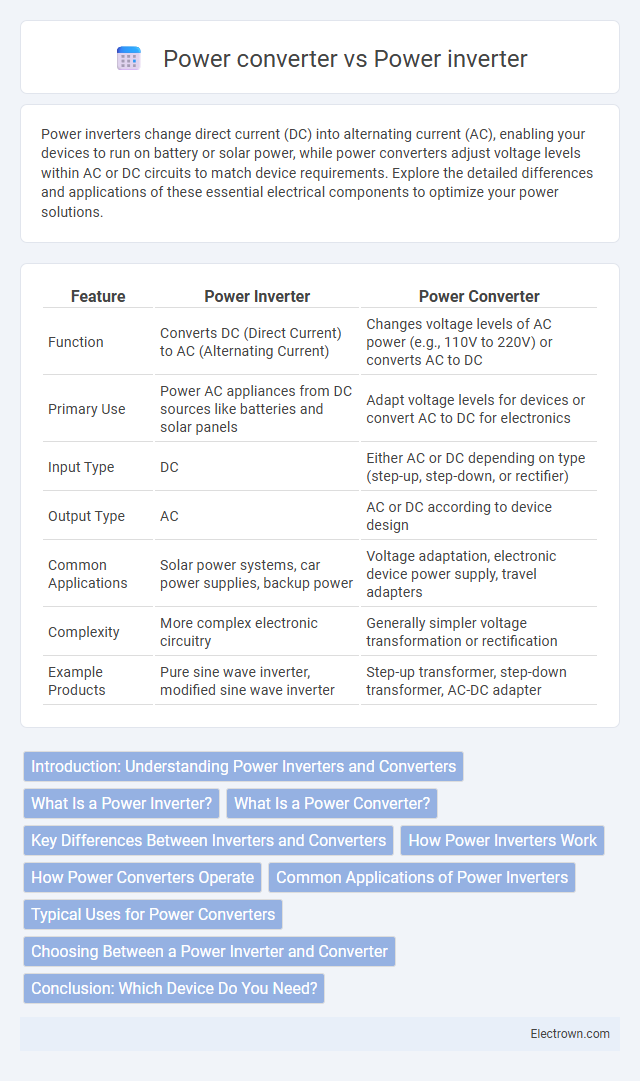
| Feature | Power Inverter | Power Converter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts DC (Direct Current) to AC (Alternating Current) | Changes voltage levels of AC power (e.g., 110V to 220V) or converts AC to DC |
| Primary Use | Power AC appliances from DC sources like batteries and solar panels | Adapt voltage levels for devices or convert AC to DC for electronics |
| Input Type | DC | Either AC or DC depending on type (step-up, step-down, or rectifier) |
| Output Type | AC | AC or DC according to device design |
| Common Applications | Solar power systems, car power supplies, backup power | Voltage adaptation, electronic device power supply, travel adapters |
| Complexity | More complex electronic circuitry | Generally simpler voltage transformation or rectification |
| Example Products | Pure sine wave inverter, modified sine wave inverter | Step-up transformer, step-down transformer, AC-DC adapter |
Introduction: Understanding Power Inverters and Converters
Power inverters transform direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), enabling you to power AC devices from DC sources like batteries or solar panels. Power converters change electrical voltage levels, stepping voltage up or down to match device requirements and ensure safe operation. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize your energy system for efficiency and compatibility.
What Is a Power Inverter?
A power inverter transforms direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC) used by most household appliances and electronic devices. Its primary function is to enable the use of AC power in locations or situations where only DC power is available, such as in vehicles or remote off-grid systems. Understanding the role of a power inverter helps you choose the right equipment for efficiently powering your AC devices from DC power sources.
What Is a Power Converter?
A power converter is an electronic device that transforms electrical energy from one form to another, such as converting AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current) or altering voltage levels to suit specific equipment needs. Unlike power inverters that primarily convert DC to AC, power converters can include rectifiers, transformers, and voltage regulators to ensure compatibility and efficiency across different electrical systems. Understanding the role of a power converter is essential for optimizing Your power supply setup, especially in applications requiring precise voltage and current modifications.
Key Differences Between Inverters and Converters
Power inverters convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) for powering AC devices from DC sources like batteries, while power converters change voltage levels within AC or DC systems, either stepping up or stepping down voltage. Inverters primarily provide AC output from DC input, crucial for applications such as solar power systems and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). Converters include devices like AC-DC converters and DC-DC converters, focusing on voltage transformation without changing current type.
How Power Inverters Work
Power inverters convert direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC) suitable for household appliances and electronic devices. They use electronic circuits such as oscillators and transformers to change the DC voltage into AC voltage with specific frequency and waveform characteristics. This conversion enables the use of DC power in AC-powered systems, improving compatibility and functionality.
How Power Converters Operate
Power converters operate by transforming electrical energy from one form to another, such as converting AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current) or adjusting voltage levels to match device requirements. They use components like diodes, transformers, and switching elements to regulate power flow efficiently and maintain stable output. This process enables compatibility between different electrical systems and devices, ensuring proper functionality and safety.
Common Applications of Power Inverters
Power inverters are commonly used in renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power setups, to convert DC electricity into usable AC power for homes and businesses. They are essential in off-grid and backup power solutions, enabling the operation of standard electrical devices from battery storage. Your ability to power appliances during outages or in mobile environments relies heavily on the efficiency and capacity of a power inverter.
Typical Uses for Power Converters
Power converters are typically used in applications requiring voltage transformation and frequency changes, such as adapting electrical devices to different power grids or converting AC to DC for electronic circuitry. Common uses include powering household appliances in countries with different voltage standards, operating industrial machinery, and supplying correct power levels for medical equipment. Their ability to efficiently regulate voltage and current makes them essential in renewable energy systems and telecommunications infrastructure.
Choosing Between a Power Inverter and Converter
Choosing between a power inverter and converter depends on your electrical system requirements and device compatibility. Power inverters convert DC battery power into usable AC electricity ideal for running household appliances from car batteries or solar systems. Power converters, on the other hand, adapt voltage levels between different electrical standards, making them essential for using devices designed for specific voltages, such as 110V equipment in 220V regions.
Conclusion: Which Device Do You Need?
Choosing between a power inverter and a power converter depends on your specific energy needs. Power inverters convert DC to AC, making them essential for using household appliances with batteries or solar power systems. Power converters modify voltage levels within the same current type, ideal for devices requiring voltage adjustment rather than current transformation; understanding this distinction ensures you select the right device to power your equipment efficiently.
Power inverter vs Power converter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com